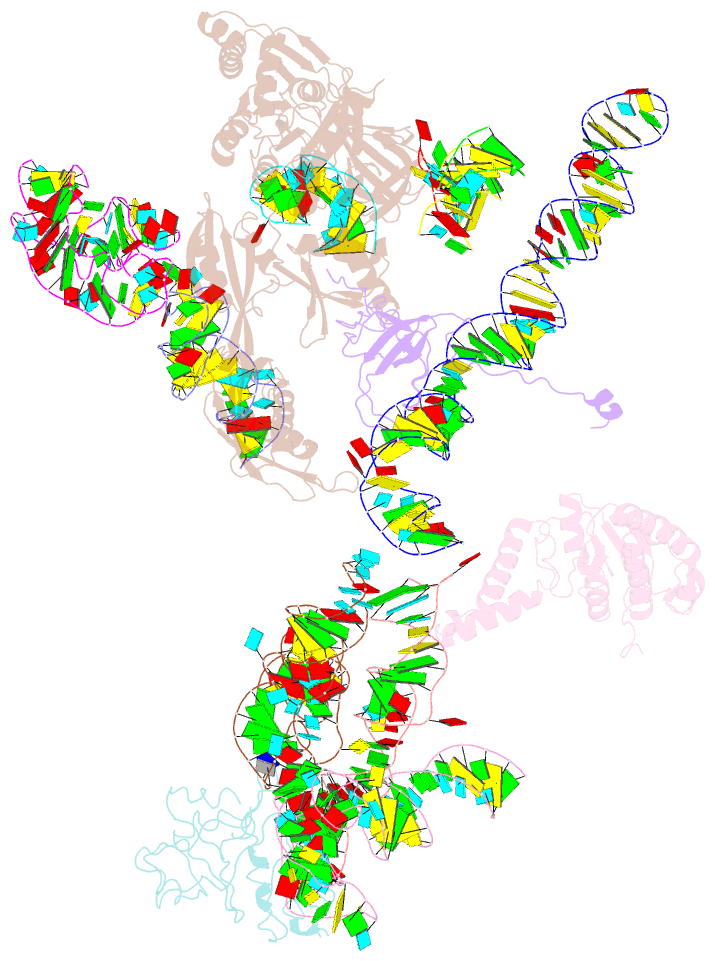
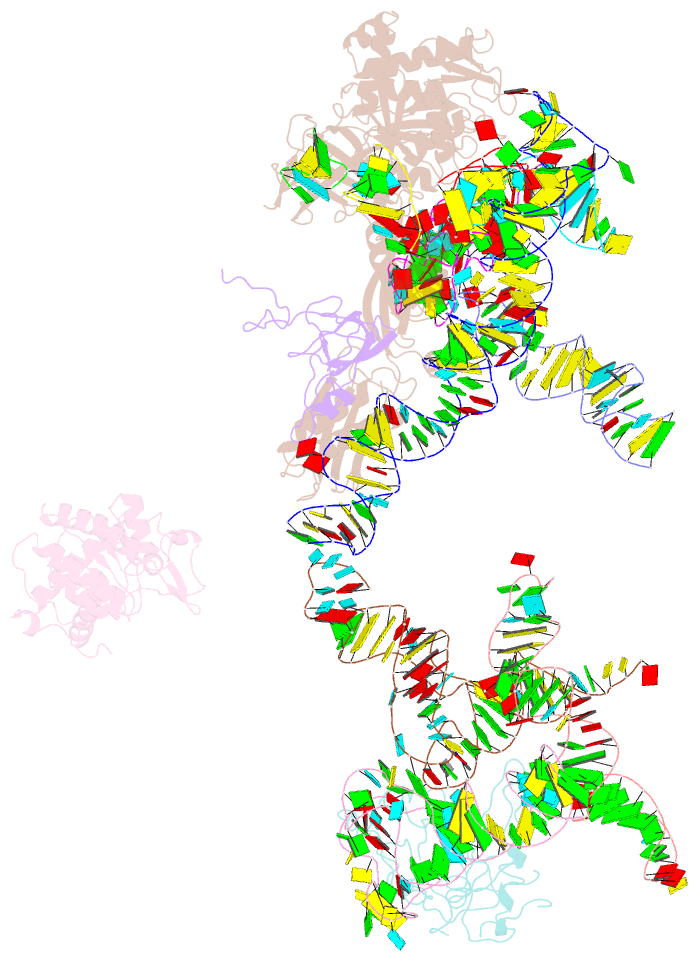
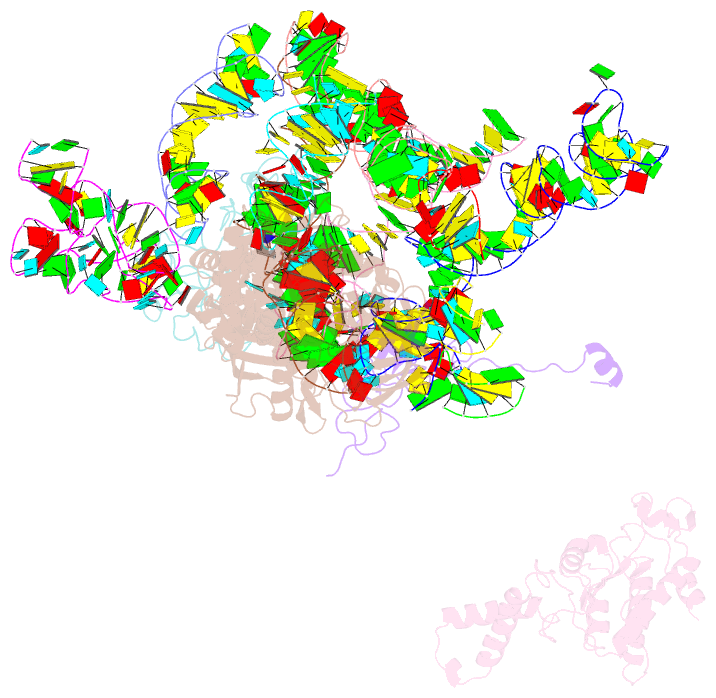
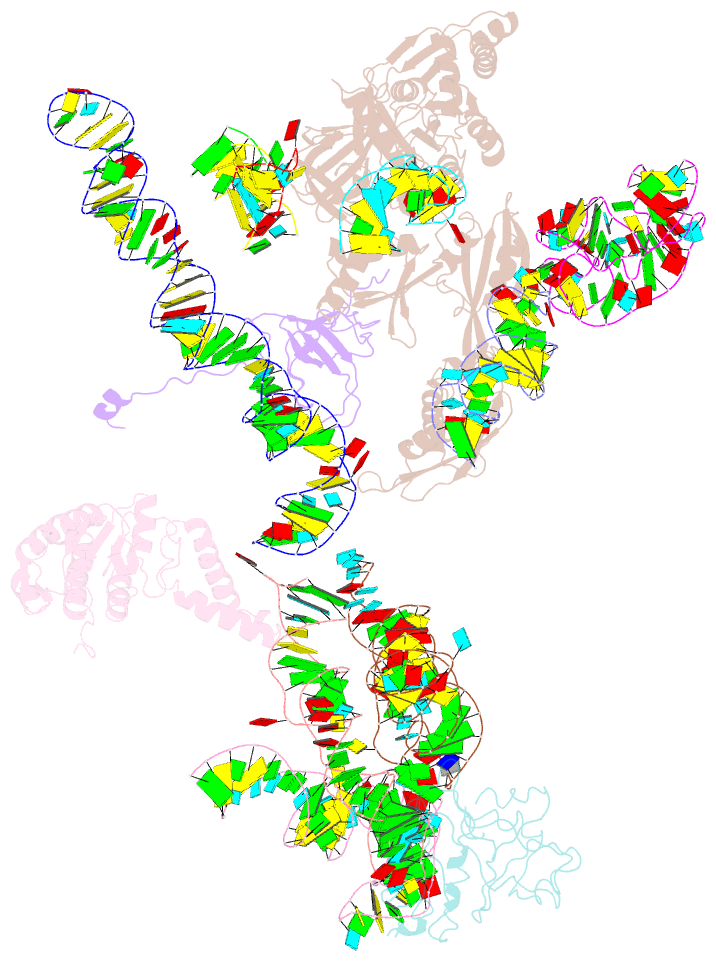
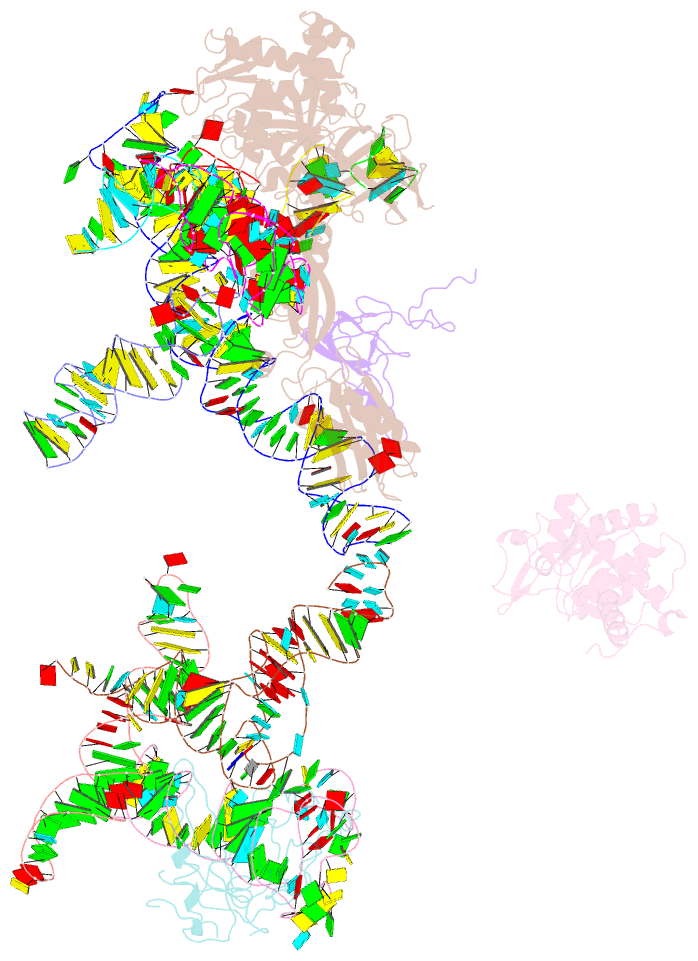
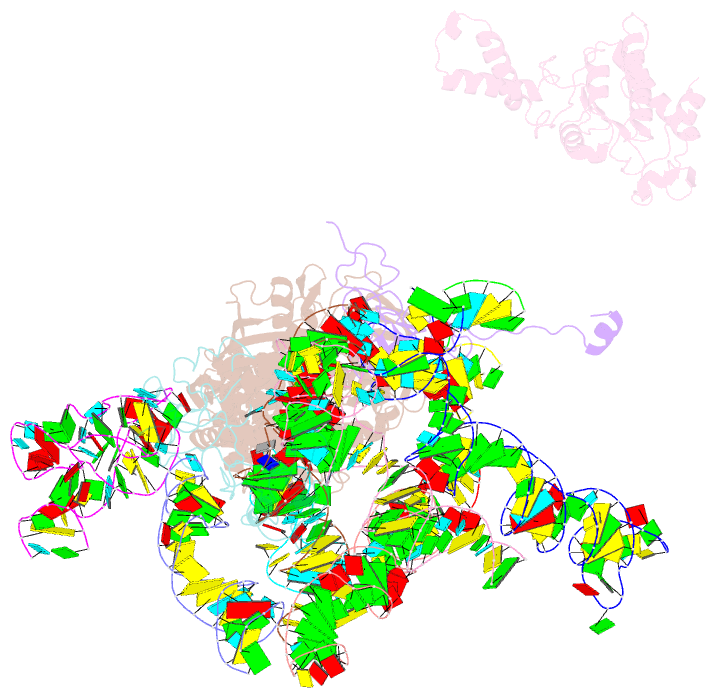
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2om7; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ribosome
- Method
- cryo-EM (7.3 Å)
- Summary
- Structural basis for interaction of the ribosome with the switch regions of gtp-bound elongation factors
- Reference
- Connell SR, Takemoto C, Wilson DN, Wang H, Murayama K, Terada T, Shirouzu M, Rost M, Schuler M, Giesebrecht J, Dabrowski M, Mielke T, Fucini P, Yokoyama S, Spahn CM (2007): "Structural basis for interaction of the ribosome with the switch regions of GTP-bound elongation factors." Mol.Cell, 25, 751-764. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.027.
- Abstract
- Elongation factor G (EF-G) catalyzes tRNA translocation on the ribosome. Here a cryo-EM reconstruction of the 70S*EF-G ribosomal complex at 7.3 A resolution and the crystal structure of EF-G-2*GTP, an EF-G homolog, at 2.2 A resolution are presented. EF-G-2*GTP is structurally distinct from previous EF-G structures, and in the context of the cryo-EM structure, the conformational changes are associated with ribosome binding and activation of the GTP binding pocket. The P loop and switch II approach A2660-A2662 in helix 95 of the 23S rRNA, indicating an important role for these conserved bases. Furthermore, the ordering of the functionally important switch I and II regions, which interact with the bound GTP, is dependent on interactions with the ribosome in the ratcheted conformation. Therefore, a network of interaction with the ribosome establishes the active GTP conformation of EF-G and thus facilitates GTP hydrolysis and tRNA translocation.