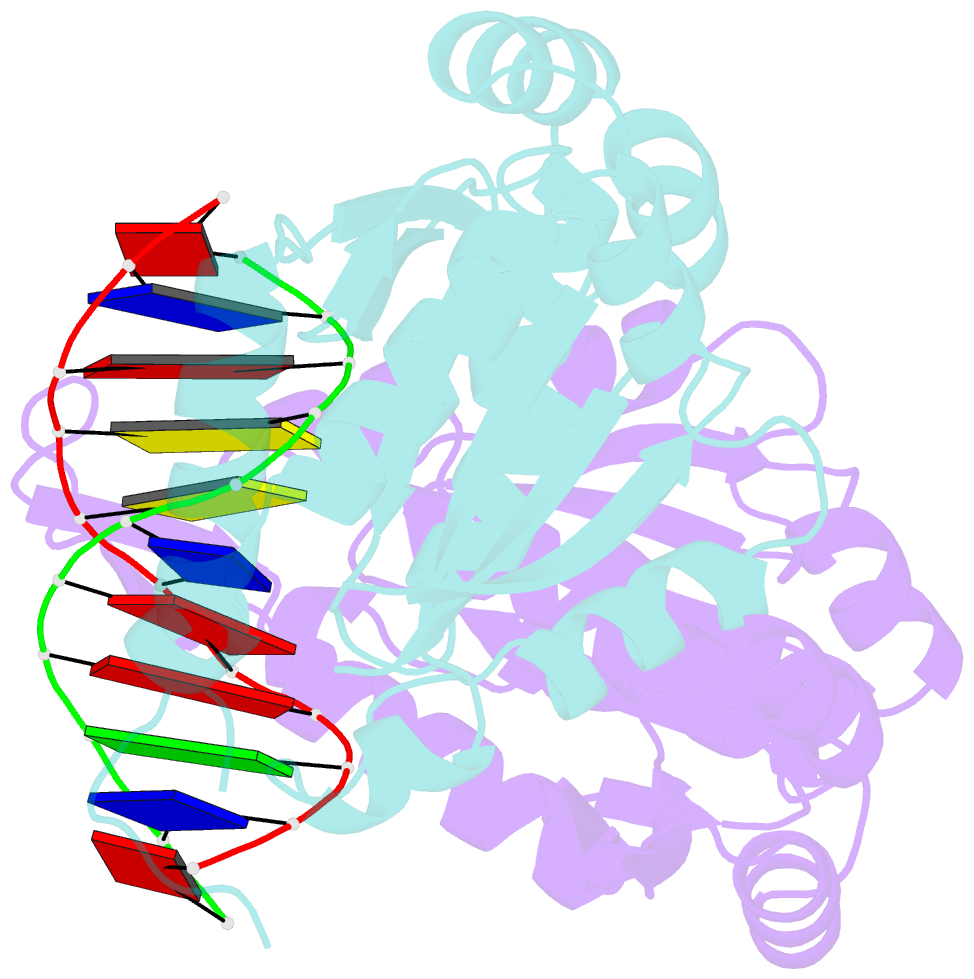
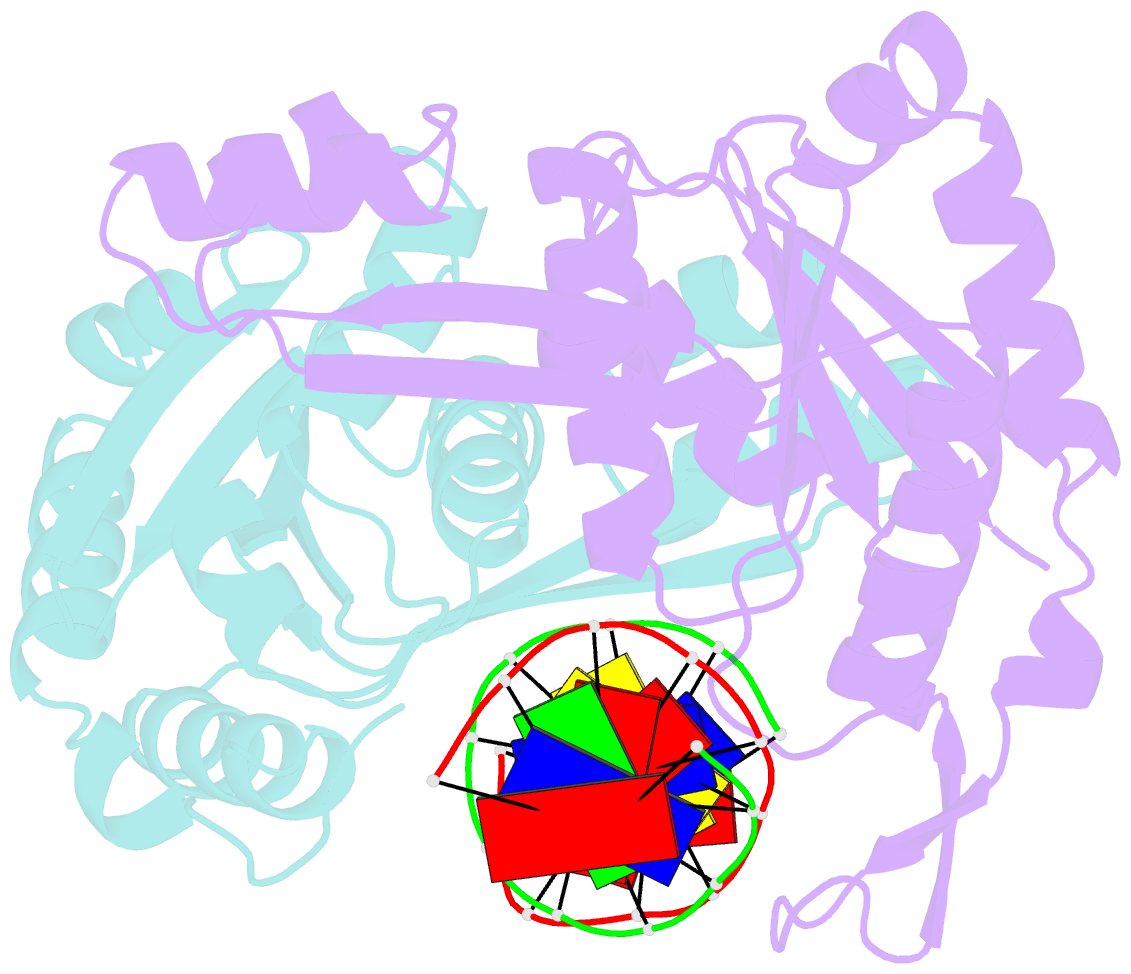
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2p0j; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.1 Å)
- Summary
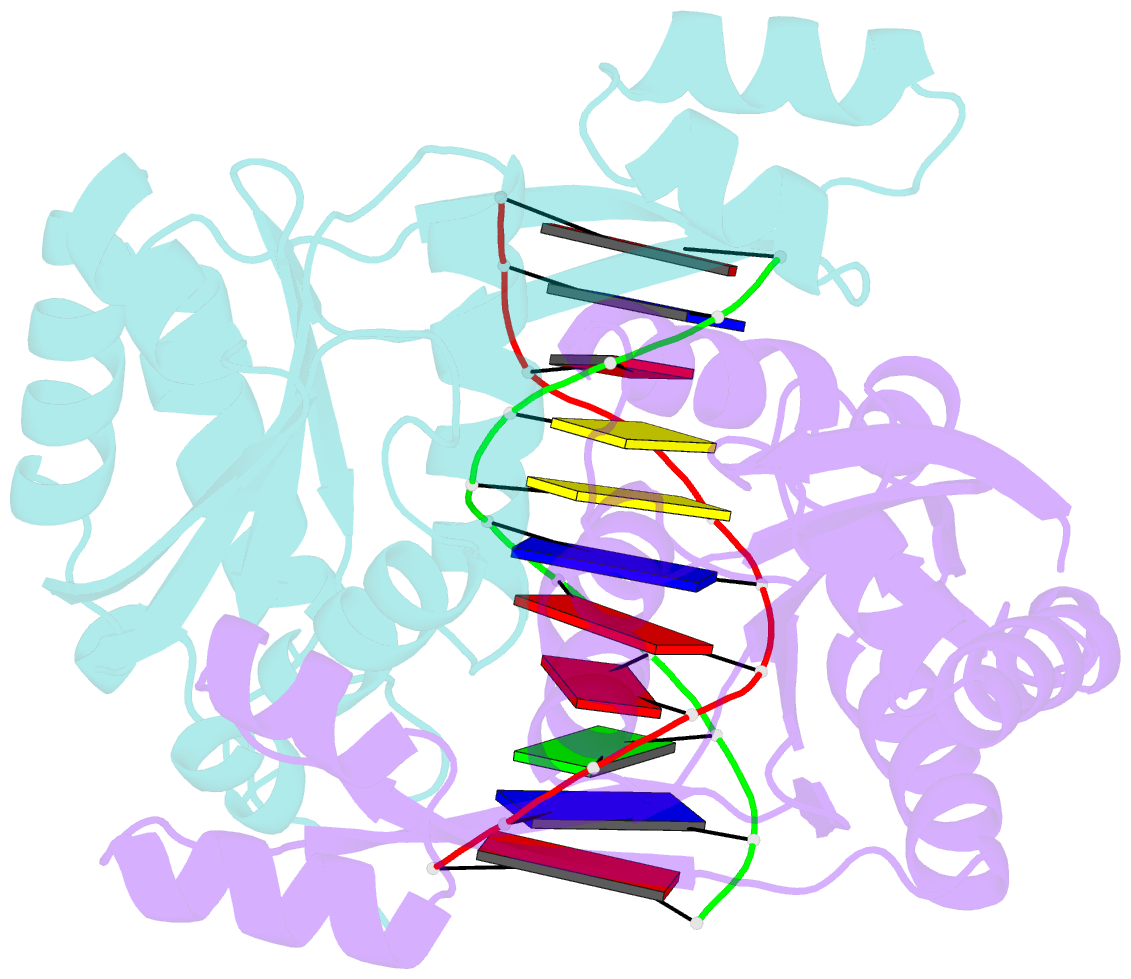
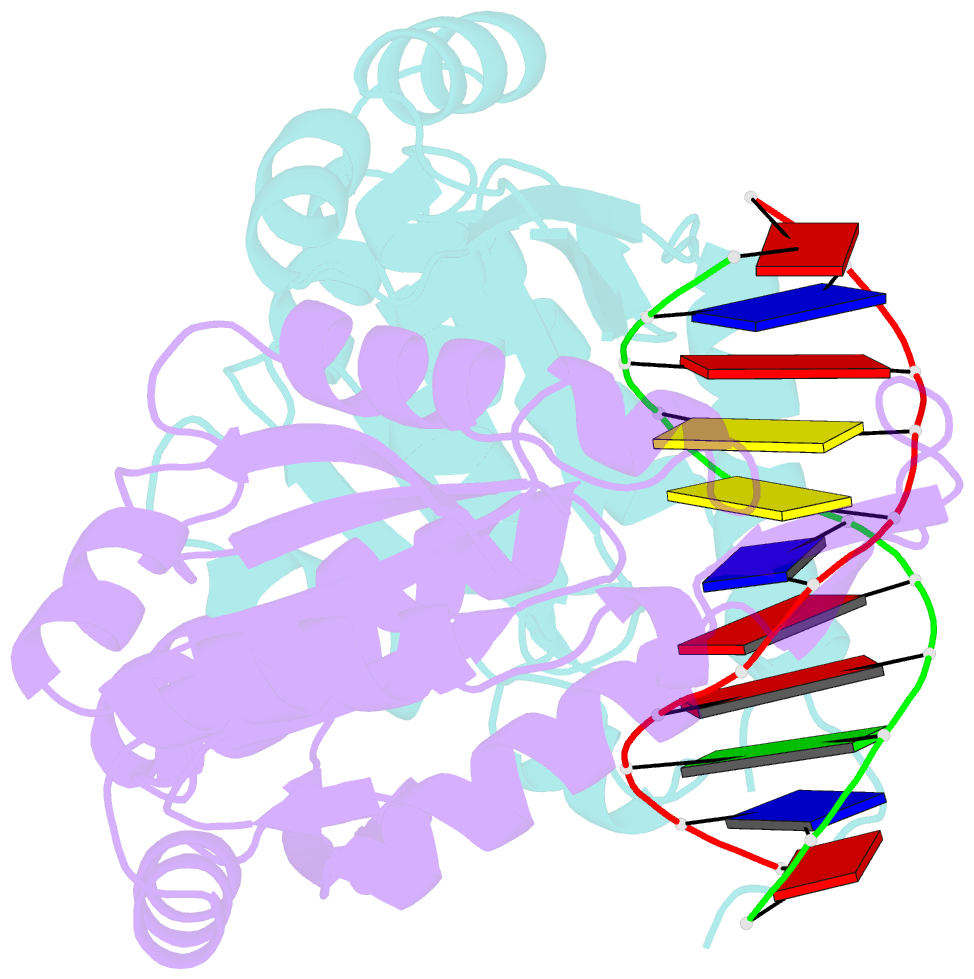
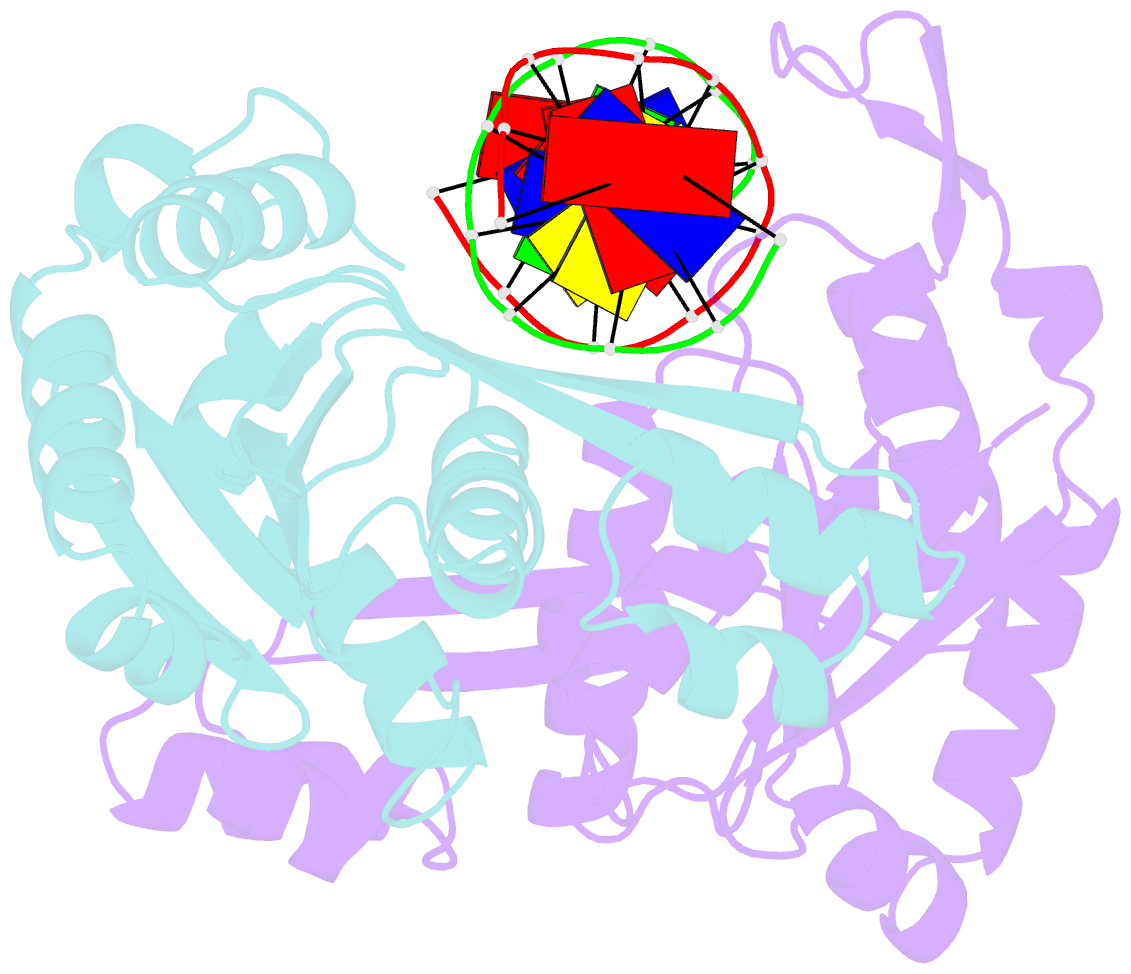
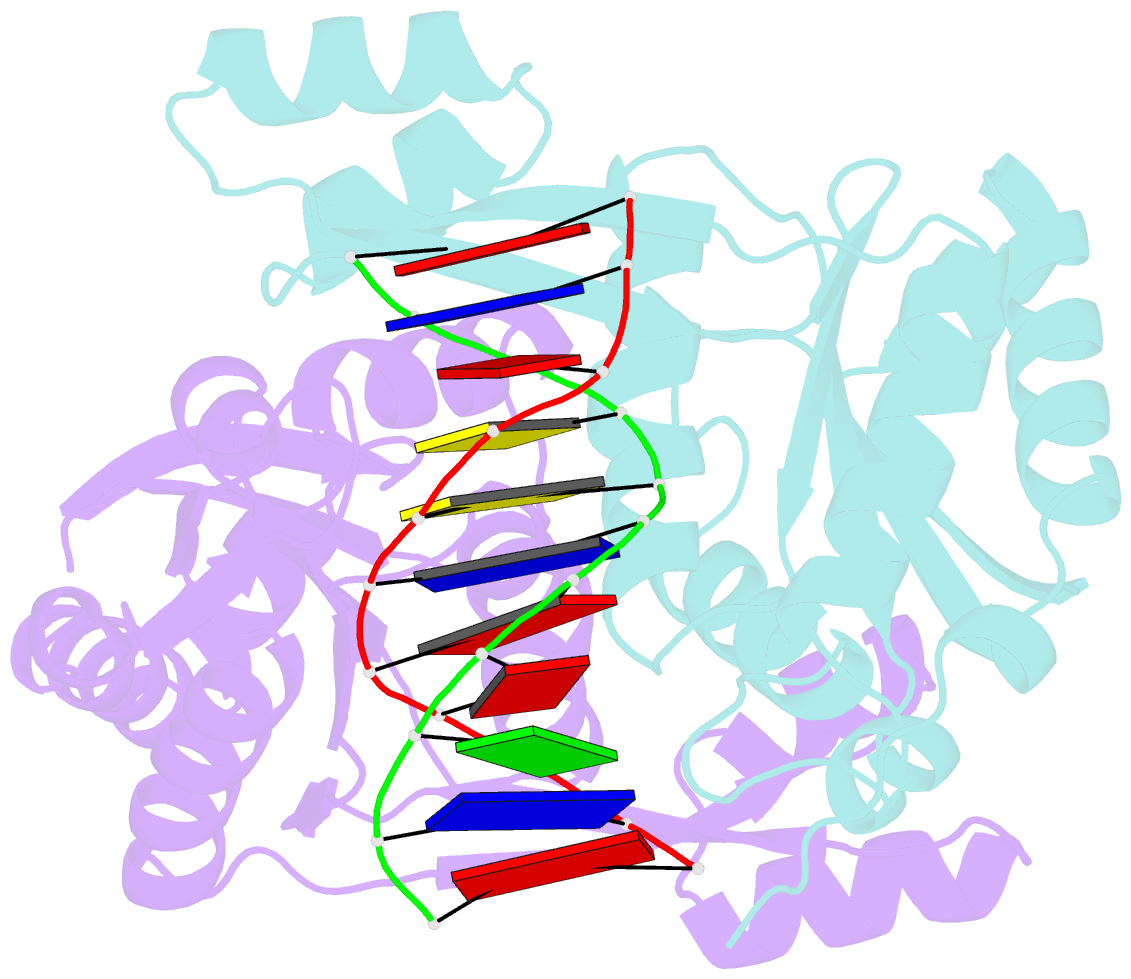
- Structure of restriction endonuclease bstyi bound to non-cognate DNA
- Reference
- Townson SA, Samuelson JC, Bao Y, Xu SY, Aggarwal AK (2007): "BstYI Bound to Noncognate DNA Reveals a "Hemispecific" Complex: Implications for DNA Scanning." Structure, 15, 449-459. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.03.002.
- Abstract
- DNA recognition by proteins is essential for specific expression of genes in a living organism. En route to a target DNA site, a protein will often sample noncognate DNA sites through nonspecific protein-DNA interactions, resulting in a variety of conformationally different binding states. We present here the crystal structure of endonuclease BstYI bound to a noncognate DNA. Surprisingly, the structure reveals the enzyme in a "hemispecific" binding state on the pathway between nonspecific and specific recognition. A single base pair change in the DNA abolishes binding of only one monomer, with the second monomer bound specifically. We show that the enzyme binds essentially as a rigid body, and that one end of the DNA is accommodated loosely in the binding cleft while the other end is held tightly. Another intriguing feature of the structure is Ser172, which has a dual role in establishing nonspecific and specific contacts. Taken together, the structure provides a snapshot of an enzyme in a "paused" intermediate state that may be part of a more general mechanism of scanning DNA.