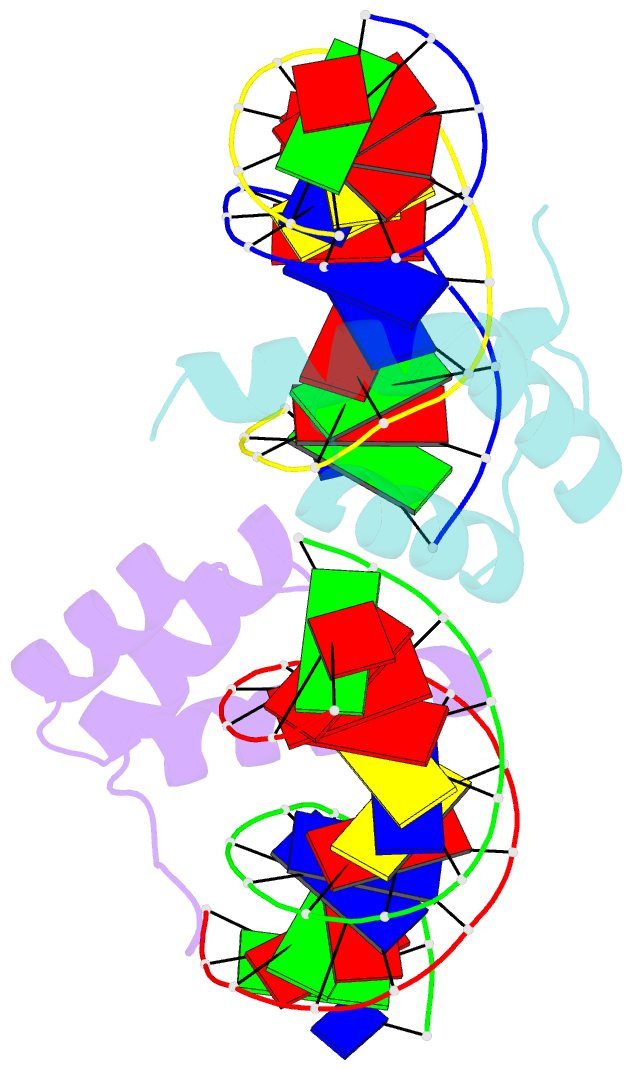
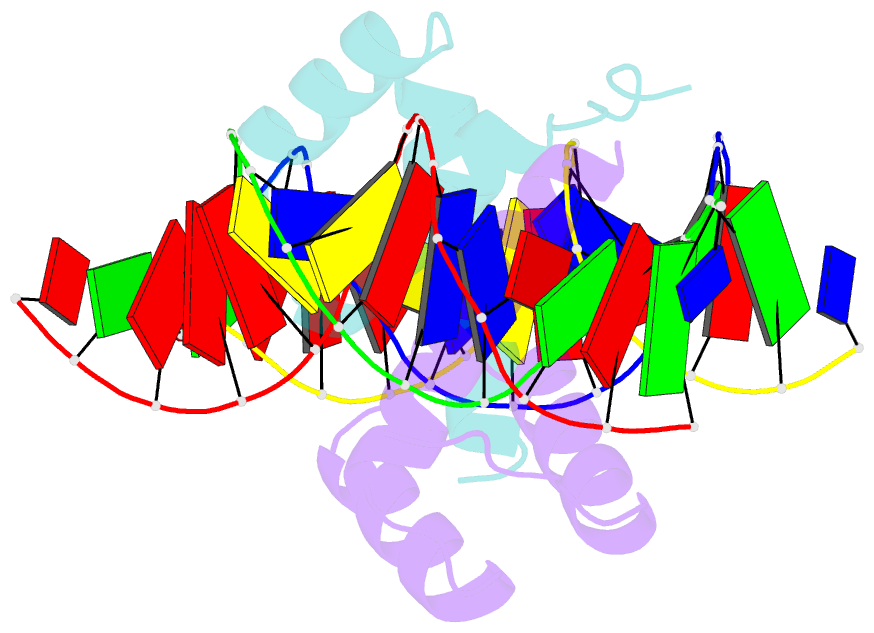
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2h1k; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.42 Å)
- Summary
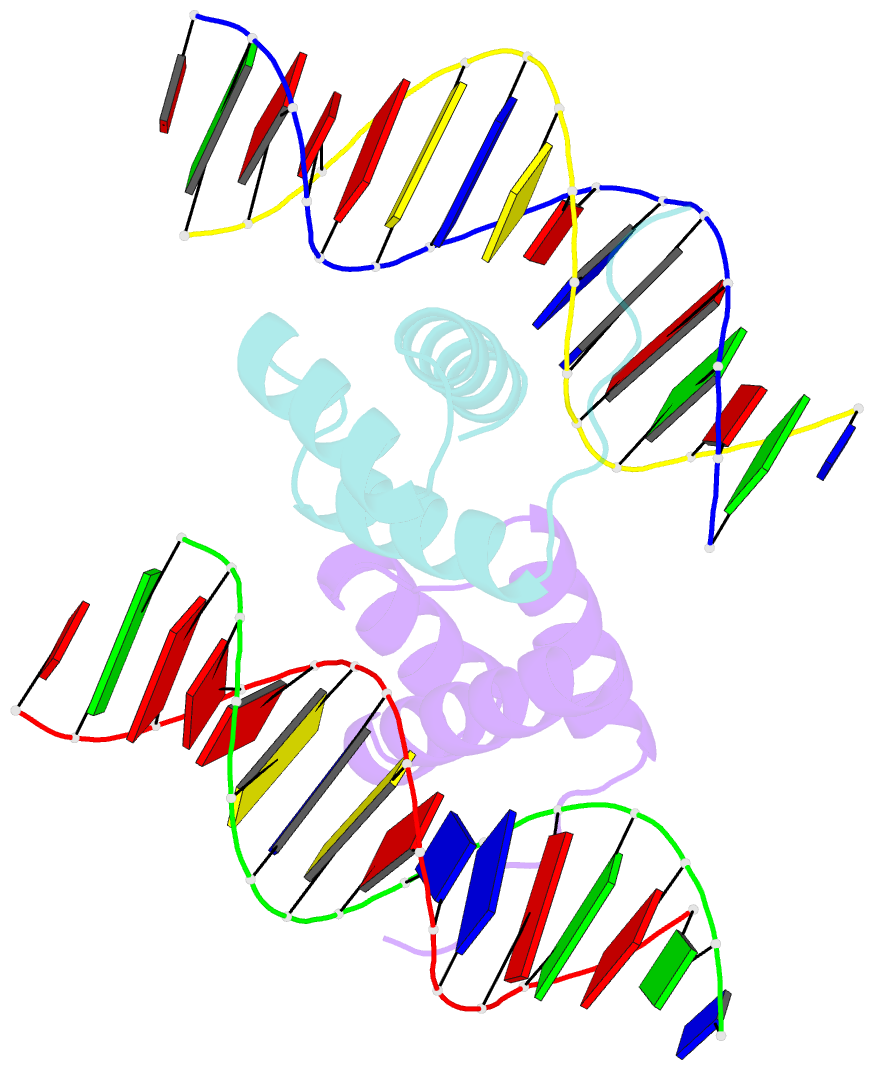
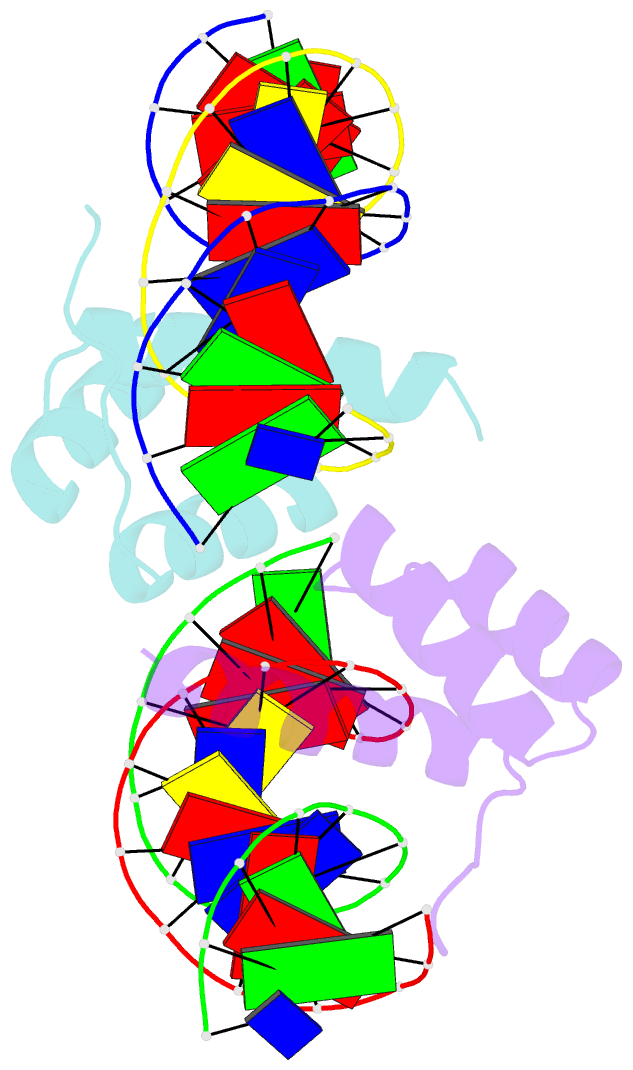
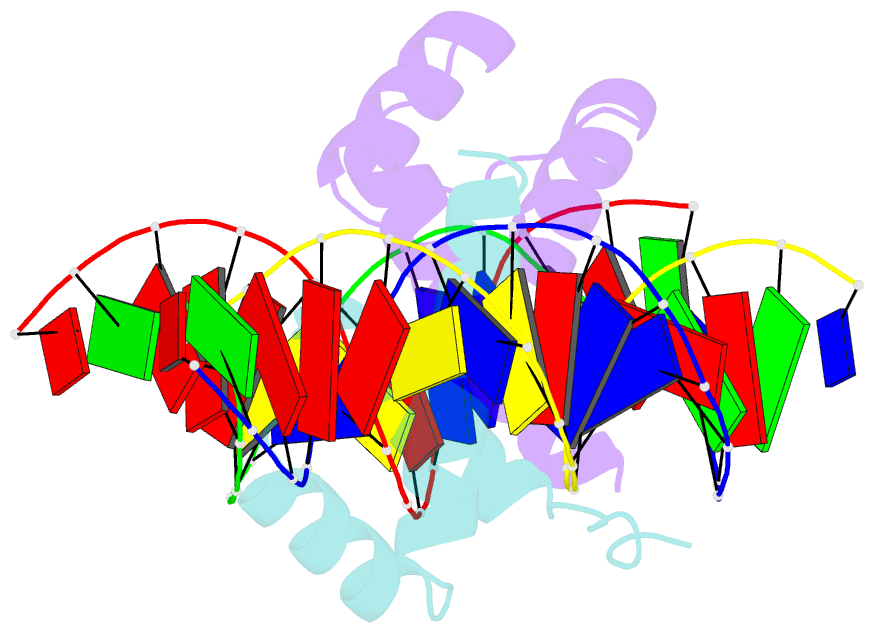
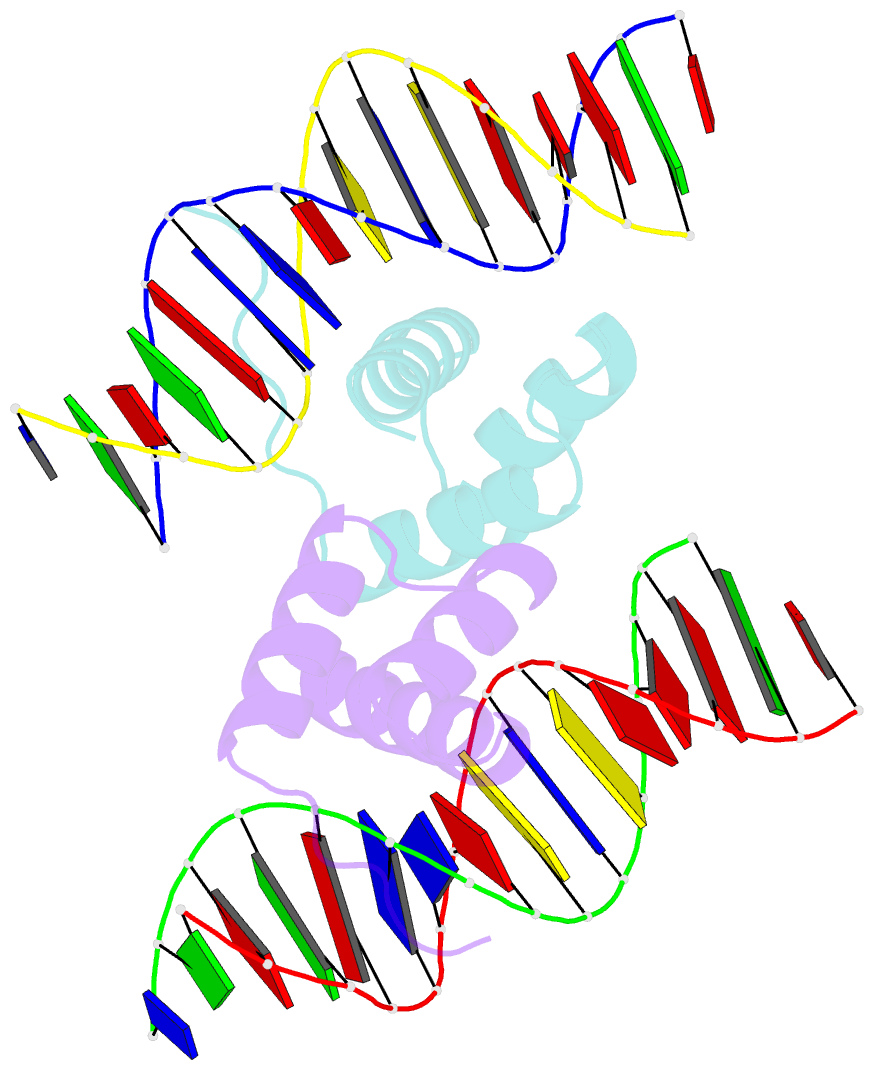
- Crystal structure of the pdx1 homeodomain in complex with DNA
- Reference
- Longo A, Guanga GP, Rose RB (2007): "Structural basis for induced fit mechanisms in DNA recognition by the pdx1 homeodomain." Biochemistry, 46, 2948-2957. doi: 10.1021/bi060969l.
- Abstract
- Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 (Pdx1) is a homeodomain transcription factor belonging to the ParaHox family. Pdx1 plays an essential role in pancreatic endocrine and exocrine cell development and maintenance of adult islet beta-cell function. Mutations in the human pdx1 gene are linked to an early onset form of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, MODY-4. We demonstrate that the homeodomain reproduces the binding specificity of the full-length protein. We report the 2.4 A resolution crystal structure of the homeodomain bound to a target DNA. The two Pdx1/DNA complexes in the asymmetric unit display conformational differences: in the DNA curvature, the orientation of the homeodomain in the major groove, and the order of the N-terminal arm. Comparing the two complexes indicates invariant protein-DNA contacts, and variant contacts that are unique to each binding orientation. An induced fit model is proposed that depends on the DNA conformation and provides a mechanism for nonlocal contributions to binding specificity.