Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2km8; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
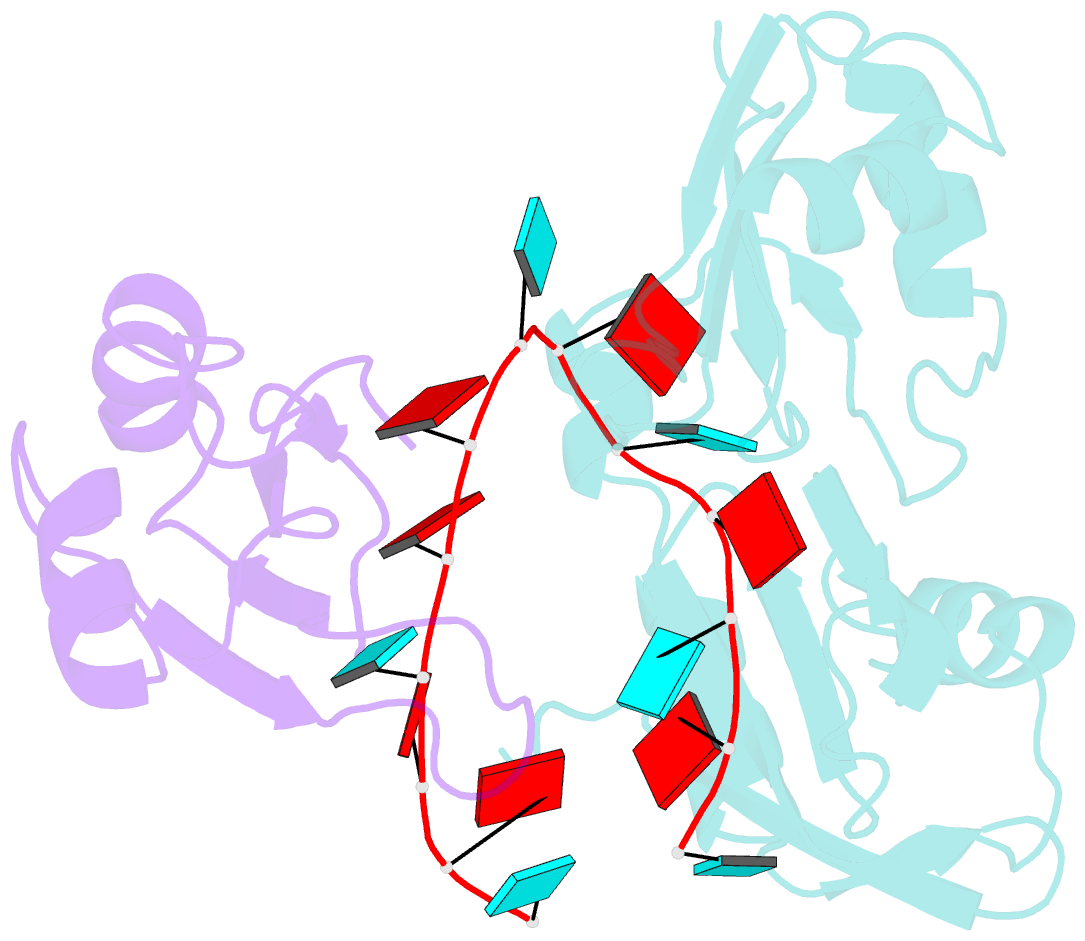
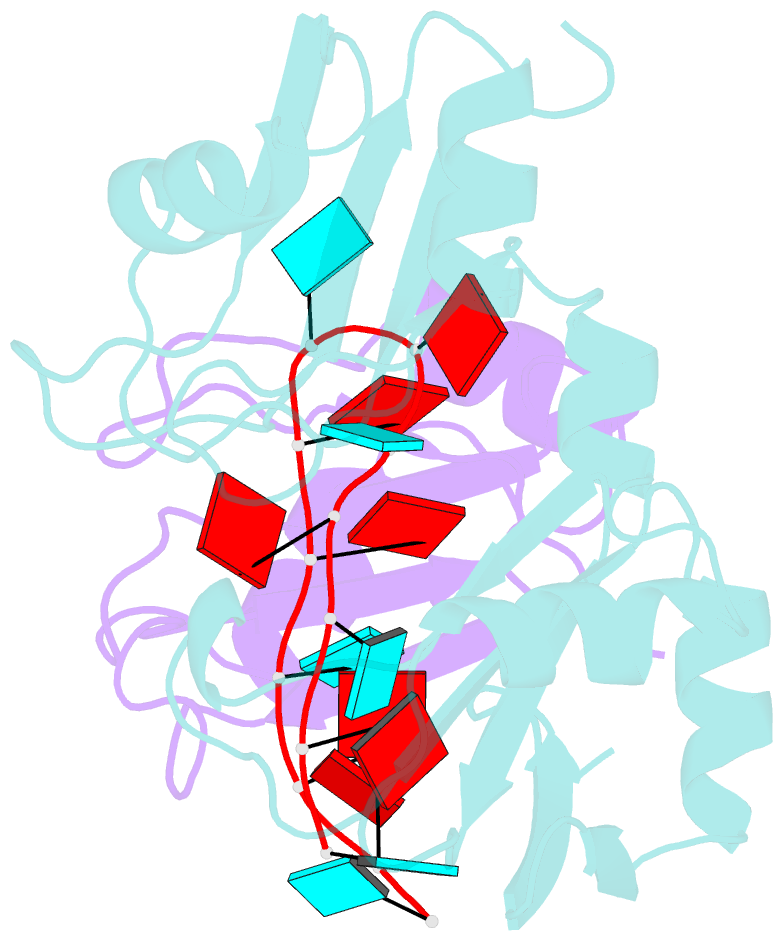
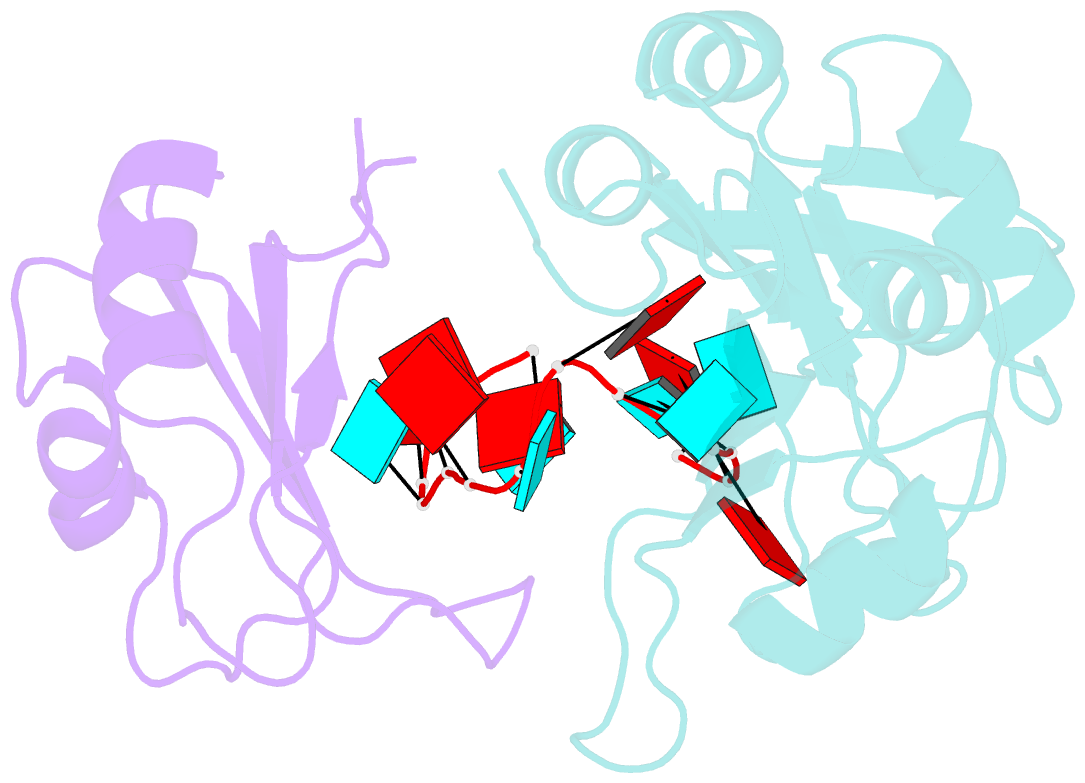
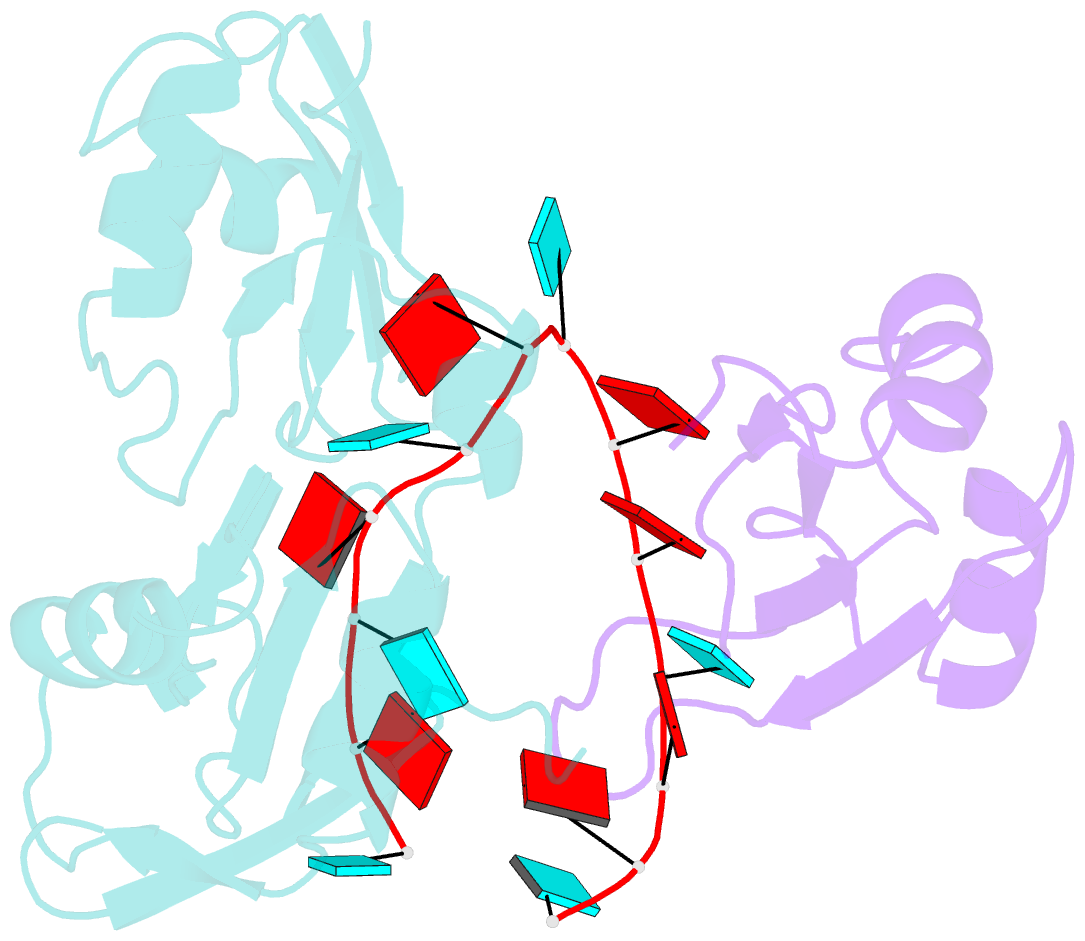
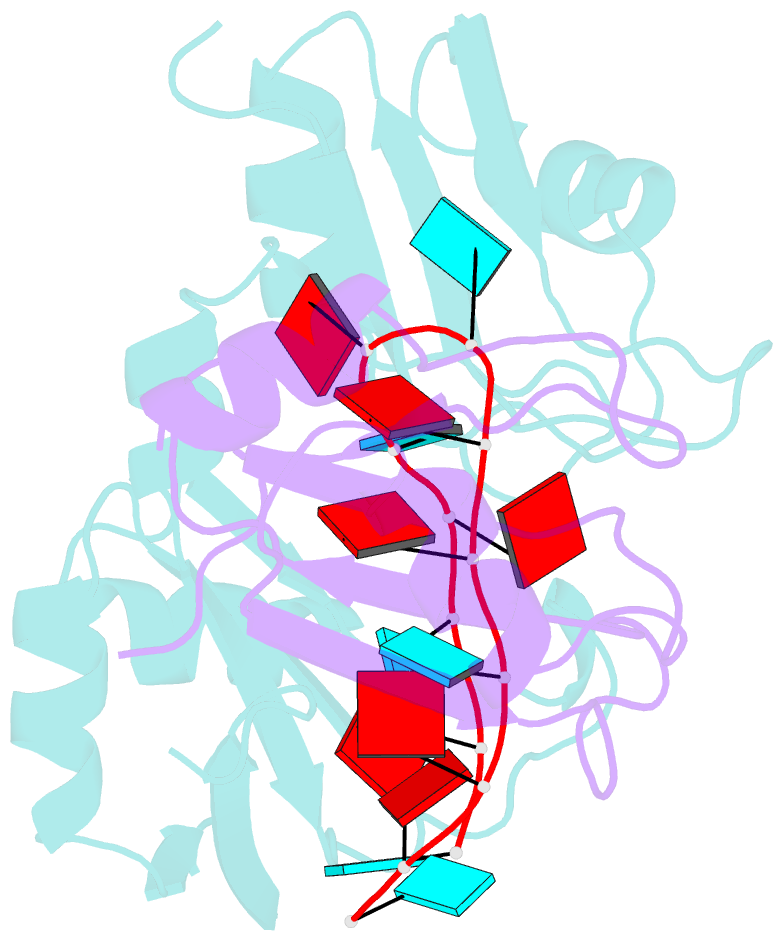
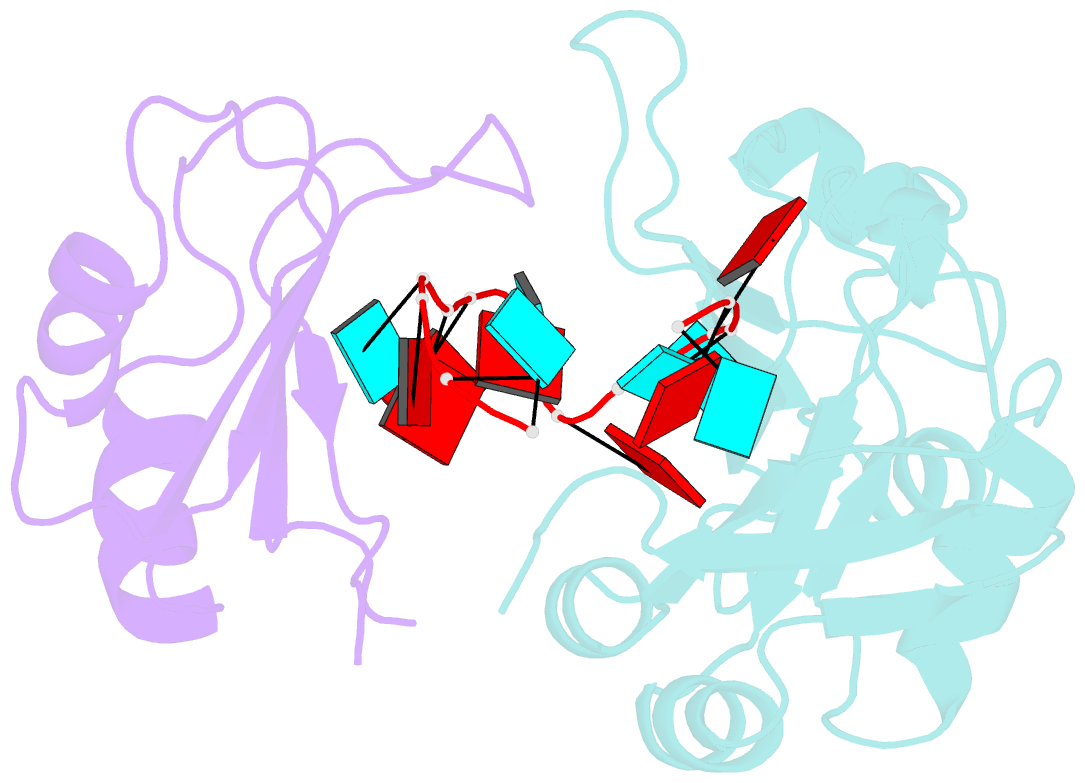
- Interdomain rrm packing contributes to RNA recognition in the rna15, hrp1, anchor RNA 3' processing ternary complex
- Reference
- Leeper TC, Qu X, Lu C, Moore C, Varani G (2010): "Novel Protein-Protein Contacts Facilitate mRNA 3'-Processing Signal Recognition by Rna15 and Hrp1." J.Mol.Biol., 401, 334-349. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.06.032.
- Abstract
- Precise 3'-end processing of mRNA is essential for correct gene expression, yet in yeast, 3'-processing signals consist of multiple ambiguous sequence elements. Two neighboring elements upstream of the cleavage site are particularly important for the accuracy (positioning element) and efficiency (efficiency element) of 3'-processing and are recognized by the RNA-binding proteins Rna15 and Hrp1, respectively. In vivo, these interactions are strengthened by the scaffolding protein Rna14 that stabilizes their association. The NMR structure of the 34 -kDa ternary complex of the RNA recognition motif (RRM) domains of Hrp1 and Rna15 bound to this pair of RNA elements was determined by residual dipolar coupling and paramagnetic relaxation experiments. It reveals how each of the proteins binds to RNA and introduces a novel class of protein-protein contact in regions of previously unknown function. These interdomain contacts had previously been overlooked in other multi-RRM structures, although a careful analysis suggests that they may be frequently present. Mutations in the regions of these contacts disrupt 3'-end processing, suggesting that they may structurally organize the ribonucleoprotein complexes responsible for RNA processing.