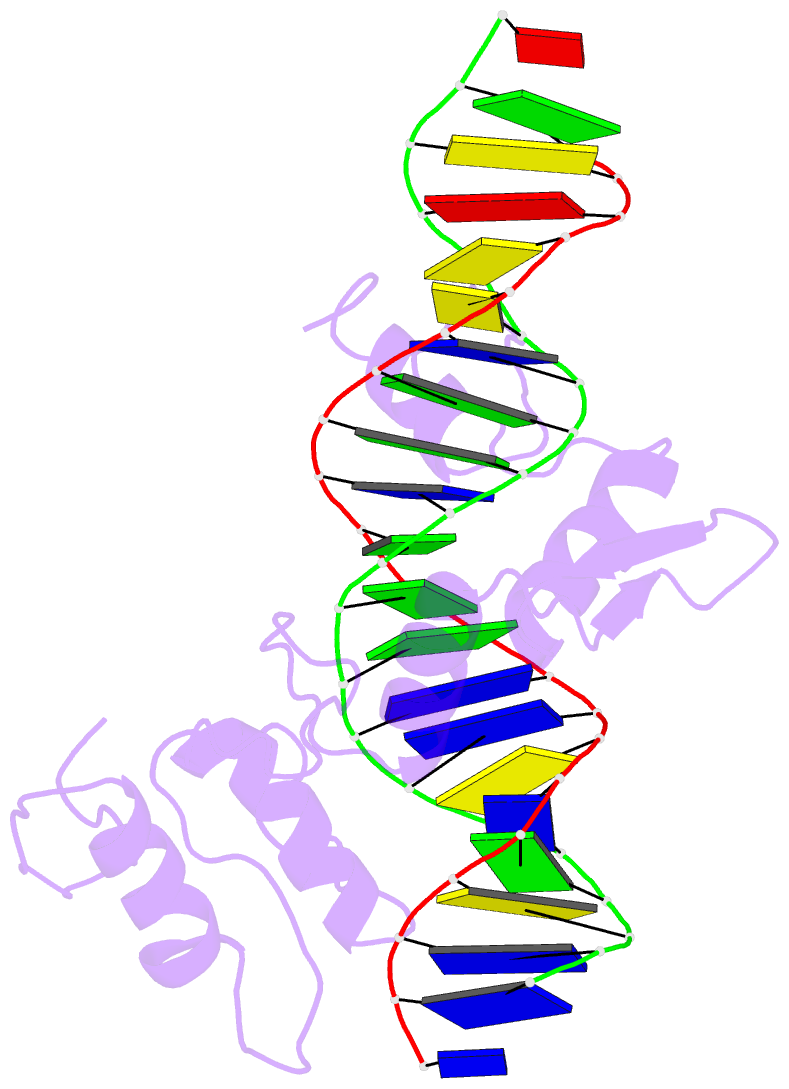
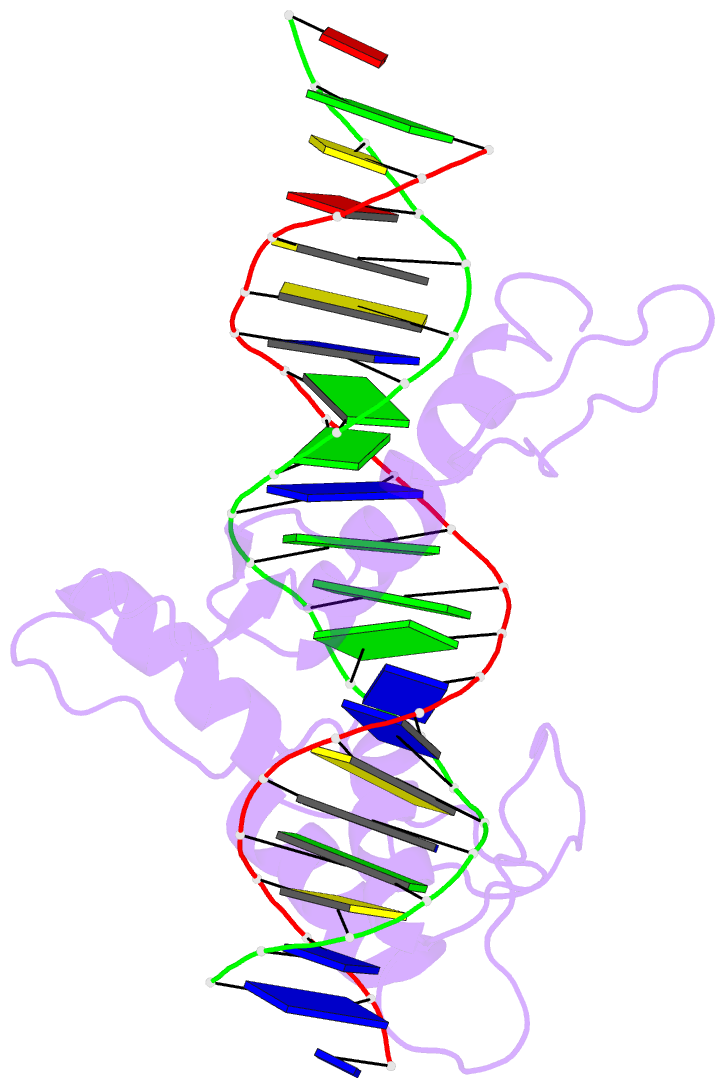
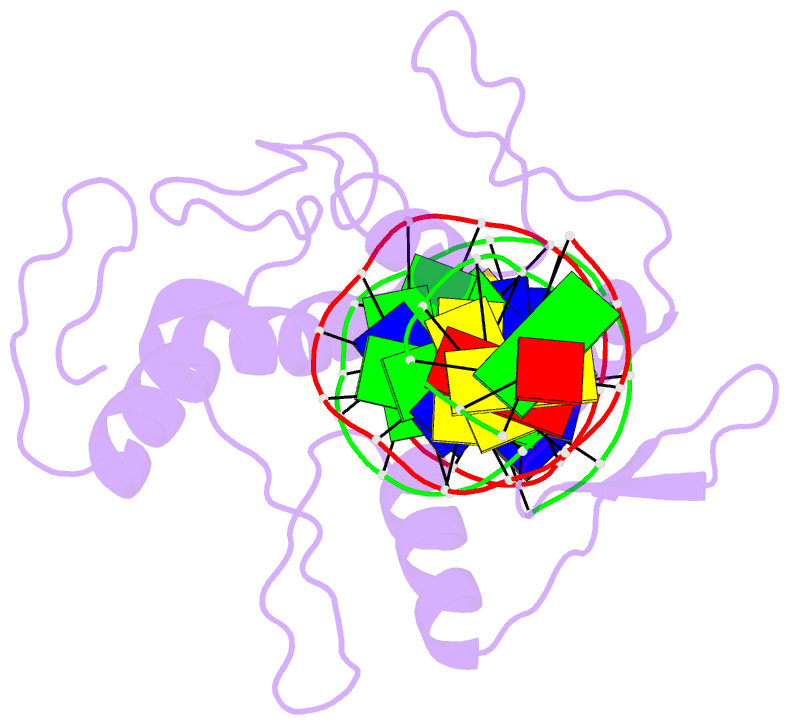
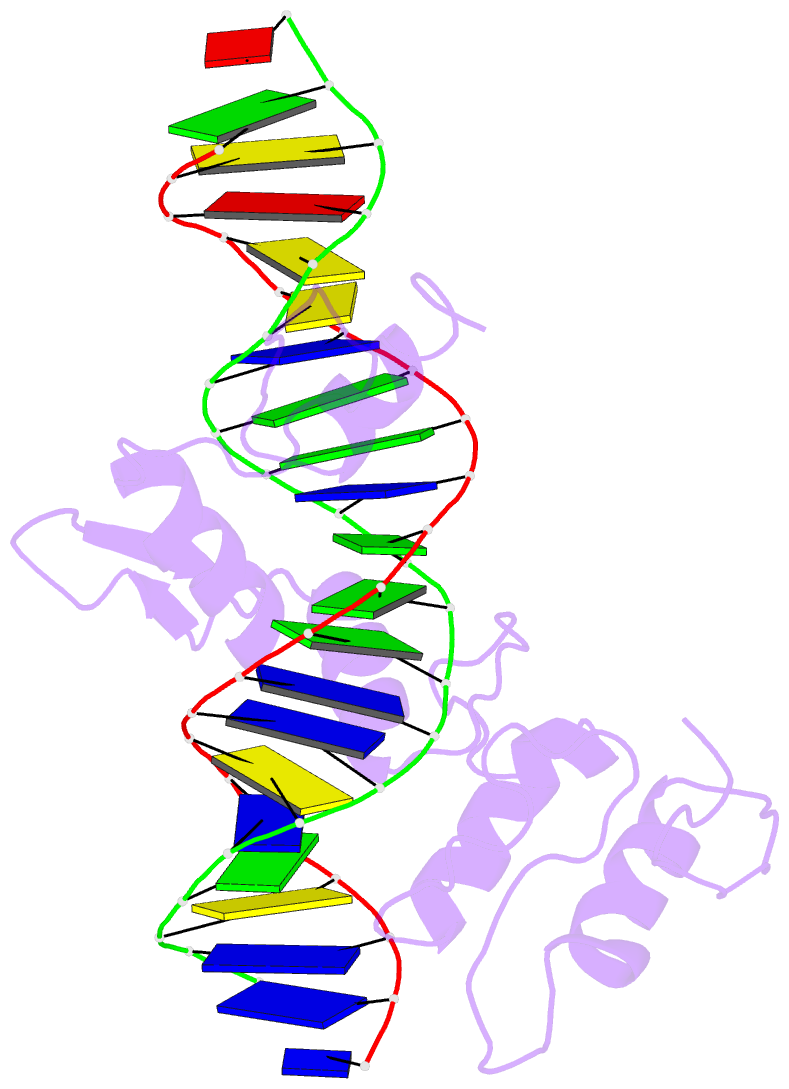
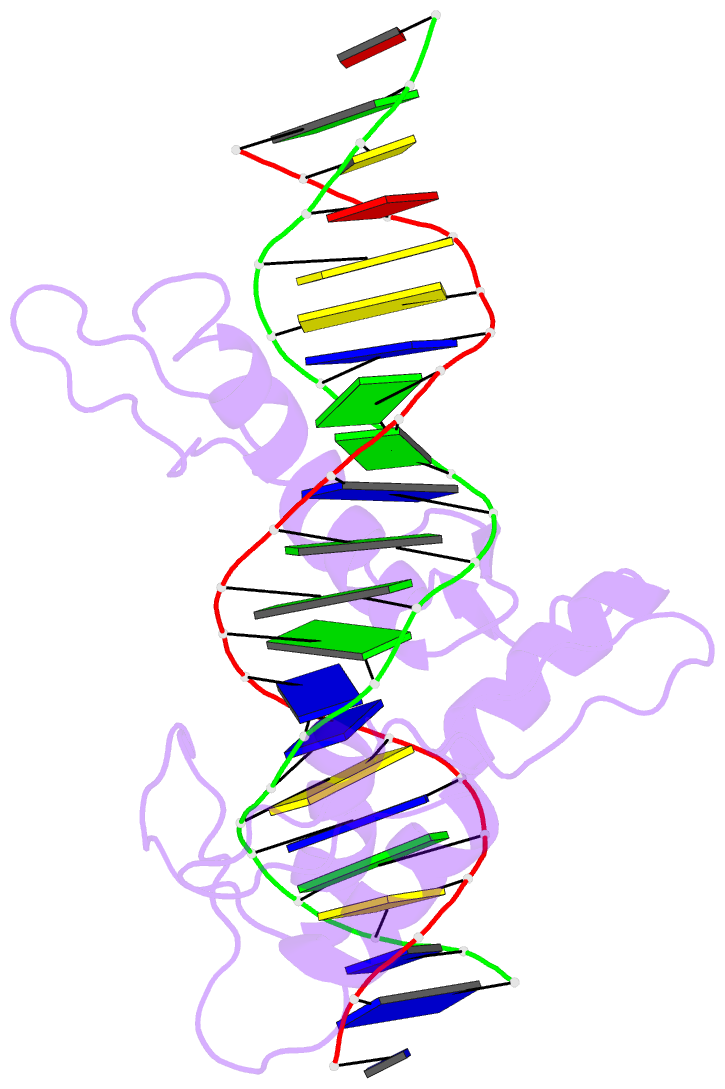
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2gli; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.6 Å)
- Summary
- Five-finger gli-DNA complex
- Reference
- Pavletich NP, Pabo CO (1993): "Crystal structure of a five-finger GLI-DNA complex: new perspectives on zinc fingers." Science, 261, 1701-1707.
- Abstract
- Zinc finger proteins, of the type first discovered in transcription factor IIIA (TFIIIA), are one of the largest and most important families of DNA-binding proteins. The crystal structure of a complex containing the five Zn fingers from the human GLI oncogene and a high-affinity DNA binding site has been determined at 2.6 A resolution. Finger one does not contact the DNA. Fingers two through five bind in the major groove and wrap around the DNA, but lack the simple, strictly periodic arrangement observed in the Zif268 complex. Fingers four and five of GLI make extensive base contacts in a conserved nine base-pair region, and this section of the DNA has a conformation intermediate between B-DNA and A-DNA. Analyzing the GLI complex and comparing it with Zif268 offers new perspectives on Zn finger-DNA recognition.