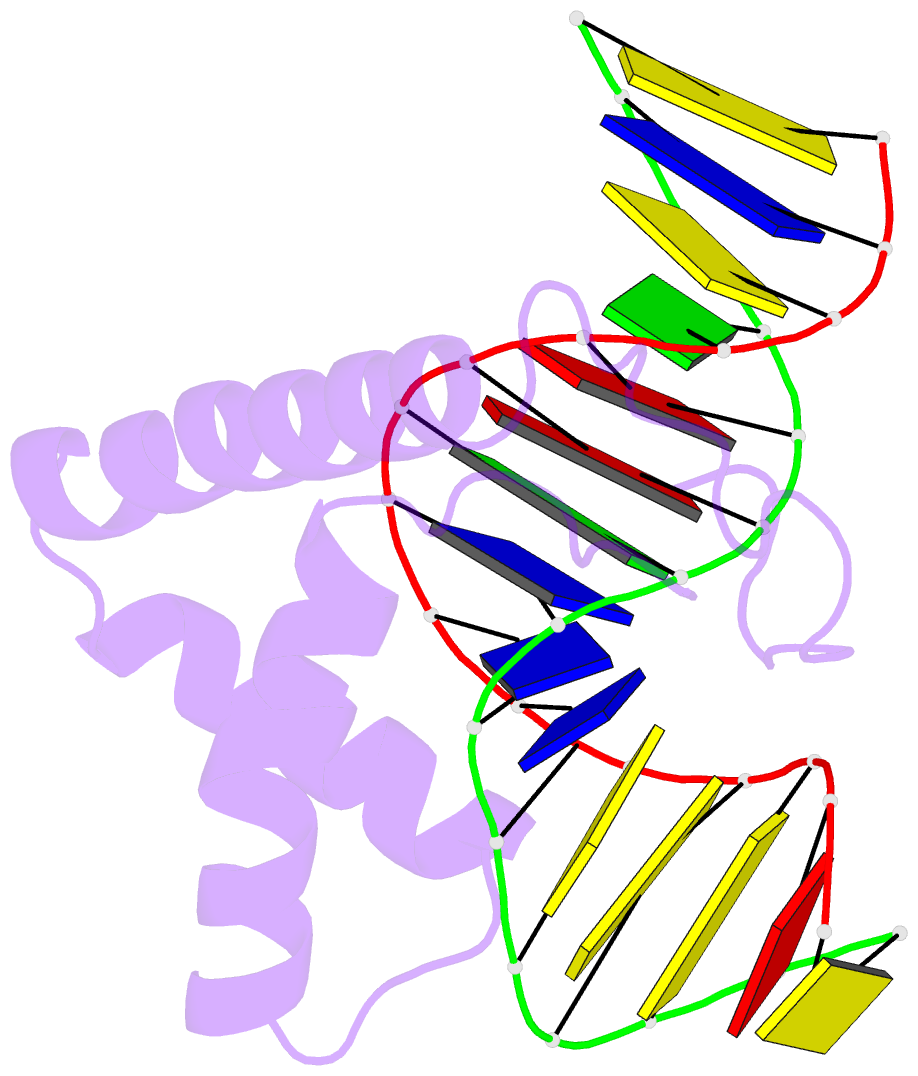
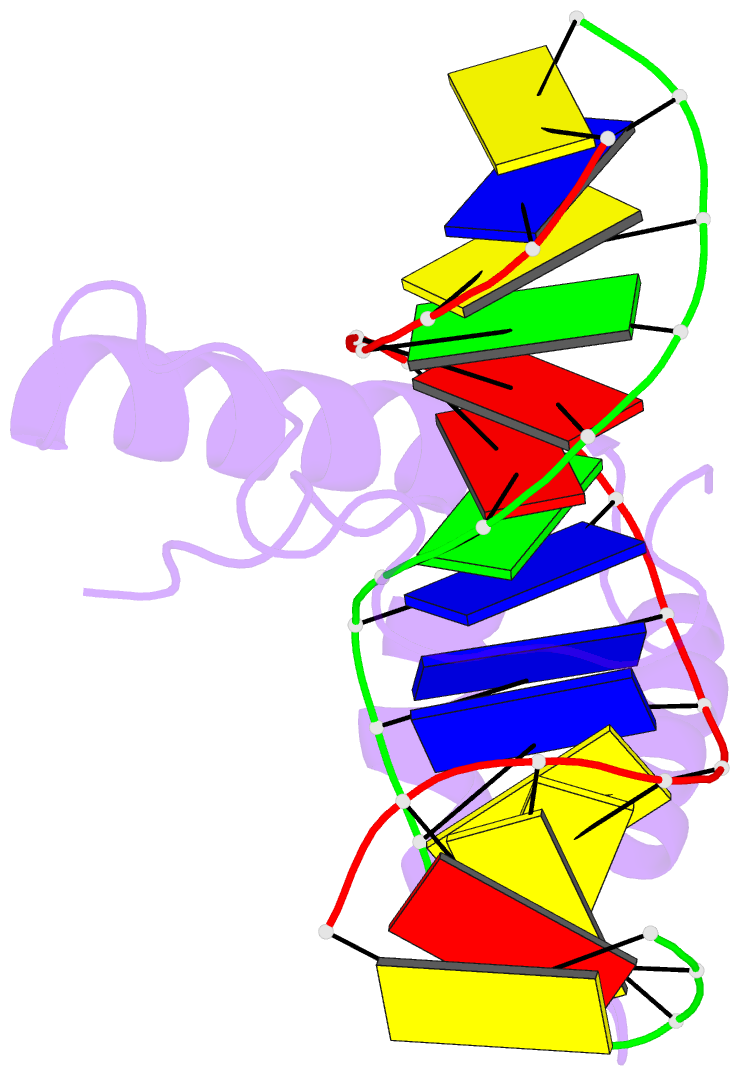
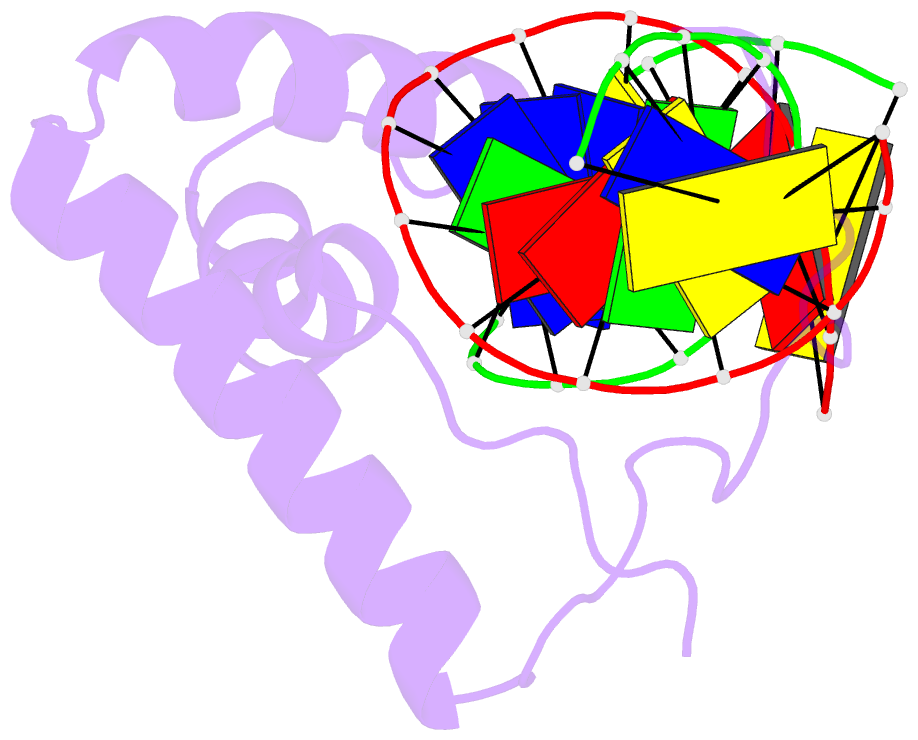
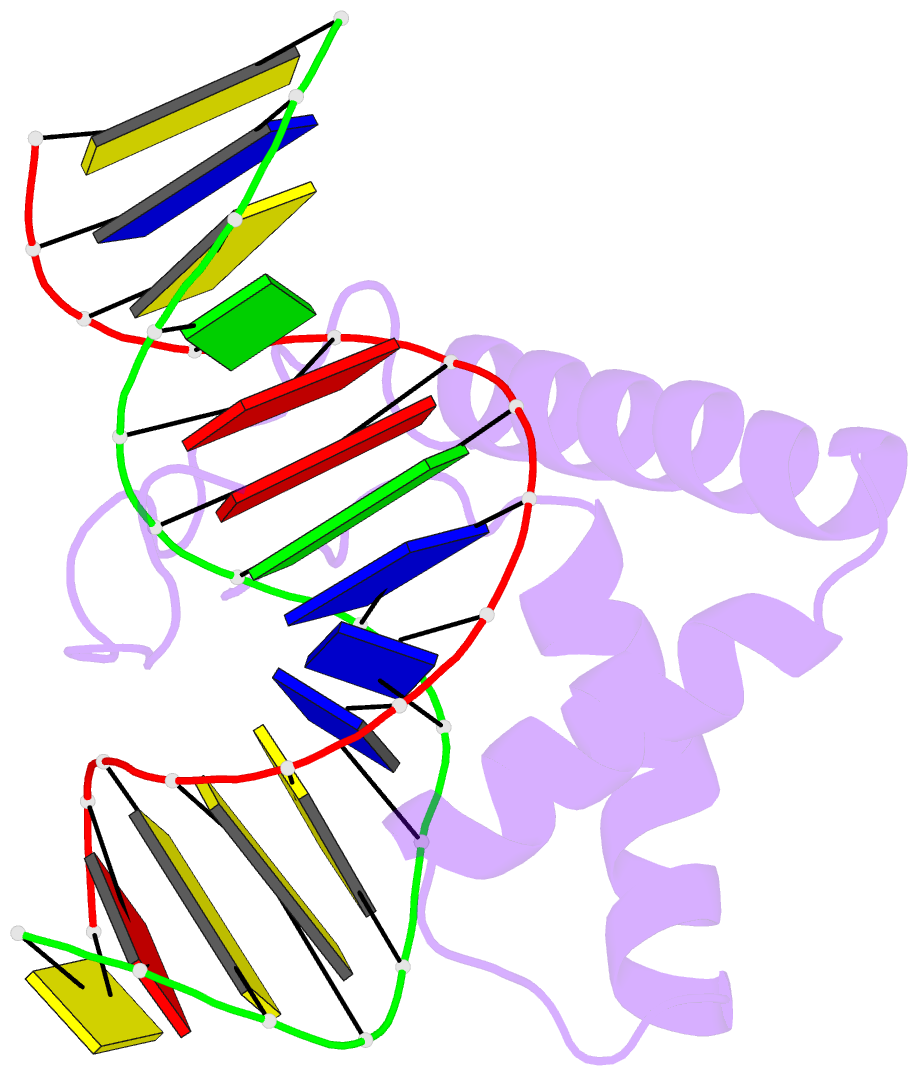
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2lef; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation-DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
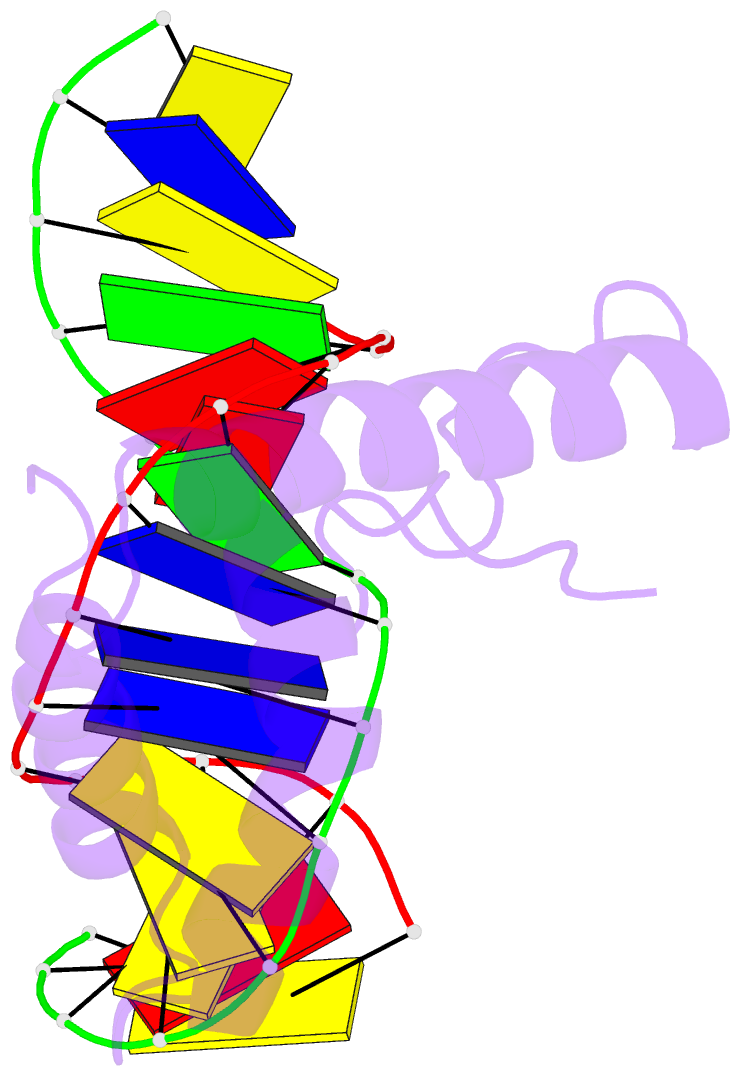
- Lef1 hmg domain (from mouse), complexed with DNA (15bp), NMR, 12 structures
- Reference
- Love JJ, Li X, Case DA, Giese K, Grosschedl R, Wright PE (1995): "Structural basis for DNA bending by the architectural transcription factor LEF-1." Nature, 376, 791-795. doi: 10.1038/376791a0.
- Abstract
- Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor (LEF-1) and the closely related T-cell factor 1 (TCF-1) are sequence-specific and cell-type-specific DNA-binding proteins that play important regulatory roles in organogenesis and thymocyte differentiation. LEF-1 participates in regulation of the enhancer associated with the T cell receptor (TCR)-alpha gene by inducing a sharp bend in the DNA and facilitating interactions between Ets-1, PEBP2-alpha, and ATF/CREB, transcription factors bound at sites flanking the LEF-1 site. It seems that LEF-1 plays an architectural role in the assembly and function of this regulatory nucleoprotein complex. LEF-1 recognizes a specific nucleotide sequence through a high-mobility-group (HMG) domain. Proteins containing HMG domains bind DNA in the minor groove, bend the double helix, and recognize four-way junctions and other irregular DNA structures. Here we report the solution structure of a complex of the LEF-1 HMG domain and adjacent basic region with its cognate DNA. The structure reveals the HMG domain bound in the widened minor groove of a markedly distorted and bent double helix. The basic region binds across the narrowed major groove and contributes to DNA recognition.