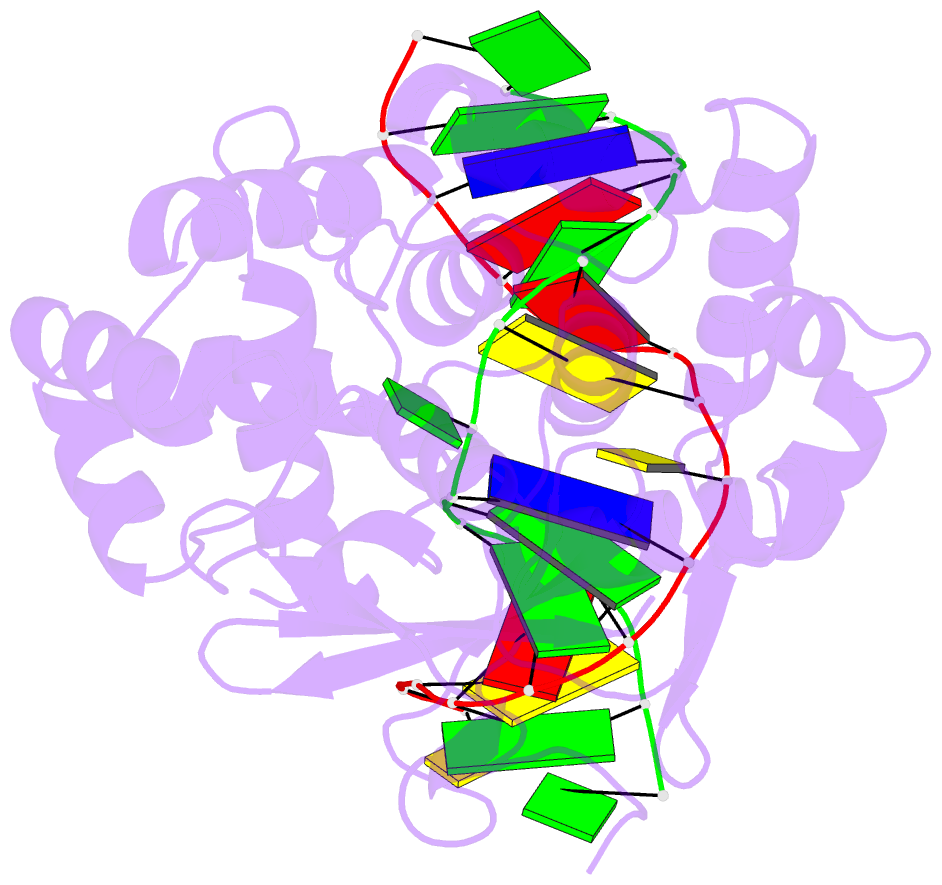
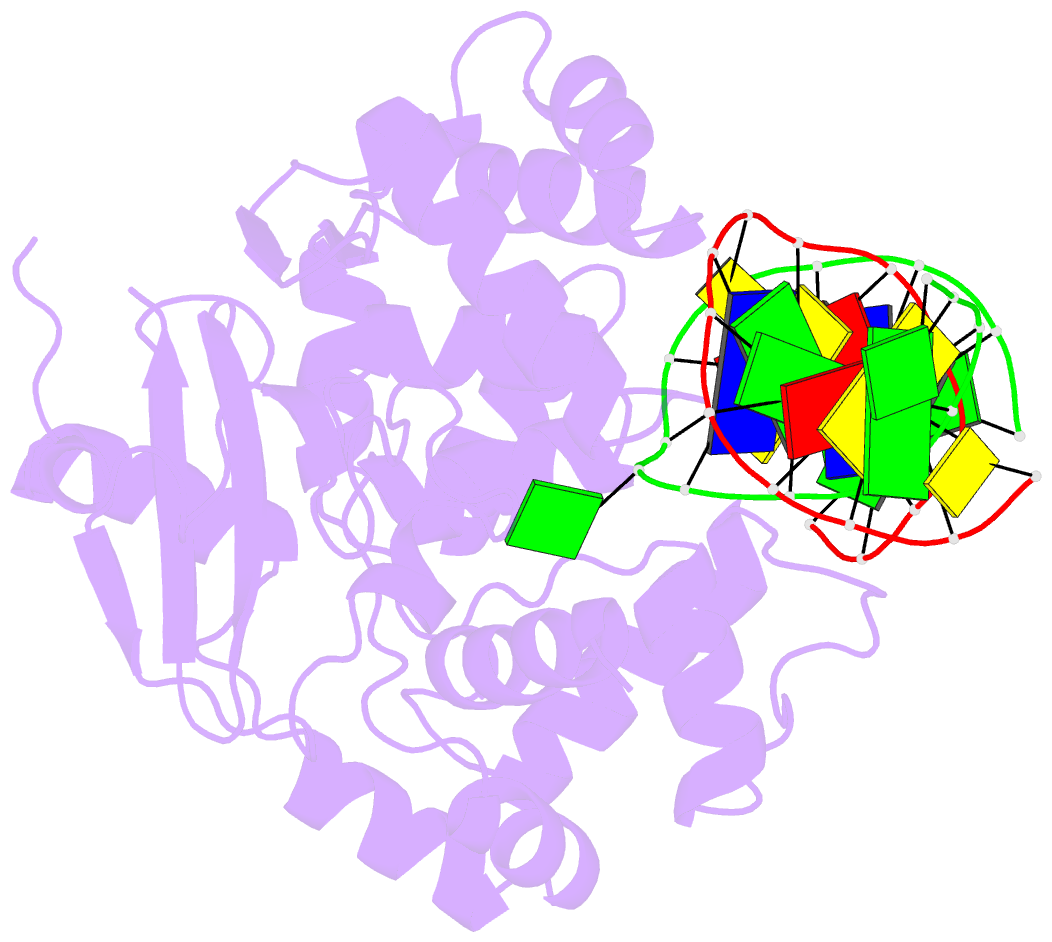
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2nol; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase, lyase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.57 Å)
- Summary
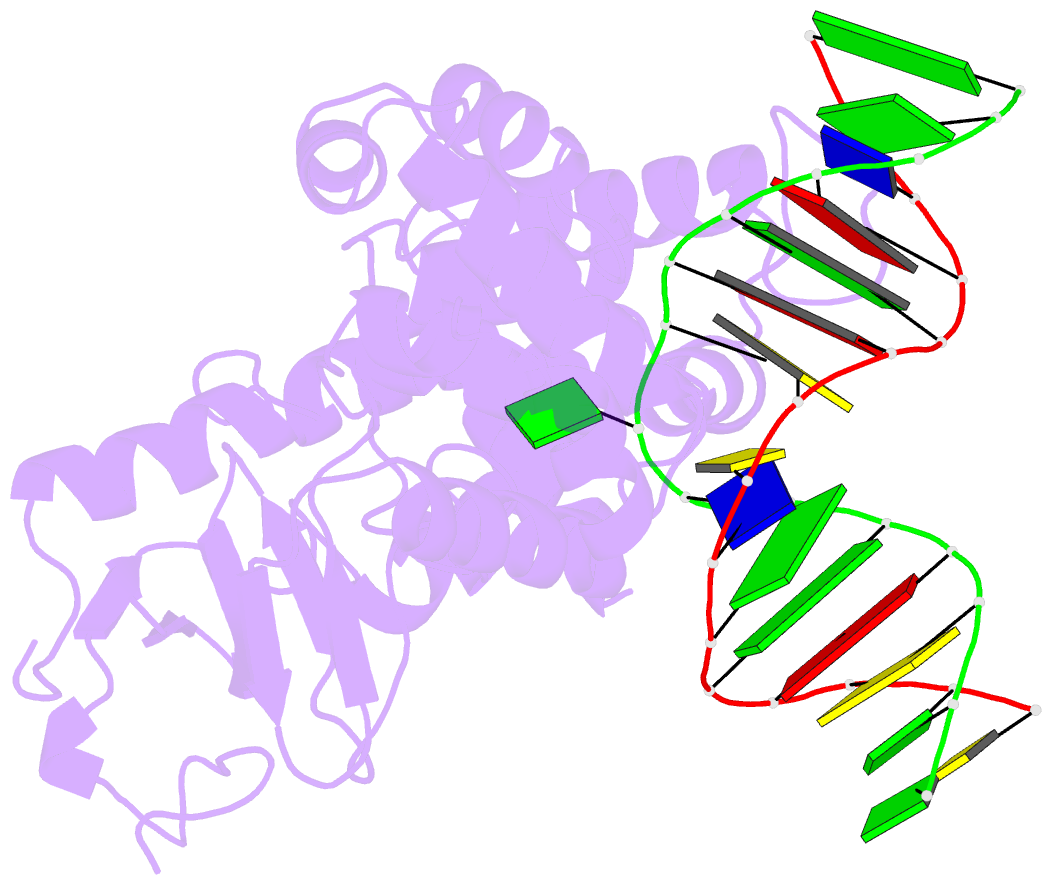
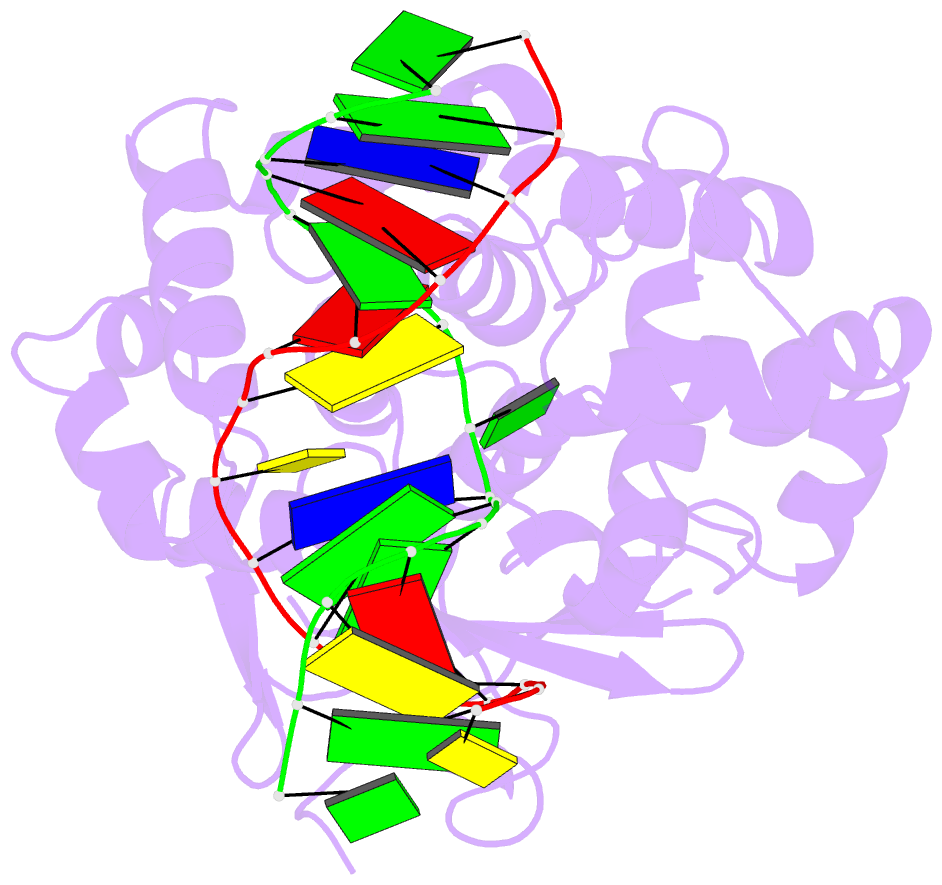
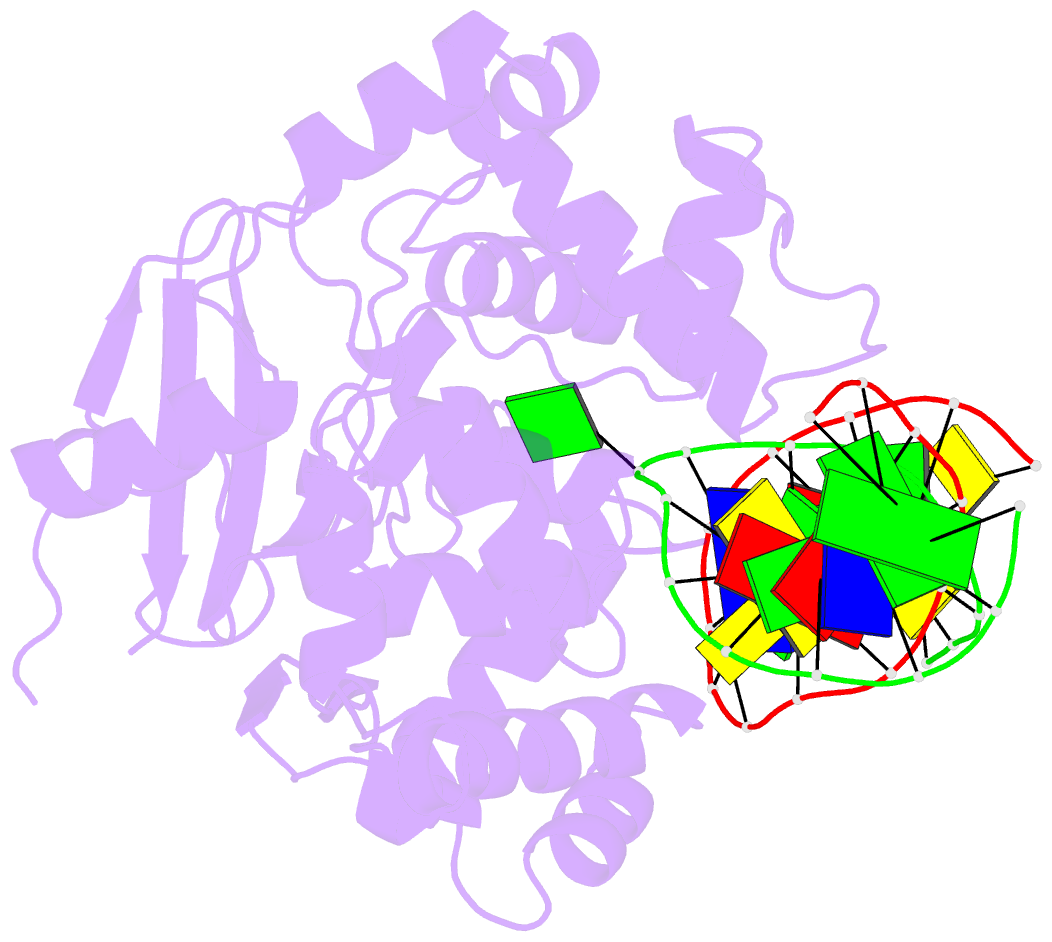
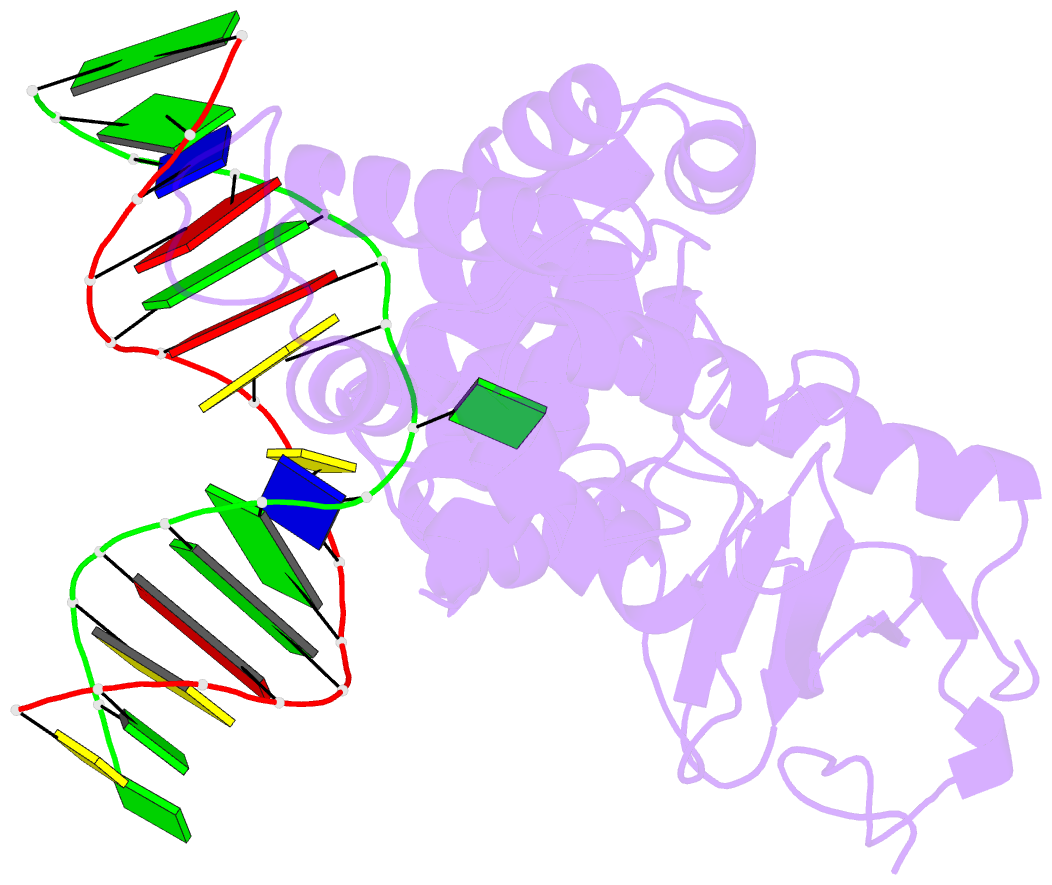
- Structure of catalytically inactive human 8-oxoguanine glycosylase distal crosslink to oxog DNA
- Reference
- Radom CT, Banerjee A, Verdine GL (2007): "Structural characterization of human 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase variants bearing active site mutations." J.Biol.Chem., 282, 9182-9194. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608989200.
- Abstract
- The human 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase (hOGG1) protein is responsible for initiating base excision DNA repair of the endogenous mutagen 8-oxoguanine. Like nearly all DNA glycosylases, hOGG1 extrudes its substrate from the DNA helix and inserts it into an extrahelical enzyme active site pocket lined with residues that participate in lesion recognition and catalysis. Structural analysis has been performed on mutant versions of hOGG1 having changes in catalytic residues but not on variants having altered 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (oxoG) contact residues. Here we report high resolution structural analysis of such recognition variants. We found that Ala substitution at residues that contact the phosphate 5' to the lesion (H270A mutation) and its Watson-Crick face (Q315A mutation) simply removed key functionality from the contact interface but otherwise had no effect on structure. Ala substitution at the only residue making an oxoG-specific contact (G42A mutation) introduced torsional stress into the DNA contact surface of hOGG1, but this was overcome by local interactions within the folded protein, indicating that this oxoG recognition motif is "hardwired." Introduction of a side chain intended to sterically obstruct the active site pocket (Q315F mutation) led to two different structures, one of which (Q315F(*149)) has the oxoG lesion in an exosite flanking the active site and the other of which (Q315F(*292)) has the oxoG inserted nearly completely into the lesion recognition pocket. The latter structure offers a view of the latest stage in the base extrusion pathway yet observed, and its lack of catalytic activity demonstrates that the transition state for displacement of the lesion base is geometrically demanding.