Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2gb7; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.7 Å)
- Summary
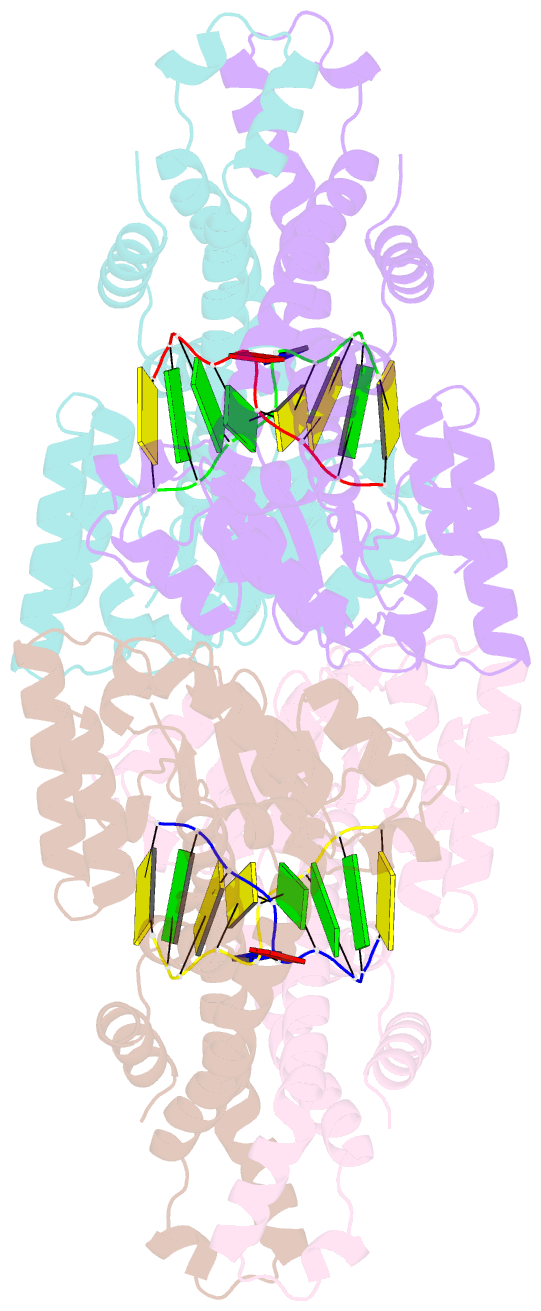
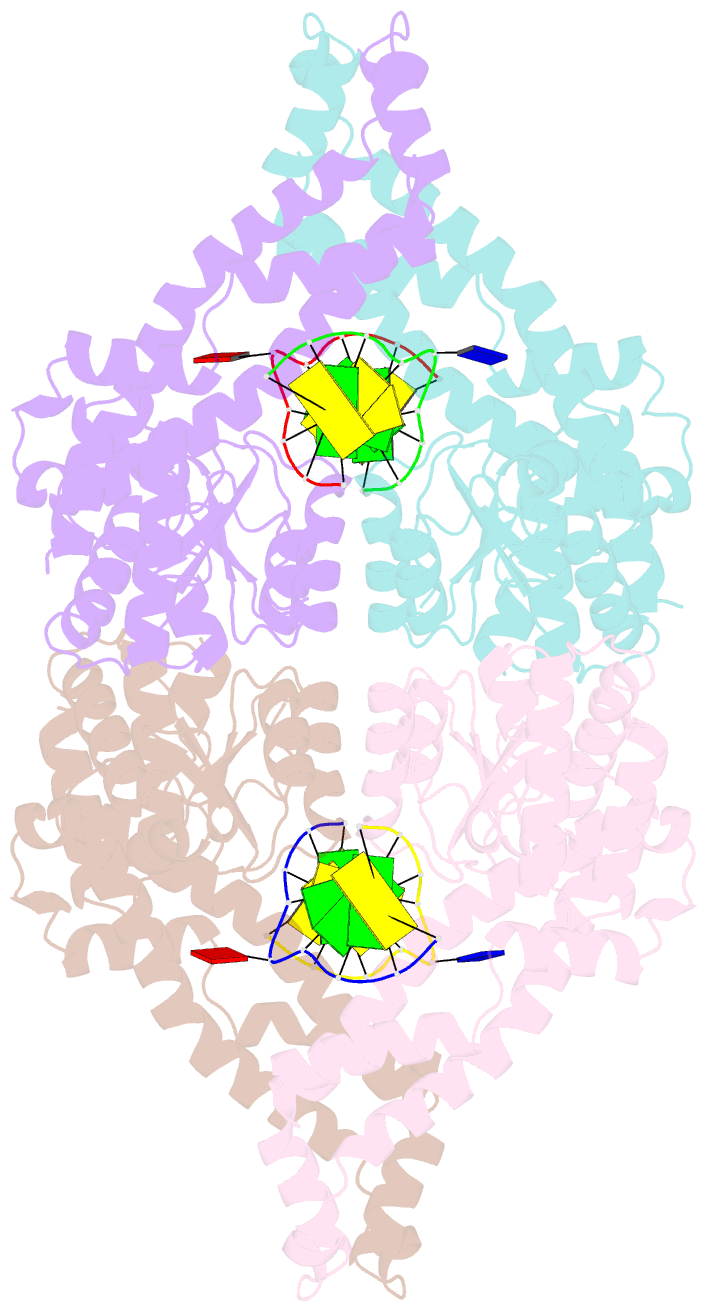
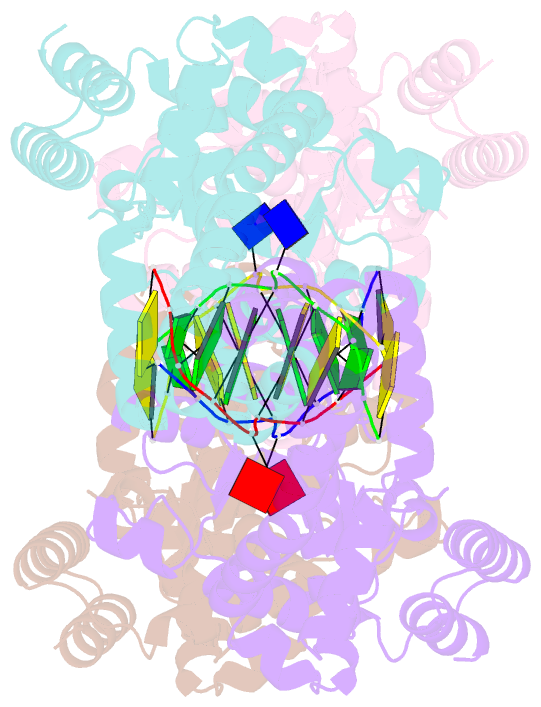
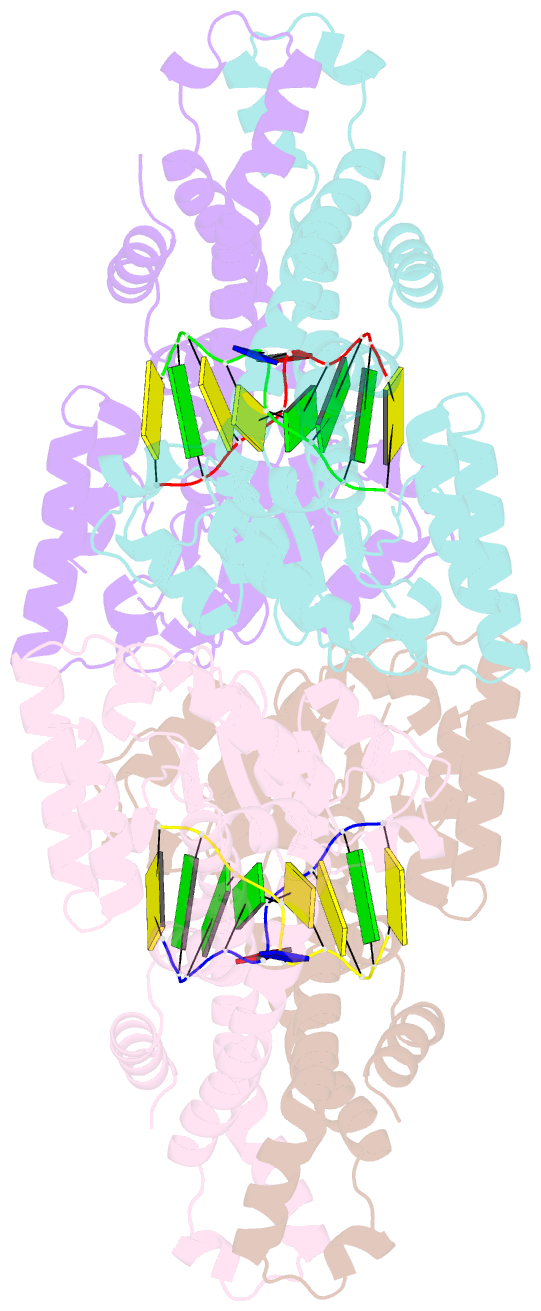
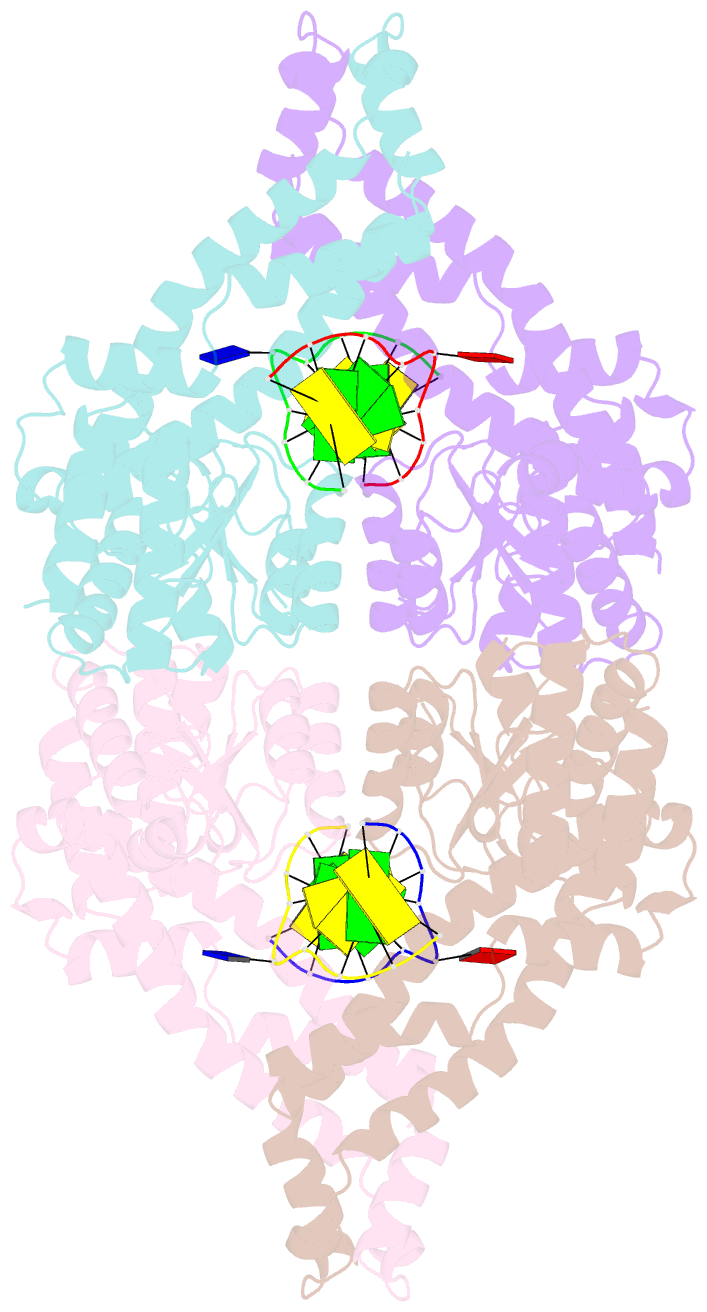
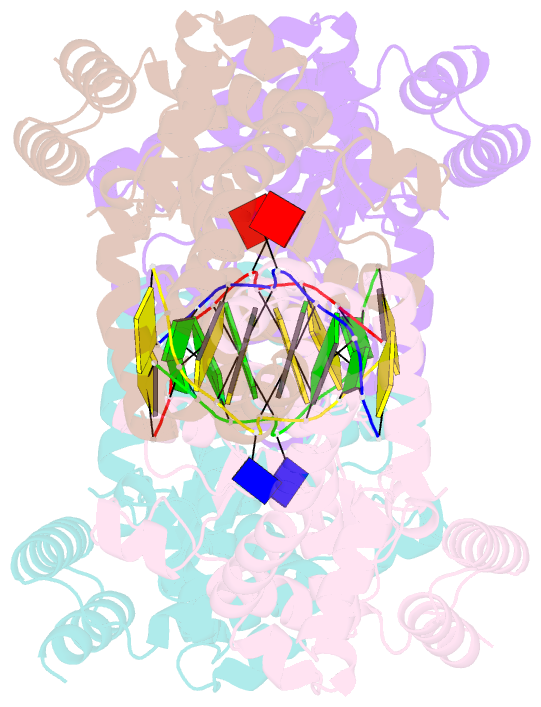
- Metal-depleted ecl18ki in complex with uncleaved, modified DNA
- Reference
- Bochtler M, Szczepanowski RH, Tamulaitis G, Grazulis S, Czapinska H, Manakova E, Siksnys V (2006): "Nucleotide flips determine the specificity of the Ecl18kI restriction endonuclease." Embo J., 25, 2219-2229. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601096.
- Abstract
- Restricion endonuclease Ecl18kI is specific for the sequence /CCNGG and cleaves it before the outer C to generate 5 nt 5'-overhangs. It has been suggested that Ecl18kI is evolutionarily related to NgoMIV, a 6-bp cutter that cleaves the sequence G/CCGGC and leaves 4 nt 5'-overhangs. Here, we report the crystal structure of the Ecl18kI-DNA complex at 1.7 A resolution and compare it with the known structure of the NgoMIV-DNA complex. We find that Ecl18kI flips both central nucleotides within the CCNGG sequence and buries the extruded bases in pockets within the protein. Nucleotide flipping disrupts Watson-Crick base pairing, induces a kink in the DNA and shifts the DNA register by 1 bp, making the distances between scissile phosphates in the Ecl18kI and NgoMIV cocrystal structures nearly identical. Therefore, the two enzymes can use a conserved DNA recognition module, yet recognize different sequences, and form superimposable dimers, yet generate different cleavage patterns. Hence, Ecl18kI is the first example of a restriction endonuclease that flips nucleotides to achieve specificity for its recognition site.