Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2hap; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
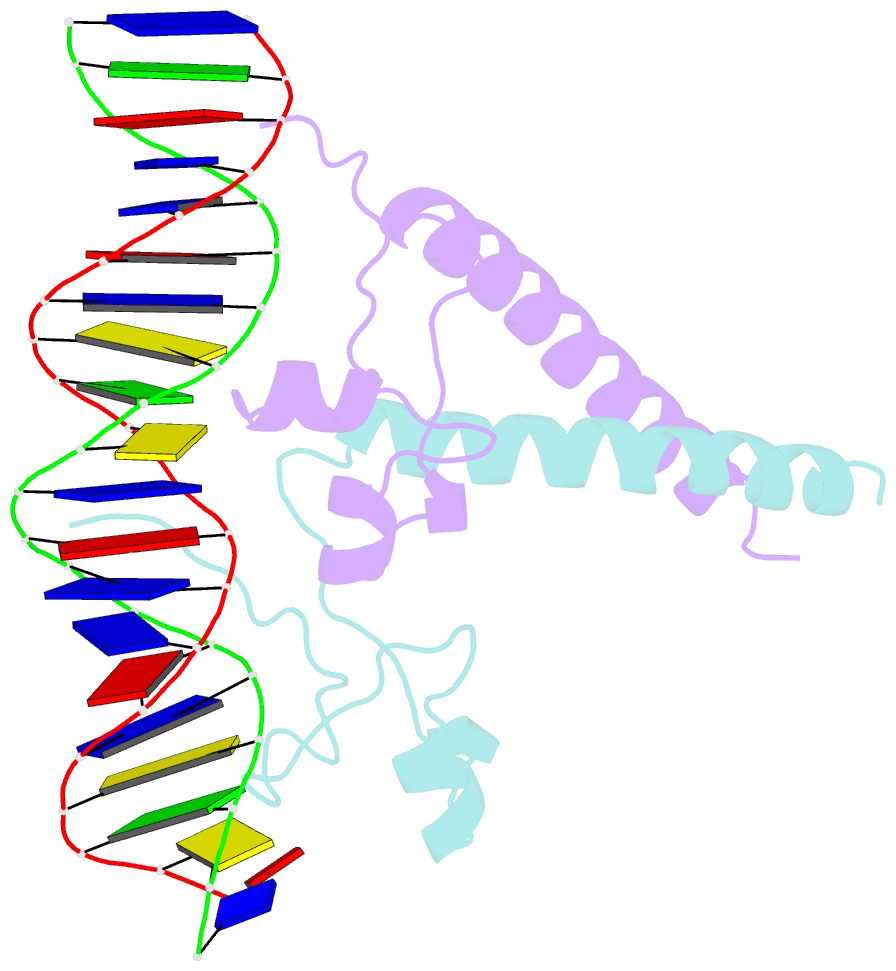
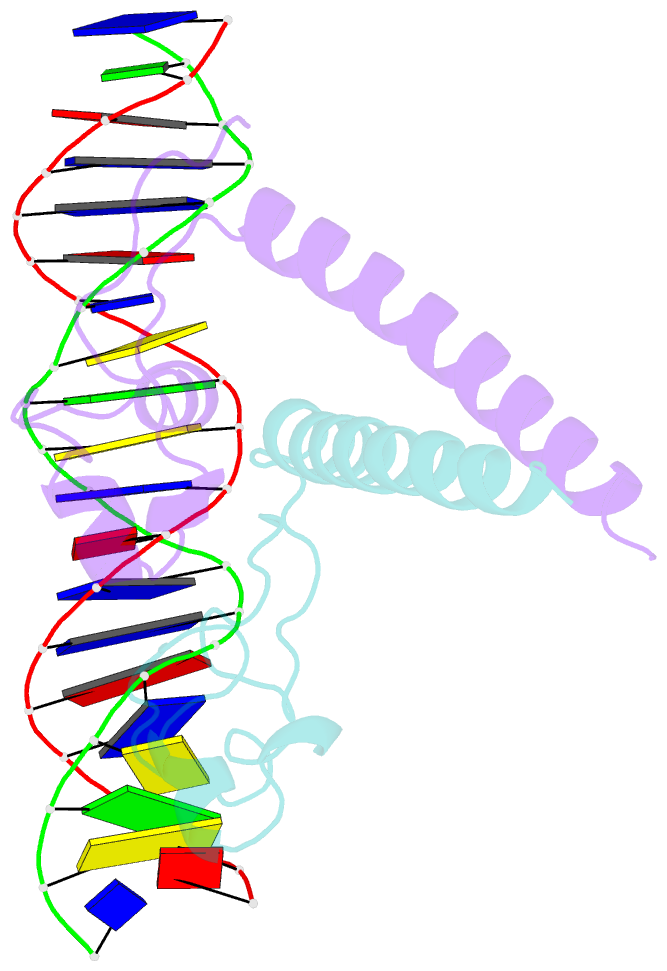
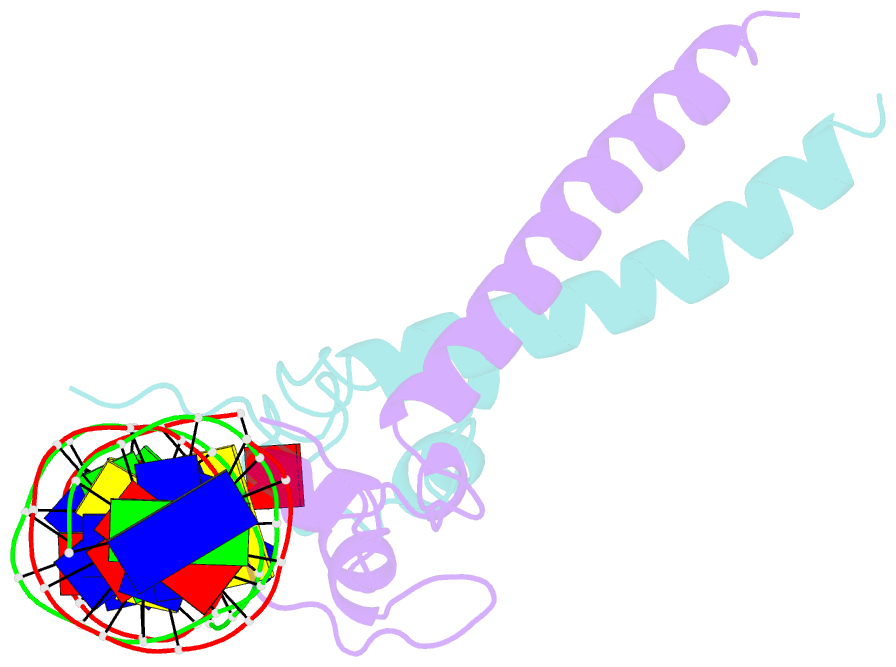
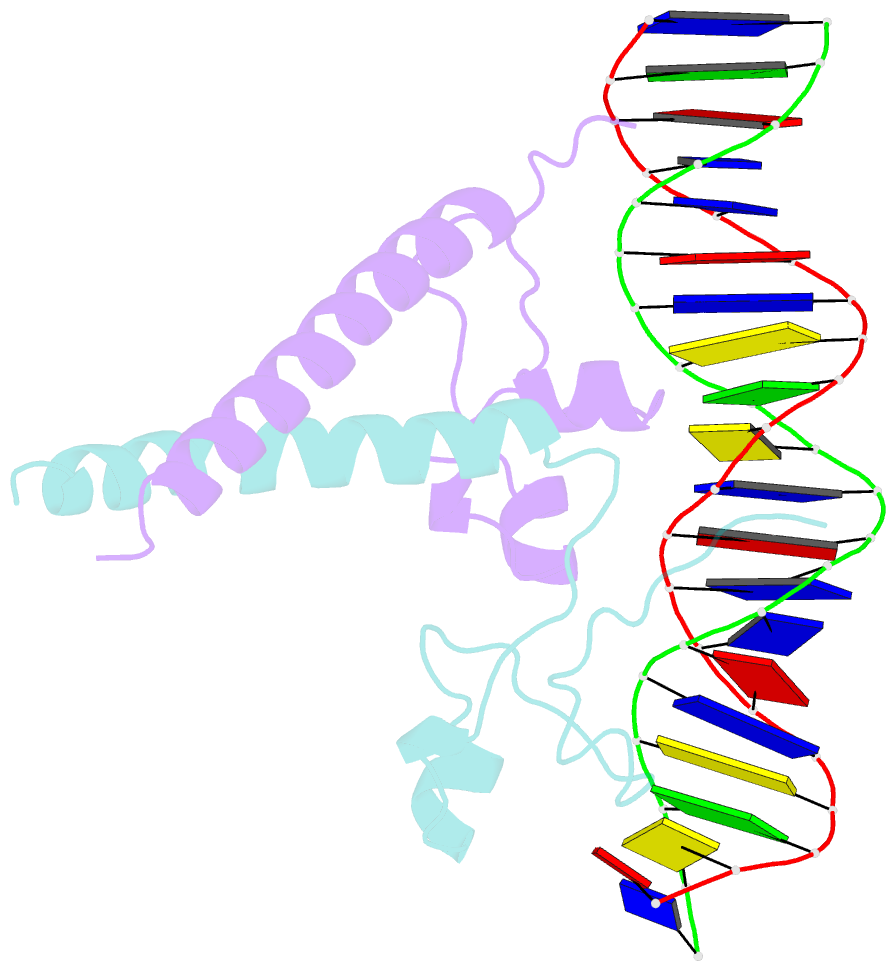
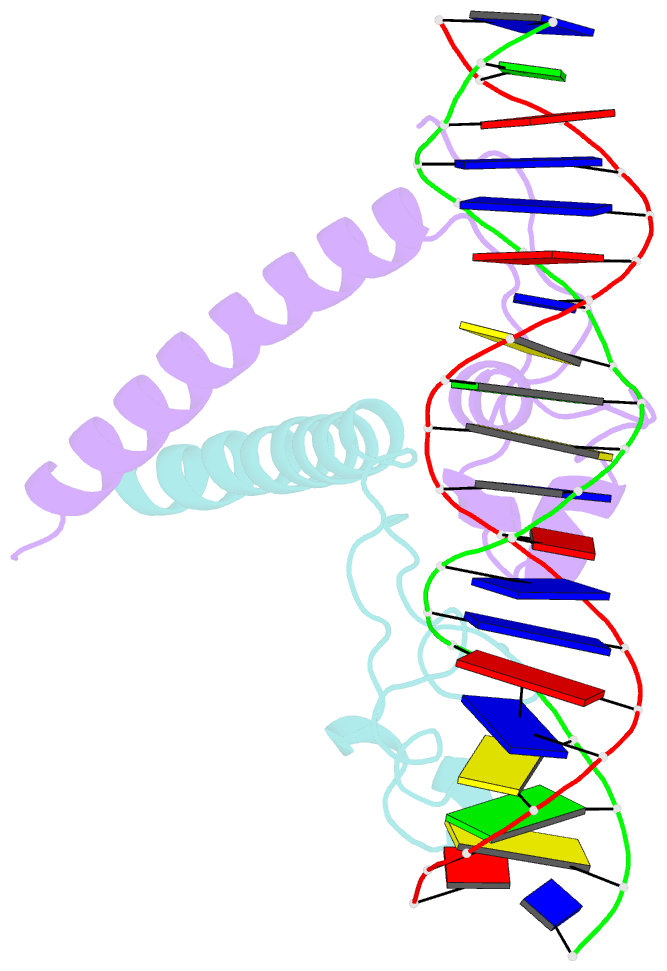
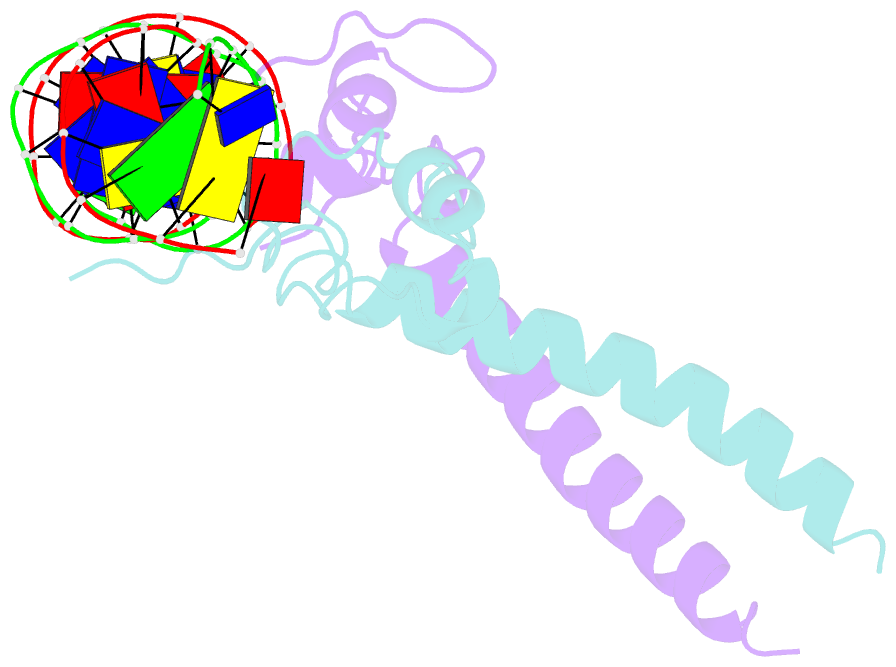
- Structure of a hap1-18-DNA complex reveals that protein-DNA interactions can have direct allosteric effects on transcriptional activation
- Reference
- King DA, Zhang L, Guarente L, Marmorstein R (1999): "Structure of HAP1-18-DNA implicates direct allosteric effect of protein-DNA interactions on transcriptional activation." Nat.Struct.Biol., 6, 22-27. doi: 10.1038/4893.
- Abstract
- HAP1 is a yeast transcriptional activator that binds with equal affinity to the dissimilar upstream activation sequences UAS1 and UAS(CYC7), but activates transcription differentially when bound to each site. HAP1-18 harbors an amino acid change in the DNA binding domain. While binding UAS1 poorly, HAP1-18 binds UAS(CYC7) with wild-type properties and activates transcription at elevated levels relative to HAP1. We have determined the structure of HAP1-18-UAS(CYC7) and have compared it to HAP1-UAS(CYC7). Unexpectedly, the single amino acid substitution in HAP1-18 nucleates a significantly altered hydrogen bond interface between the protein and DNA resulting in DNA conformational changes and an ordering of one N-terminal arm of the protein dimer along the DNA minor groove. These observations, together with a large subset of transcriptionally defective mutations in the HAP1 DNA-binding domain that map to the HAP1-DNA interface, suggest that protein-DNA interactions may have direct allosteric effects on transcriptional activation.