Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2kn7; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
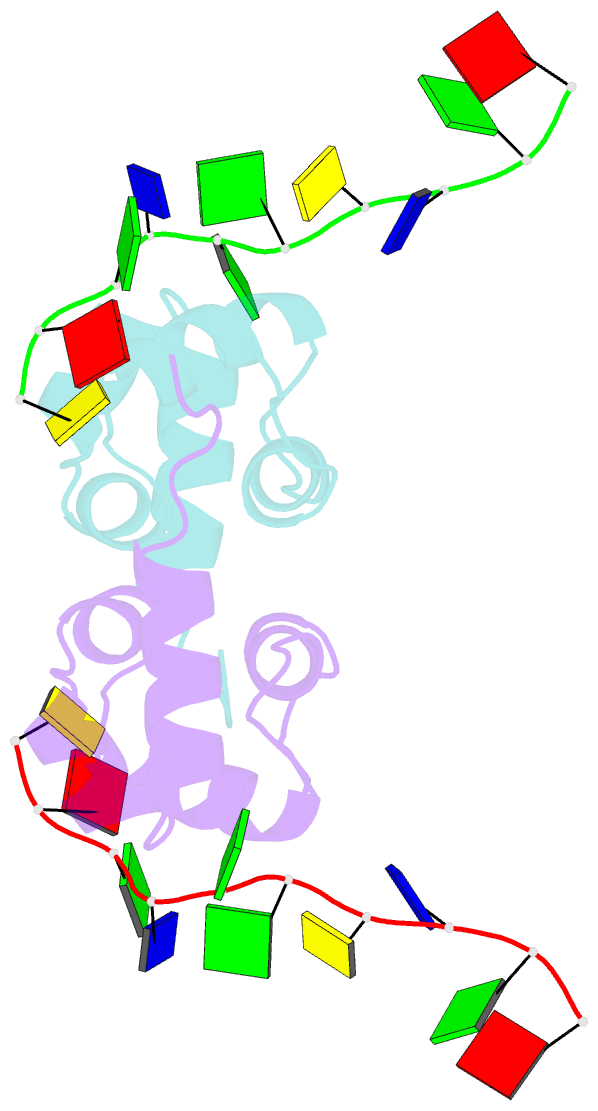
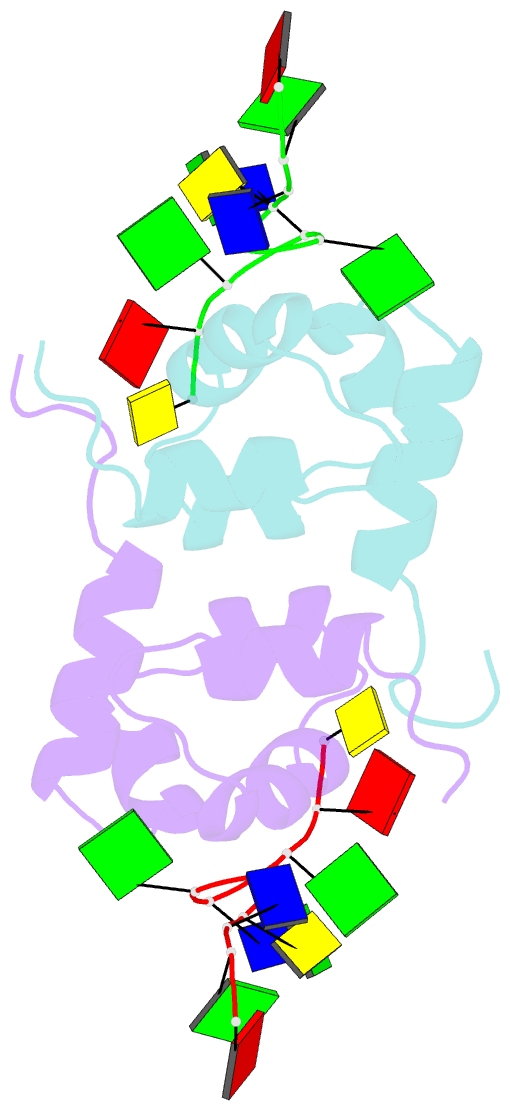
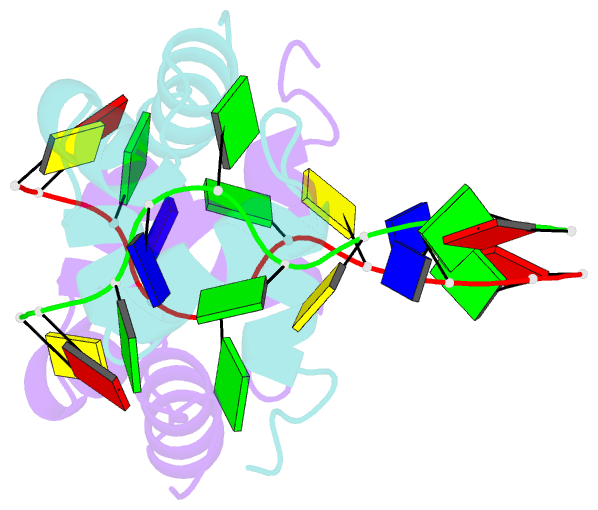
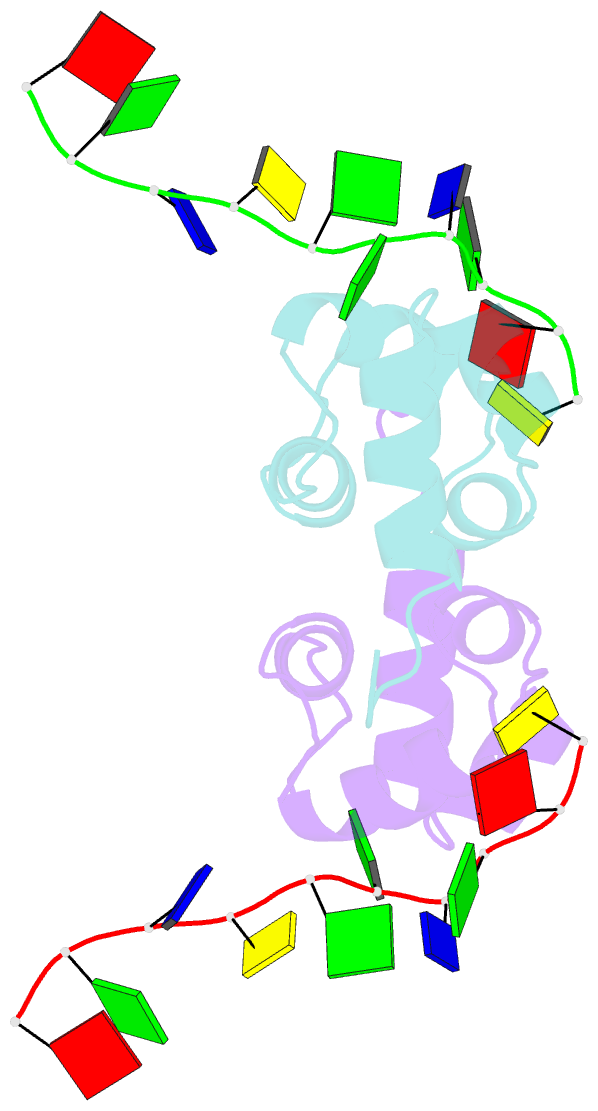
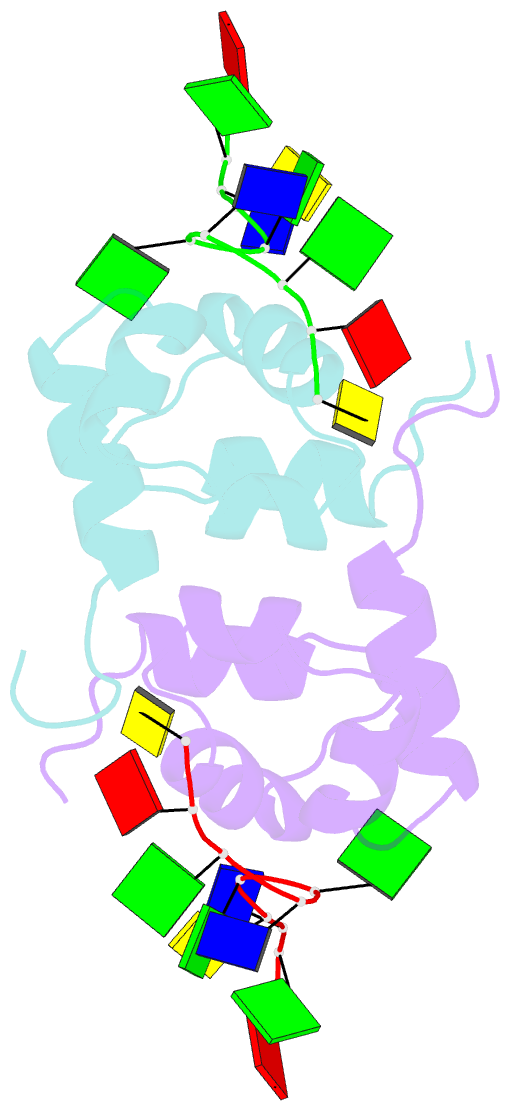
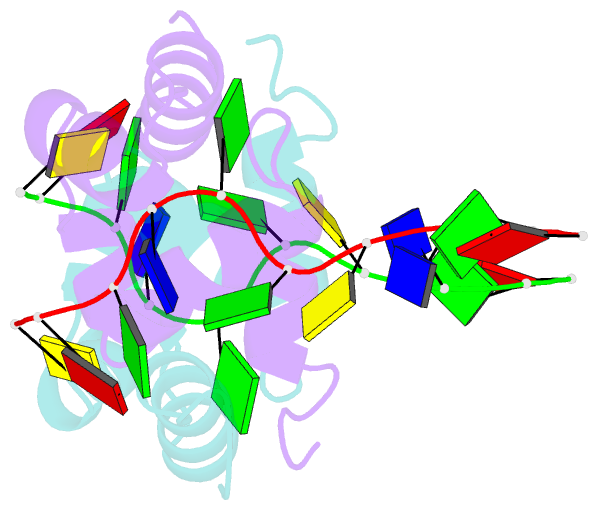
- Structure of the xpf-single strand DNA complex
- Reference
- Das D, Folkers GE, van Dijk M, Jaspers NGJ, Hoeijmakers JHJ, Kaptein R, Boelens R (2012): "The structure of the XPF-ssDNA complex underscores the distinct roles of the XPF and ERCC1 helix- hairpin-helix domains in ss/ds DNA recognition." Structure, 20, 667-675. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.02.009.
- Abstract
- Human XPF/ERCC1 is a structure-specific DNA endonuclease that nicks the damaged DNA strand at the 5' end during nucleotide excision repair. We determined the structure of the complex of the C-terminal domain of XPF with 10 nt ssDNA. A positively charged region within the second helix of the first HhH motif contacts the ssDNA phosphate backbone. One guanine base is flipped out of register and positioned in a pocket contacting residues from both HhH motifs of XPF. Comparison to other HhH-containing proteins indicates a one-residue deletion in the second HhH motif of XPF that has altered the hairpin conformation, thereby permitting ssDNA interactions. Previous nuclear magnetic resonance studies showed that ERCC1 in the XPF-ERCC1 heterodimer can bind dsDNA. Combining the two observations gives a model that underscores the asymmetry of the human XPF/ERCC1 heterodimer in binding at an ss/ds DNA junction.