Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2gzk; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA-structural protein
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
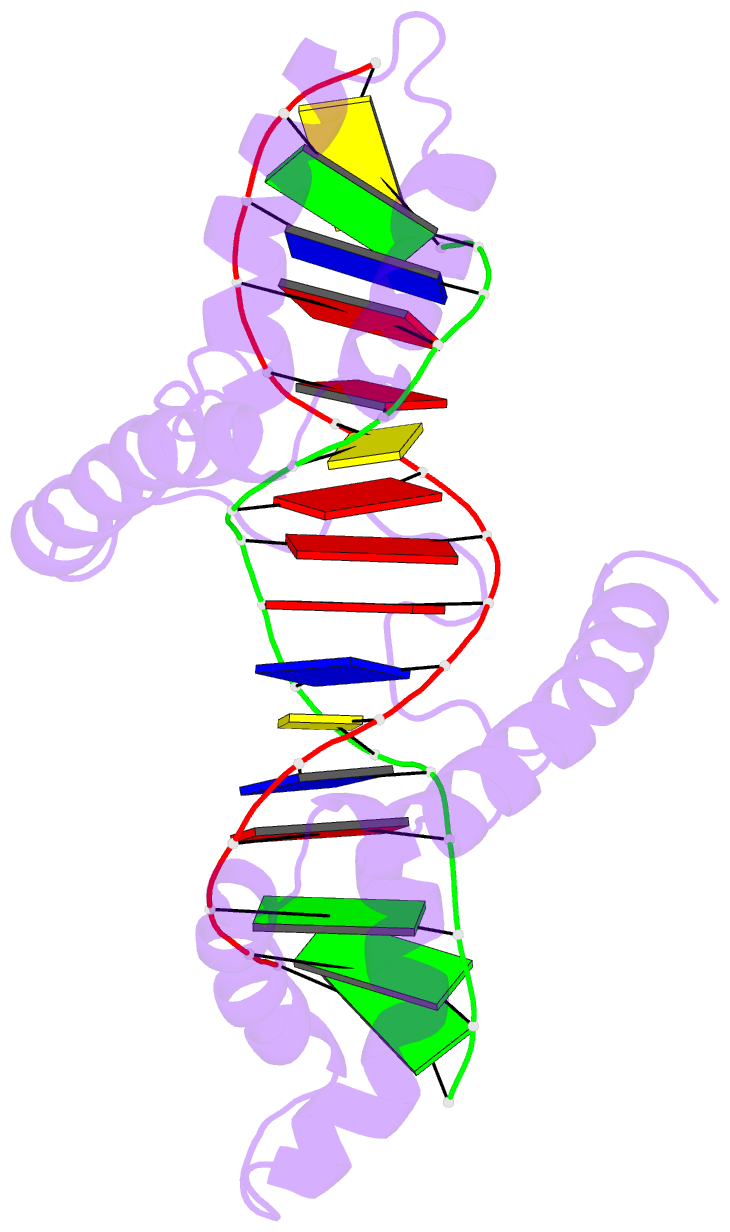
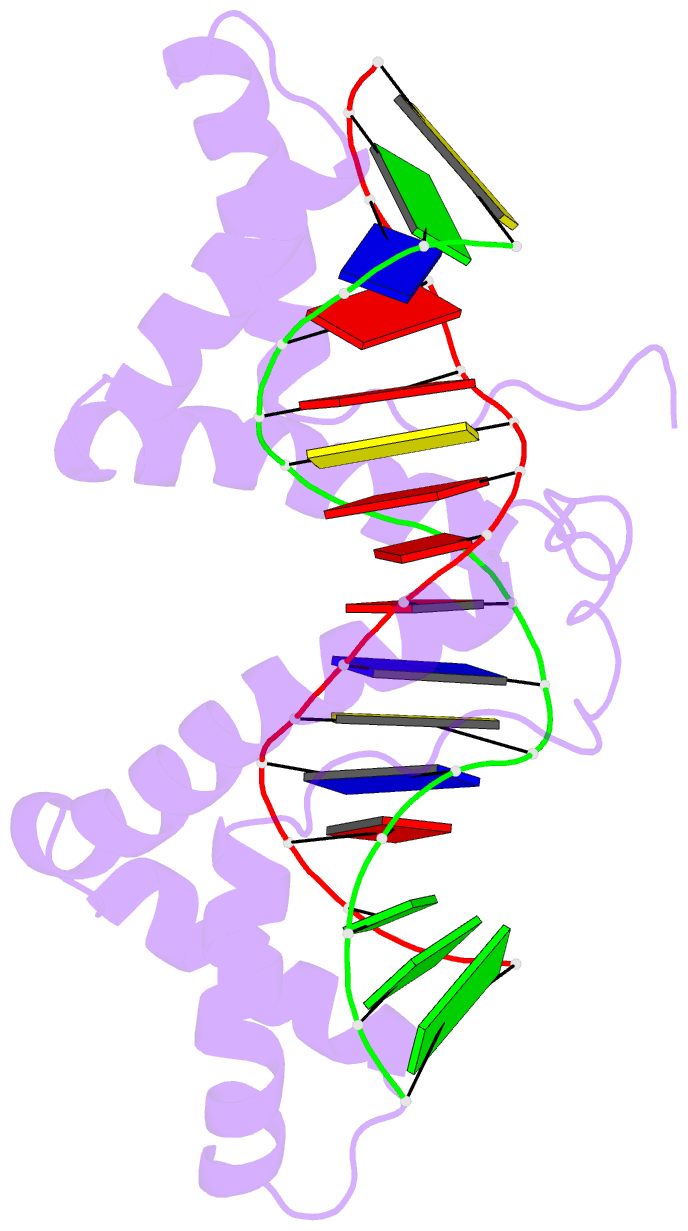
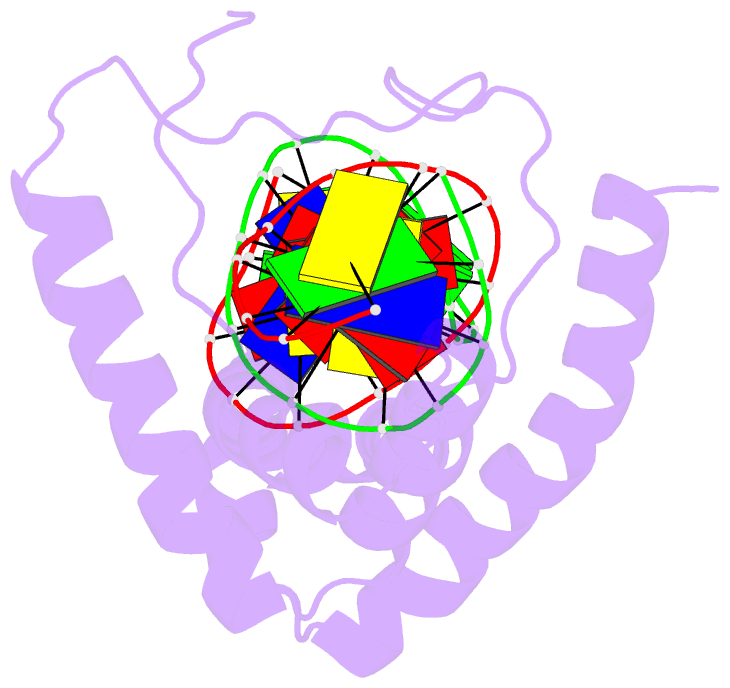
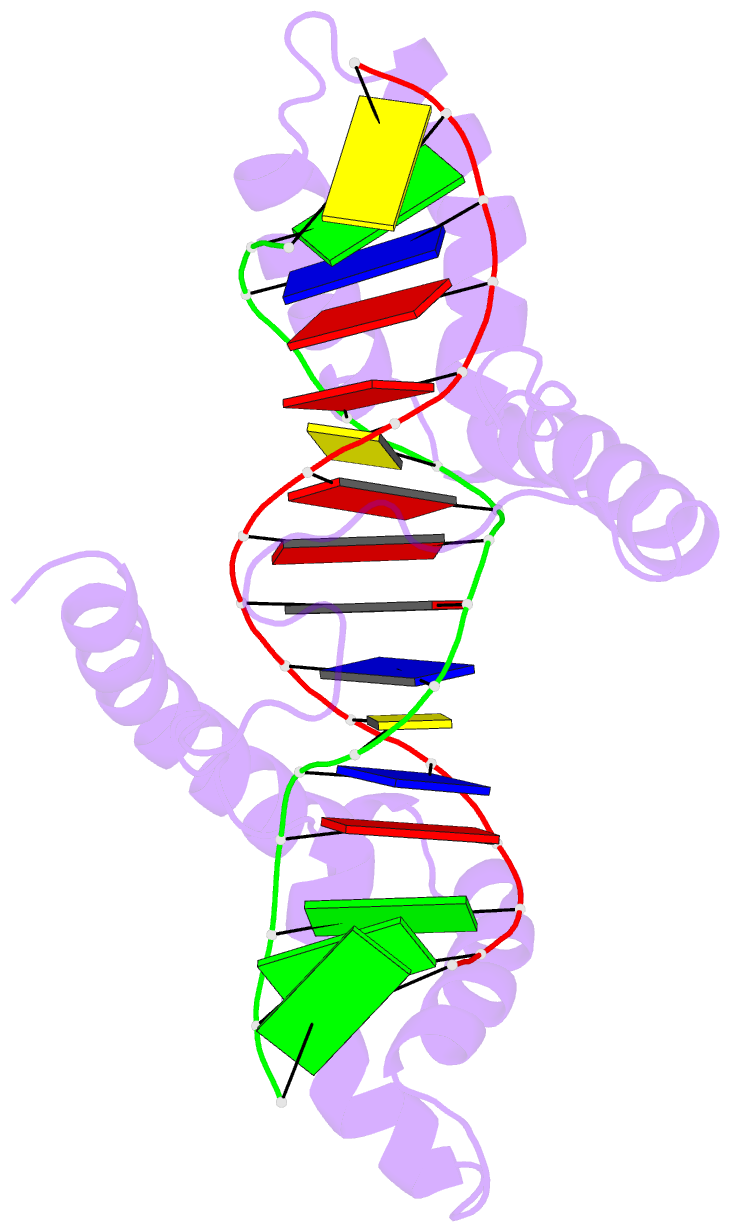
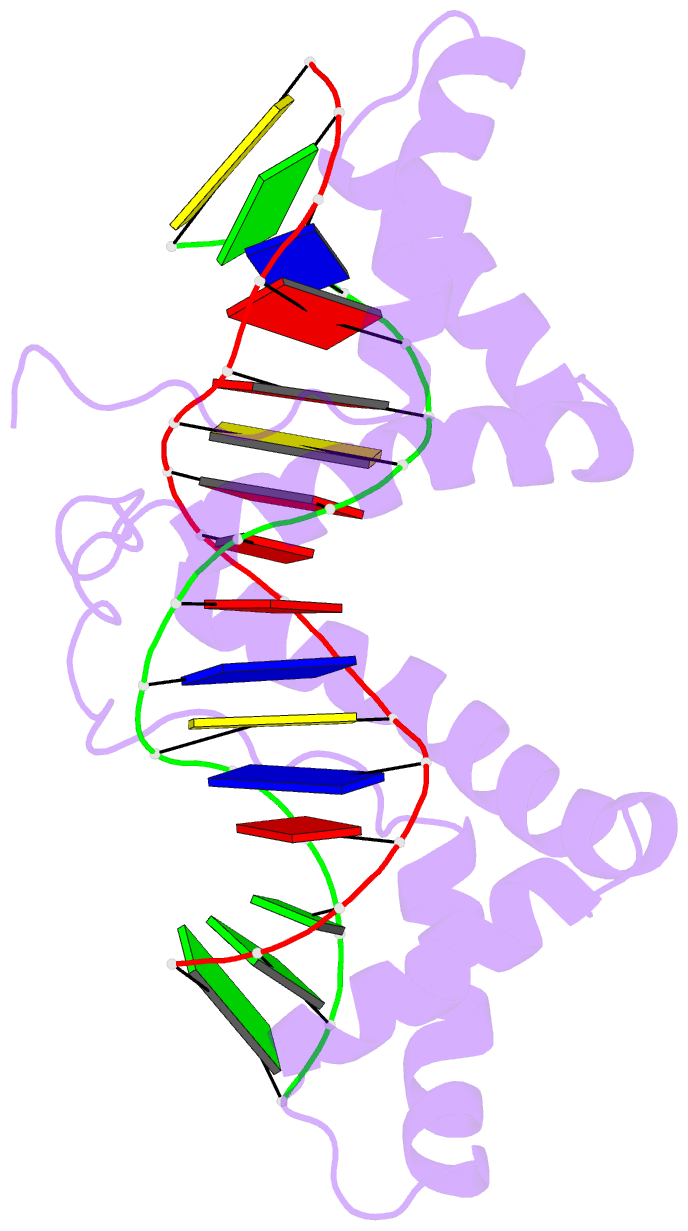
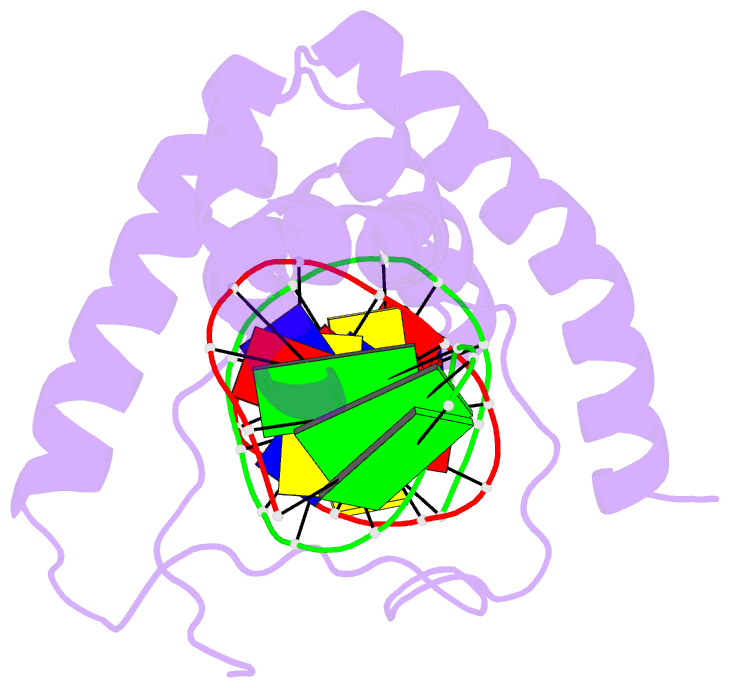
- Structure of a complex of tandem hmg boxes and DNA
- Reference
- Stott K, Tang GS, Lee KB, Thomas JO (2006): "Structure of a Complex of Tandem HMG Boxes and DNA." J.Mol.Biol., 360, 90-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.04.059.
- Abstract
- The high-mobility group protein HMGB1 contains two tandem DNA-binding HMG box domains, A and B, linked by a short flexible linker that allows the two domains to behave independently in the free protein. There is no structural information on how the linked domains and linker behave when bound to DNA, mainly due to the lack of any DNA-sequence preference of HMGB1. We report the structure determination, by NMR spectroscopy, of a well-defined complex of two tandem HMG boxes bound to a 16 bp oligonucleotide. The protein is an engineered version of the AB di-domain of HMGB1, in which the A box has been replaced by the HMG box of the sequence-specific transcription factor SRY, to give SRY.B. In the SRY.B/DNA complex, both HMG boxes bind in the minor groove and contribute to the overall DNA bending by intercalation of bulky hydrophobic residues between base-pairs; the bends reinforce each other, and the basic linker lies partly in the minor groove. As well as being the first structure of an HMG-box di-domain bound to DNA, this provides the first structure of the B domain of HMGB1 bound to DNA.