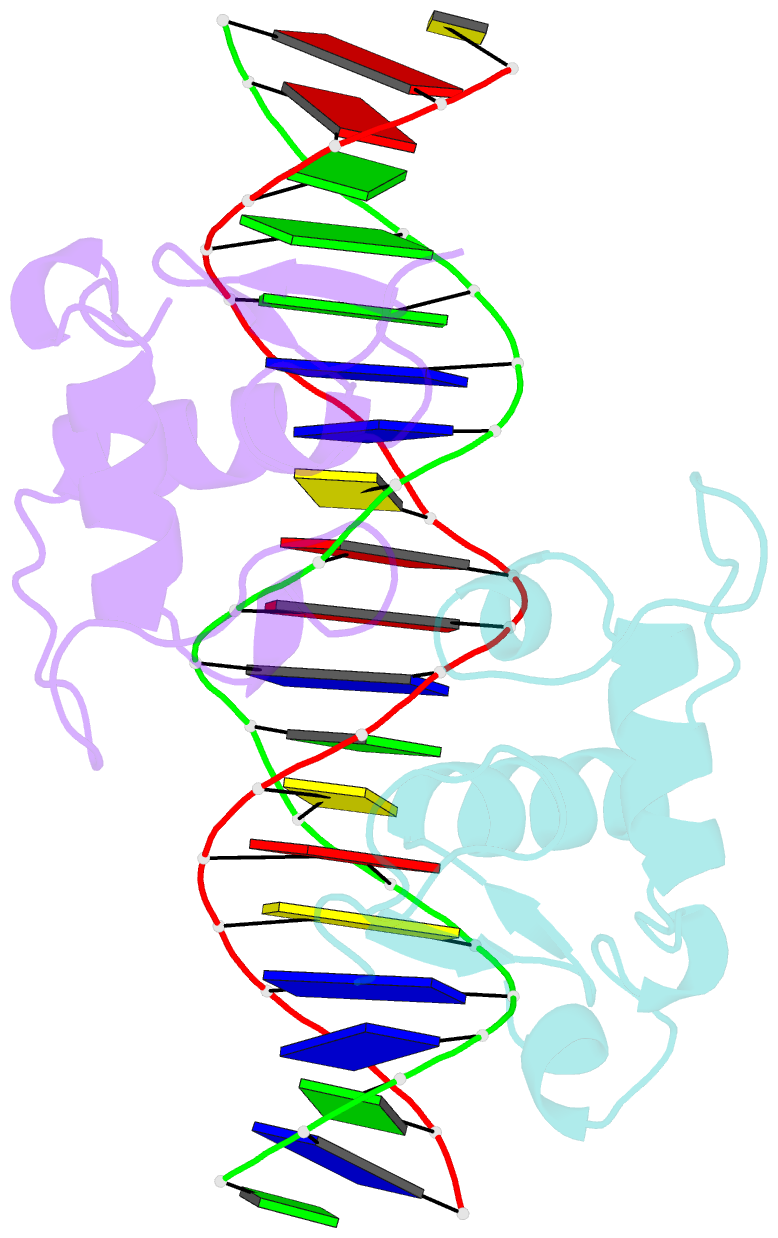
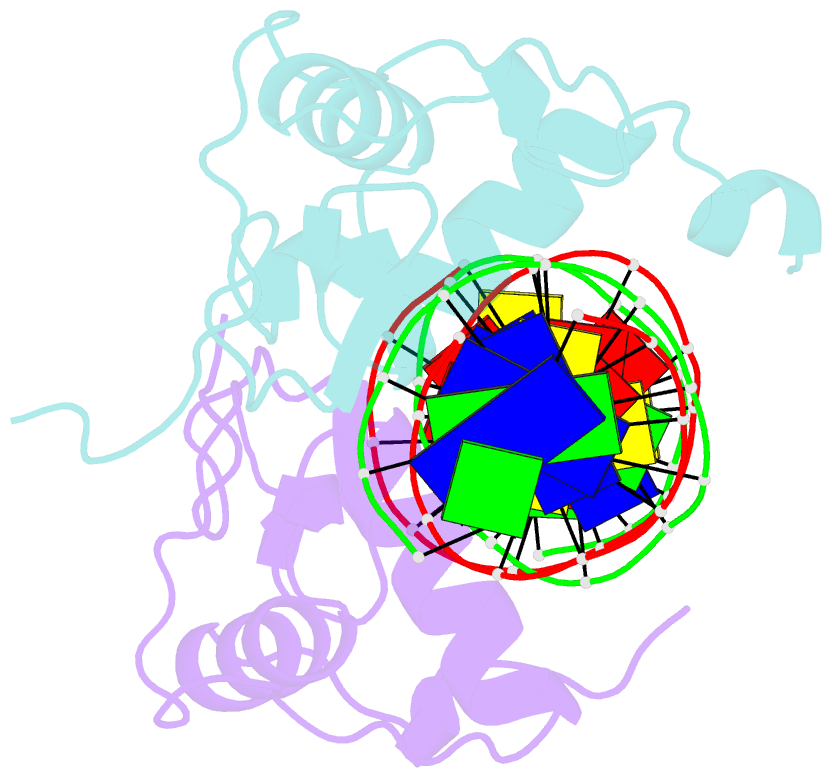
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2han; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.95 Å)
- Summary
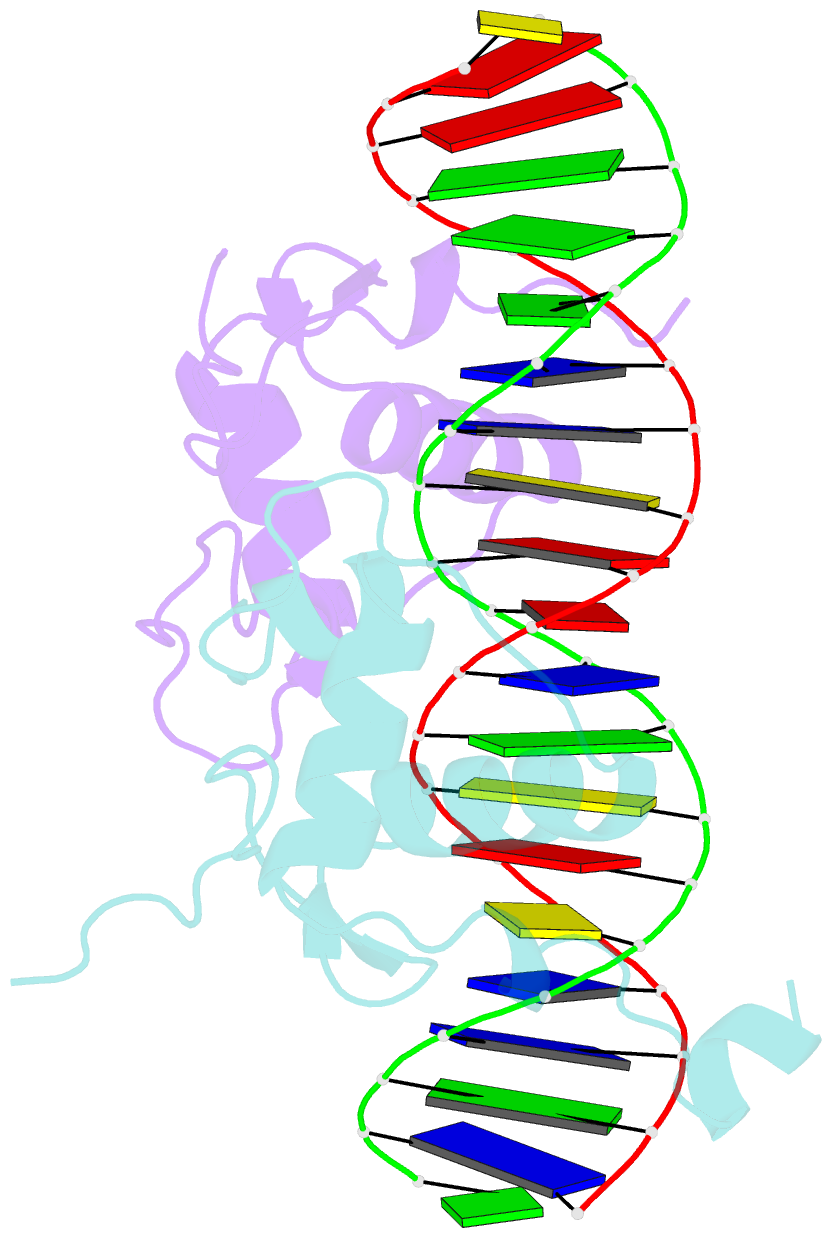
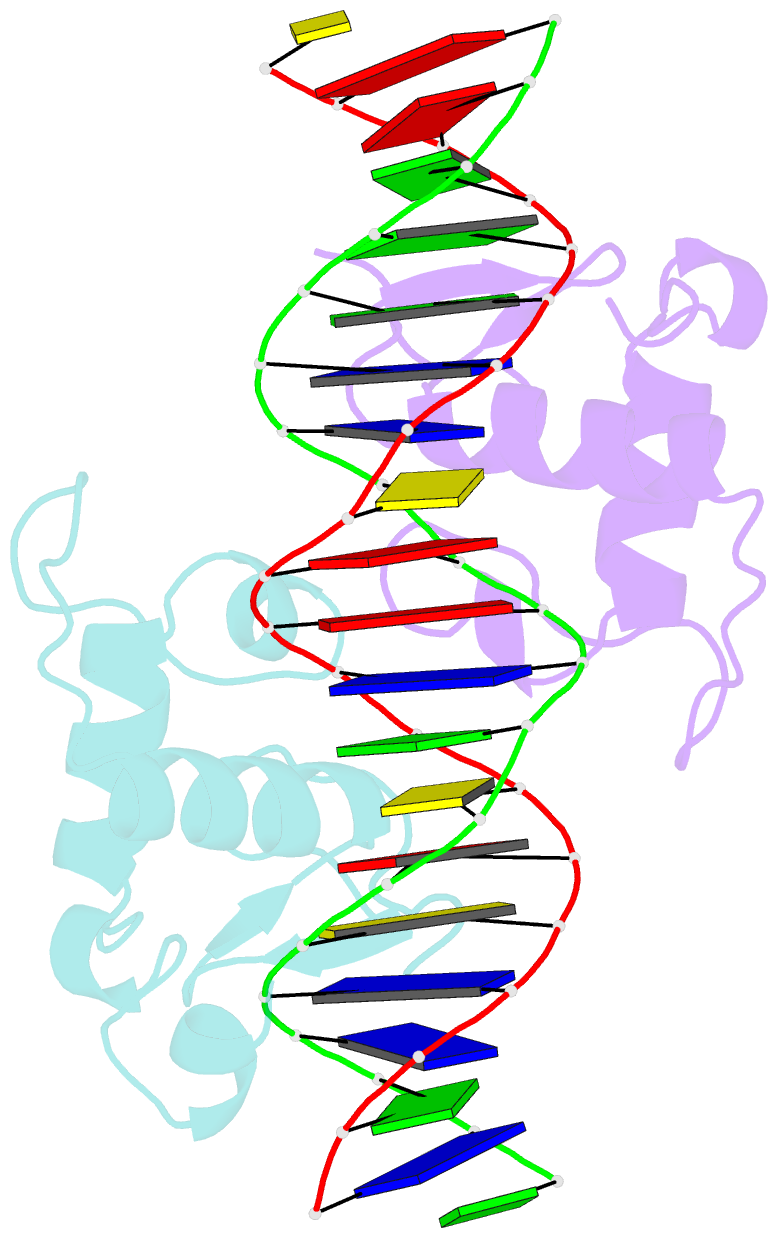
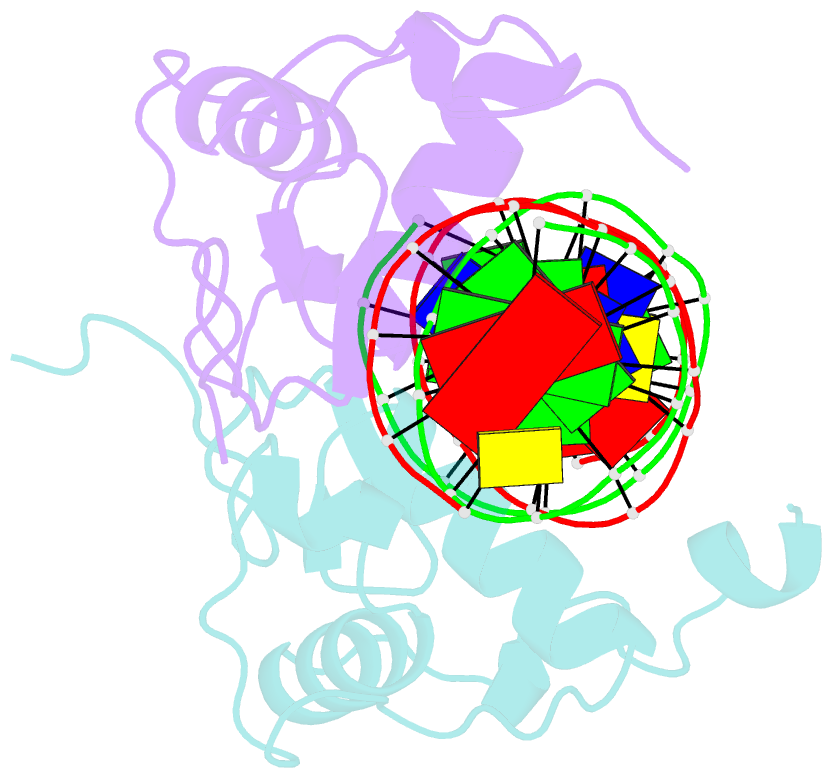
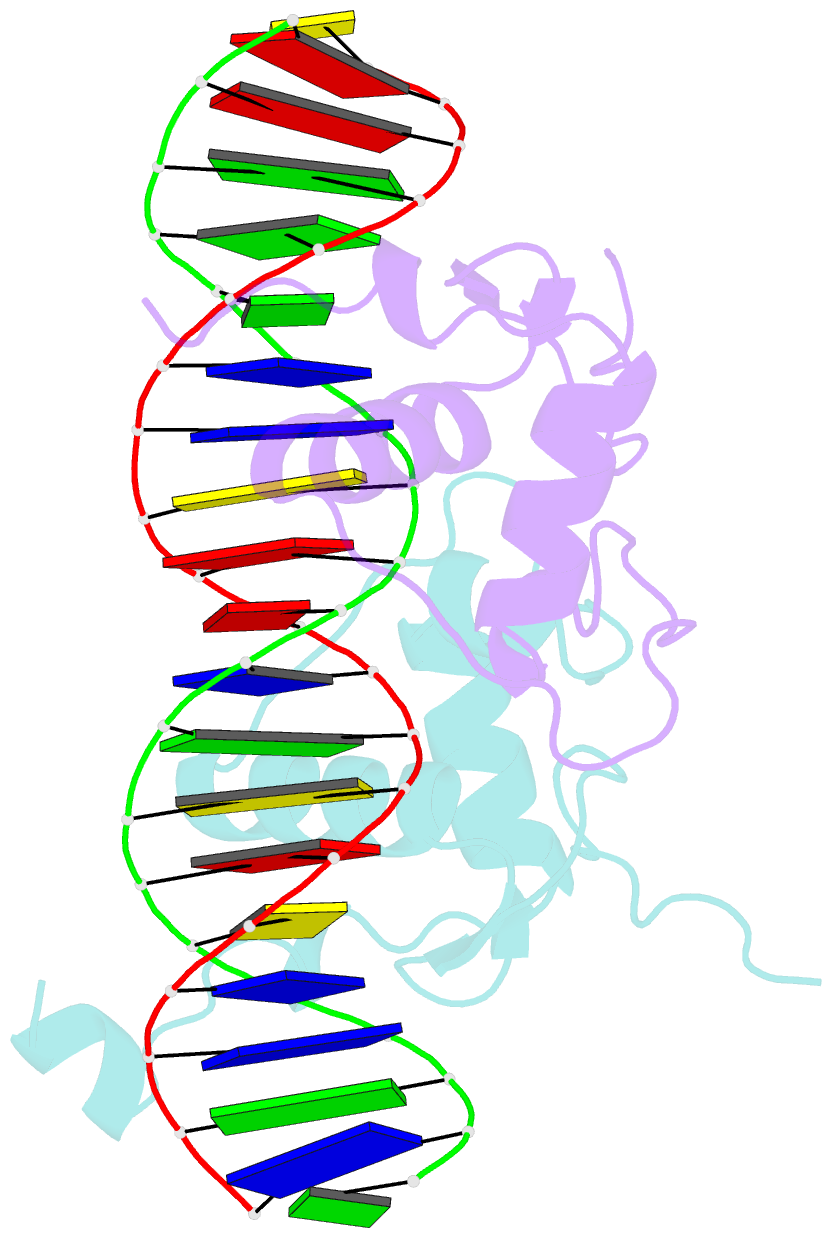
- Structural basis of heterodimeric ecdysteroid receptor interaction with natural response element hsp27 gene promoter
- Reference
- Jakob M, Kolodziejczyk R, Orlowski M, Krzywda S, Kowalska A, Dutko-Gwozdz J, Gwozdz T, Kochman M, Jaskolski M, Ozyhar A (2007): "Novel DNA-binding element within the C-terminal extension of the nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain." Nucleic Acids Res., 35, 2705-2718. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm162.
- Abstract
- The heterodimer of the ecdysone receptor (EcR) and ultraspiracle (Usp), members of the nuclear receptors superfamily, is considered as the functional receptor for ecdysteroids initiating molting and metamorphosis in insects. Here we report the 1.95 A structure of the complex formed by the DNA-binding domains (DBDs) the EcR and the Usp, bound to the natural pseudopalindromic response element. Comparison of the structure with that obtained previously, using an idealized response element, shows how the EcRDBD, which has been previously reported to possess extraordinary flexibility, accommodates DNA-induced structural changes. Part of the C-terminal extension (CTE) of the EcRDBD folds into an alpha-helix whose location in the minor groove does not match any of the locations previously observed for nuclear receptors. Mutational analyses suggest that the alpha-helix is a component of EcR-box, a novel element indispensable for DNA-binding and located within the nuclear receptor CTE. This element seems to be a general feature of all known EcRs.