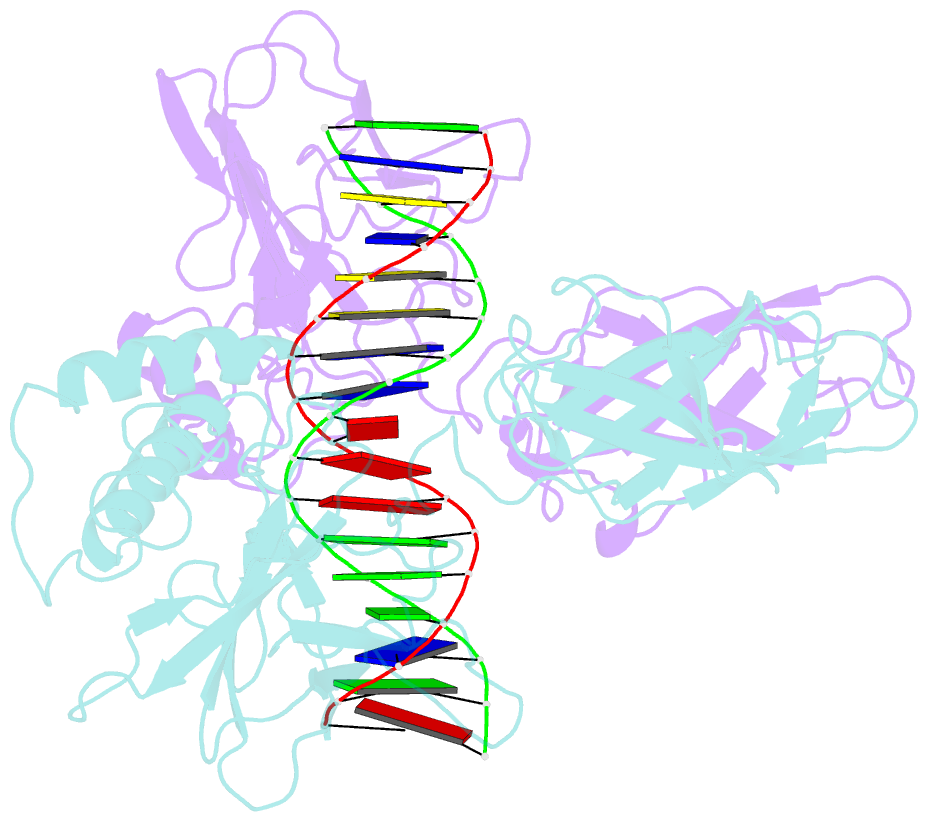
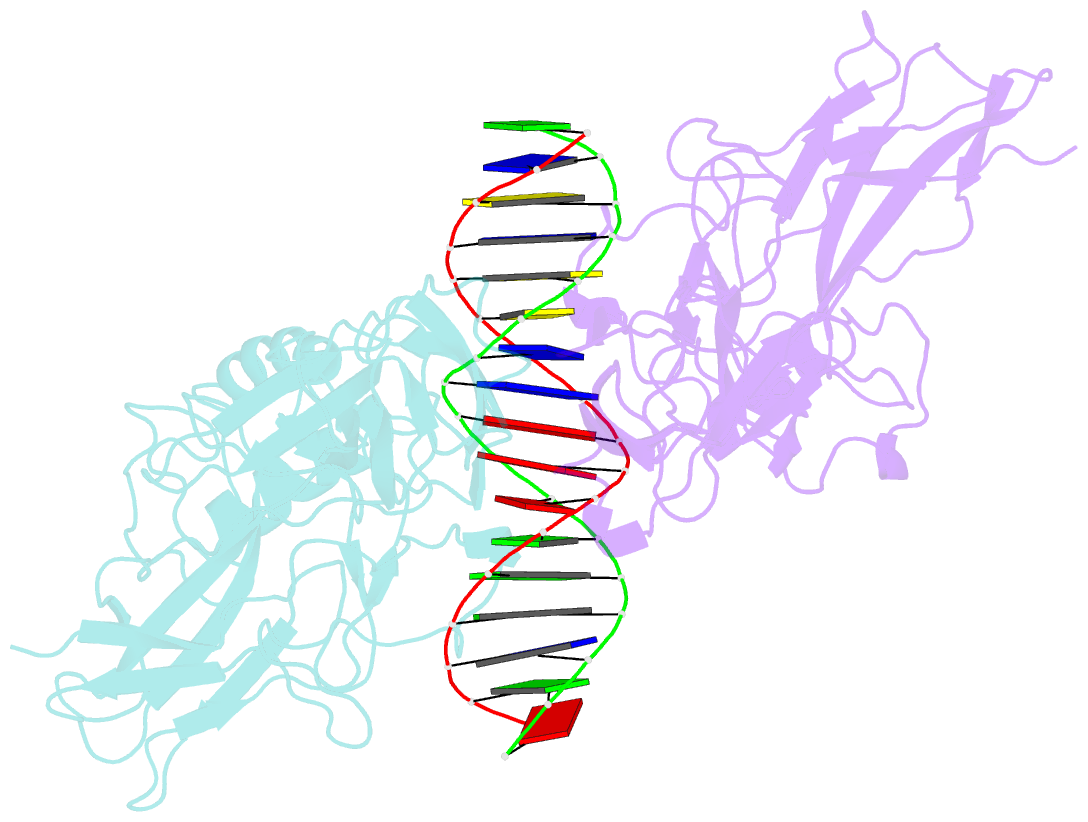
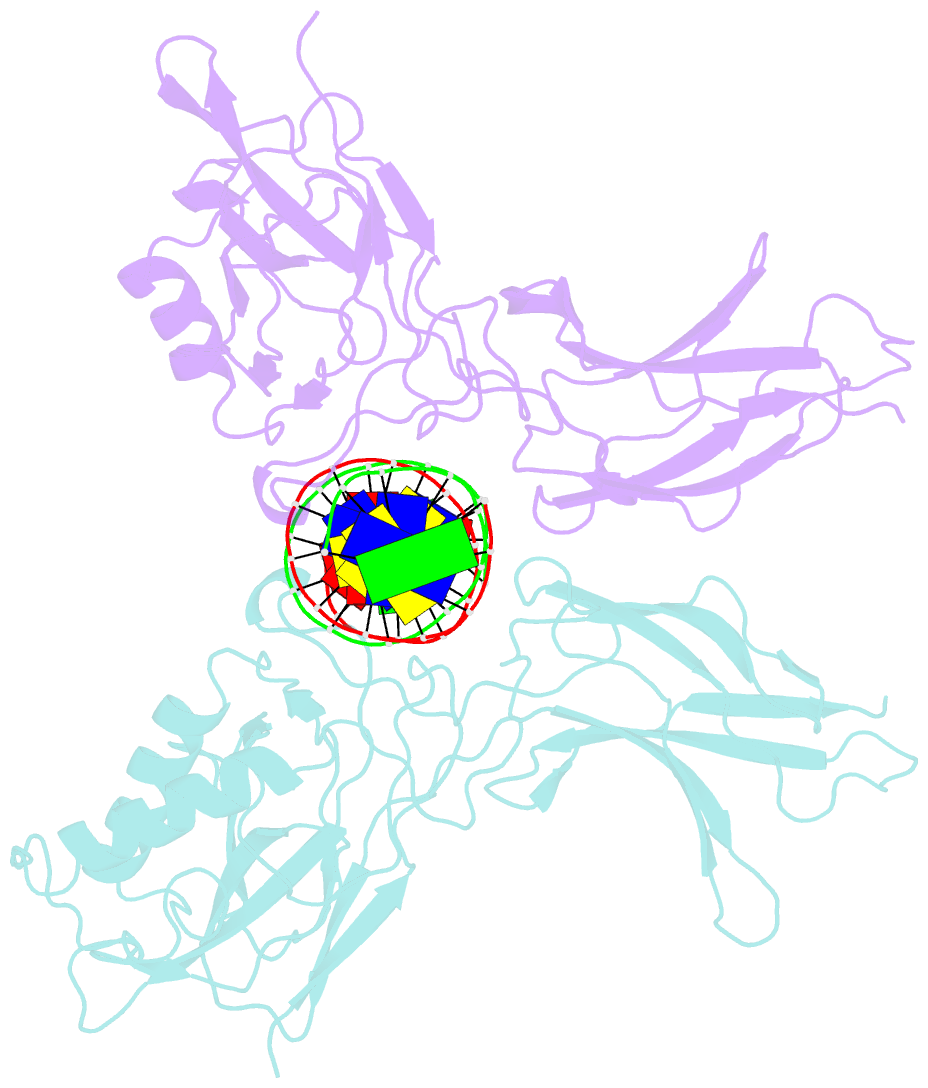
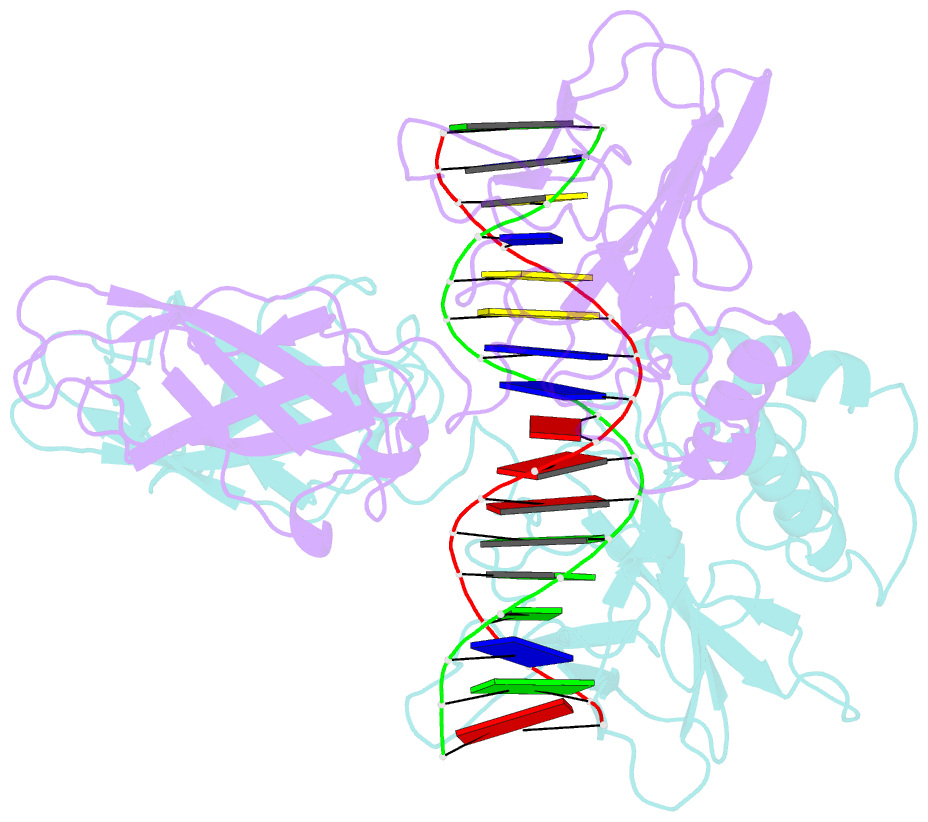
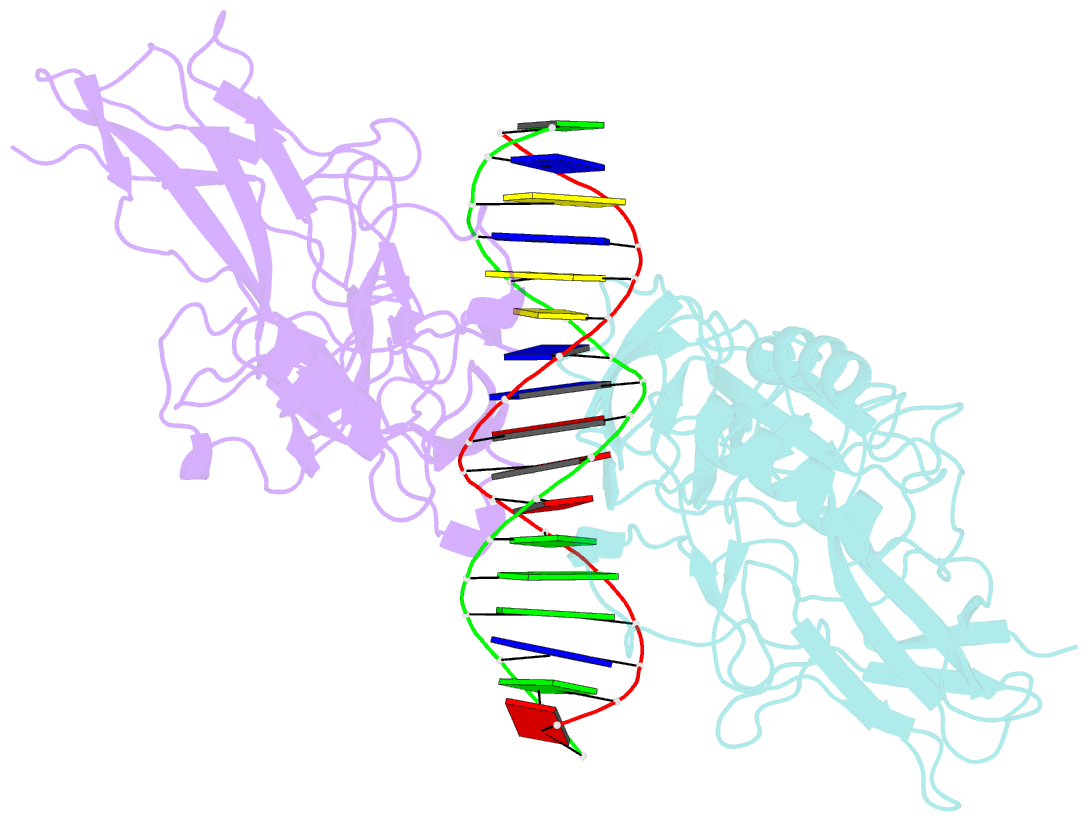
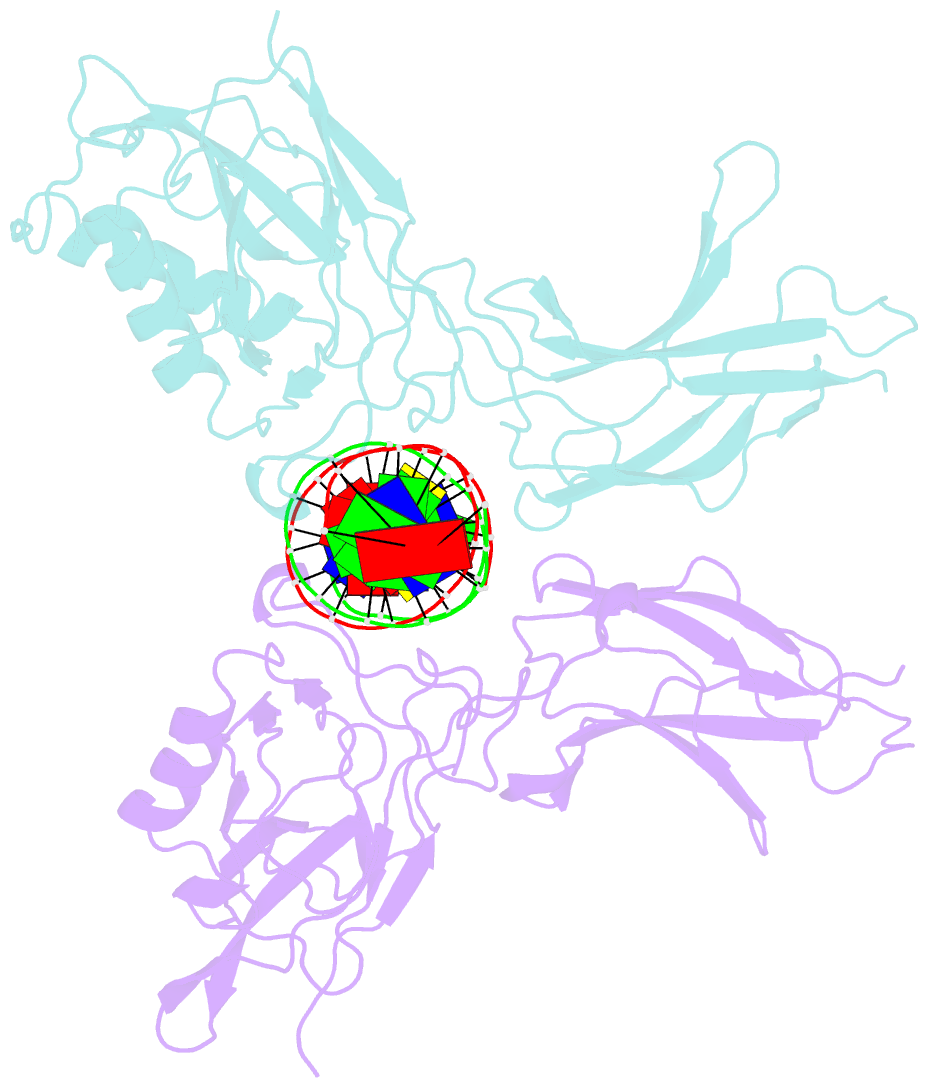
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2i9t; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.8 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of nf-kb p65-p50 heterodimer bound to prdii element of b-interferon promoter
- Reference
- Escalante CR, Shen L, Thanos D, Aggarwal AK (2002): "Structure of NF-kappaB p50/p65 heterodimer bound to the PRDII DNA element from the interferon-beta promoter." Structure, 10, 383-391. doi: 10.1016/S0969-2126(02)00723-2.
- Abstract
- Upon viral infection, NF-kappaB translocates to the nucleus and activates the IFN-beta gene by binding to the PRDII element. Strikingly, NF-kappaB loses its ability to activate the IFN-beta gene when the PRDII element is substituted by closely related sites. We report here the crystal structure of NF-kappaB p50/p65 heterodimer bound to the PRDII element from the IFN-beta promoter. The structure reveals an unexpected alteration in configuration, in which the p50 specificity domain moves by as much as approximately 9 A when compared to NF-kappaB heterodimer bound to the immunoglobulin kappaB site (Ig-kappaB) while maintaining the same base-specific contacts with the DNA. Taken together, the structure offers new insights into the allosteric effects of closely related DNA sites on the configuration of NF-kappaB and its transcriptional selectivity.