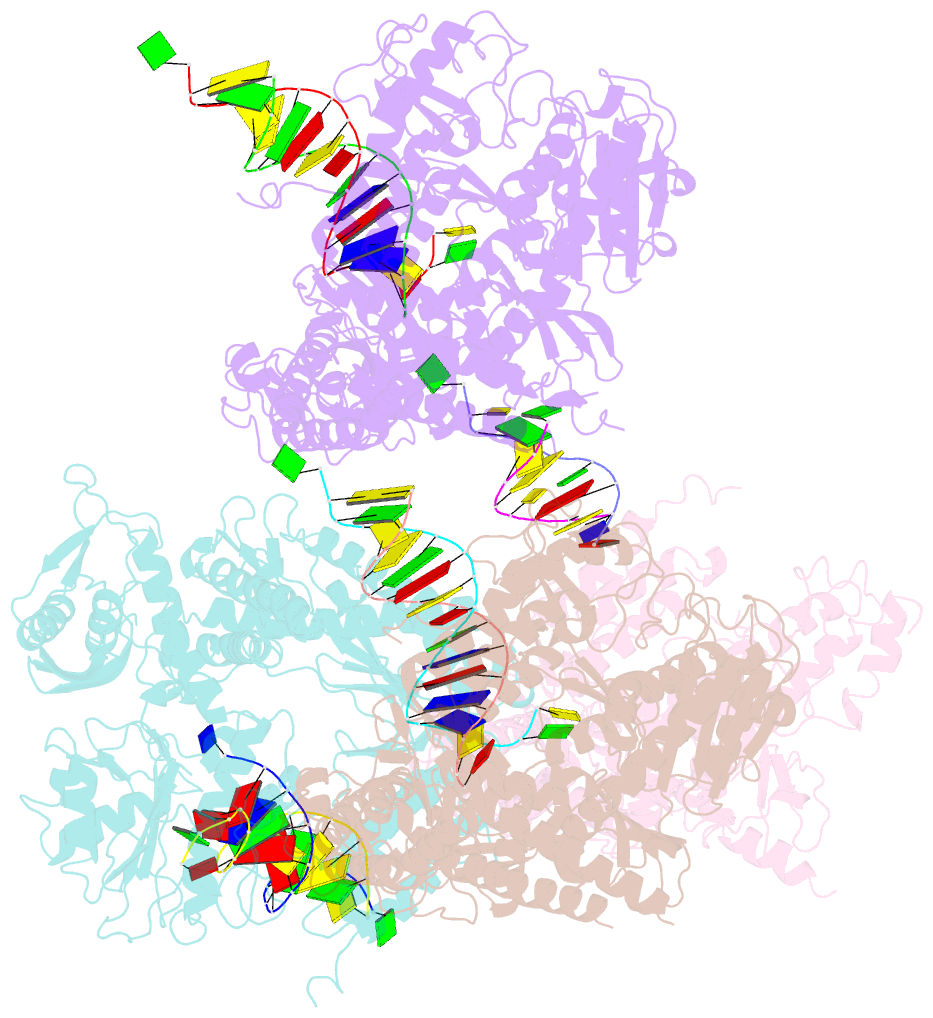
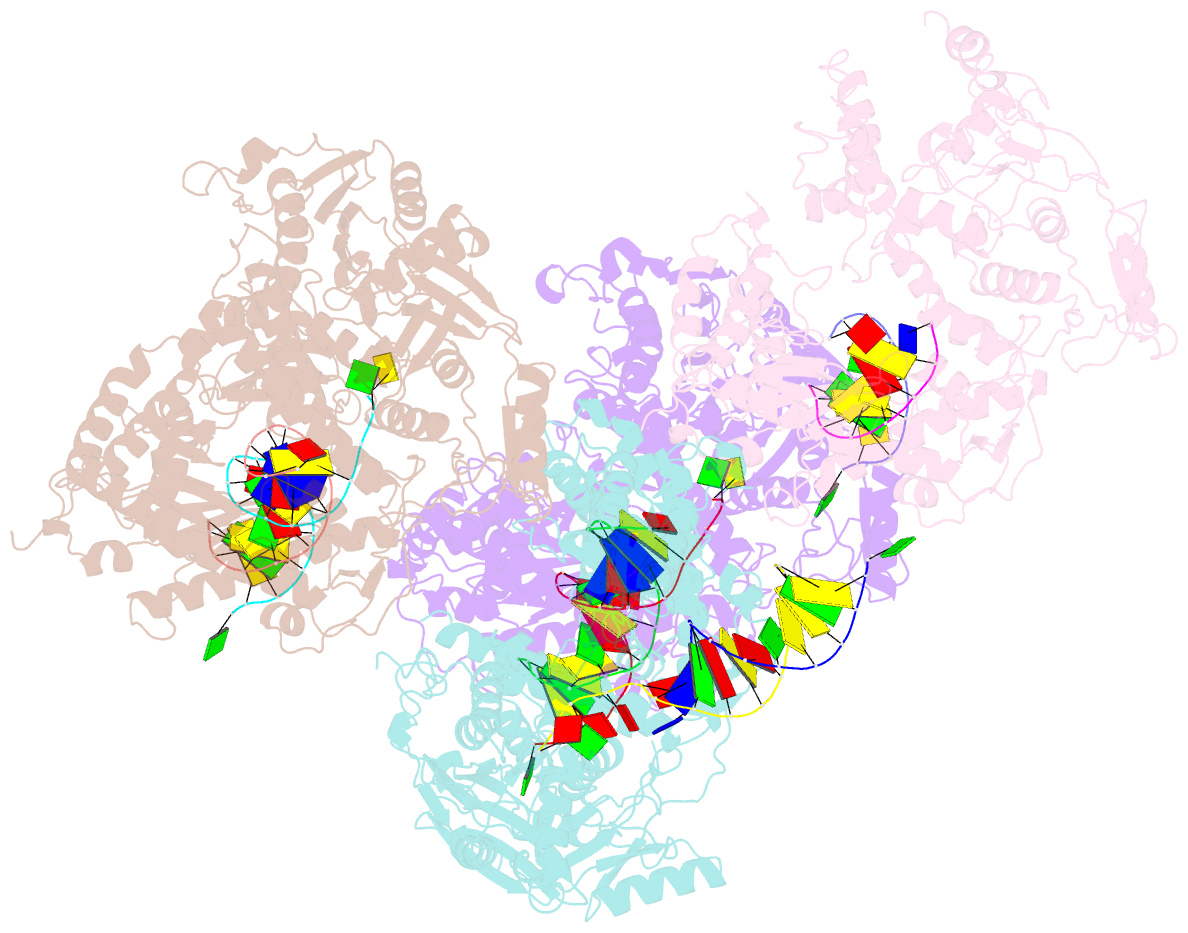
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2p5o; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.8 Å)
- Summary
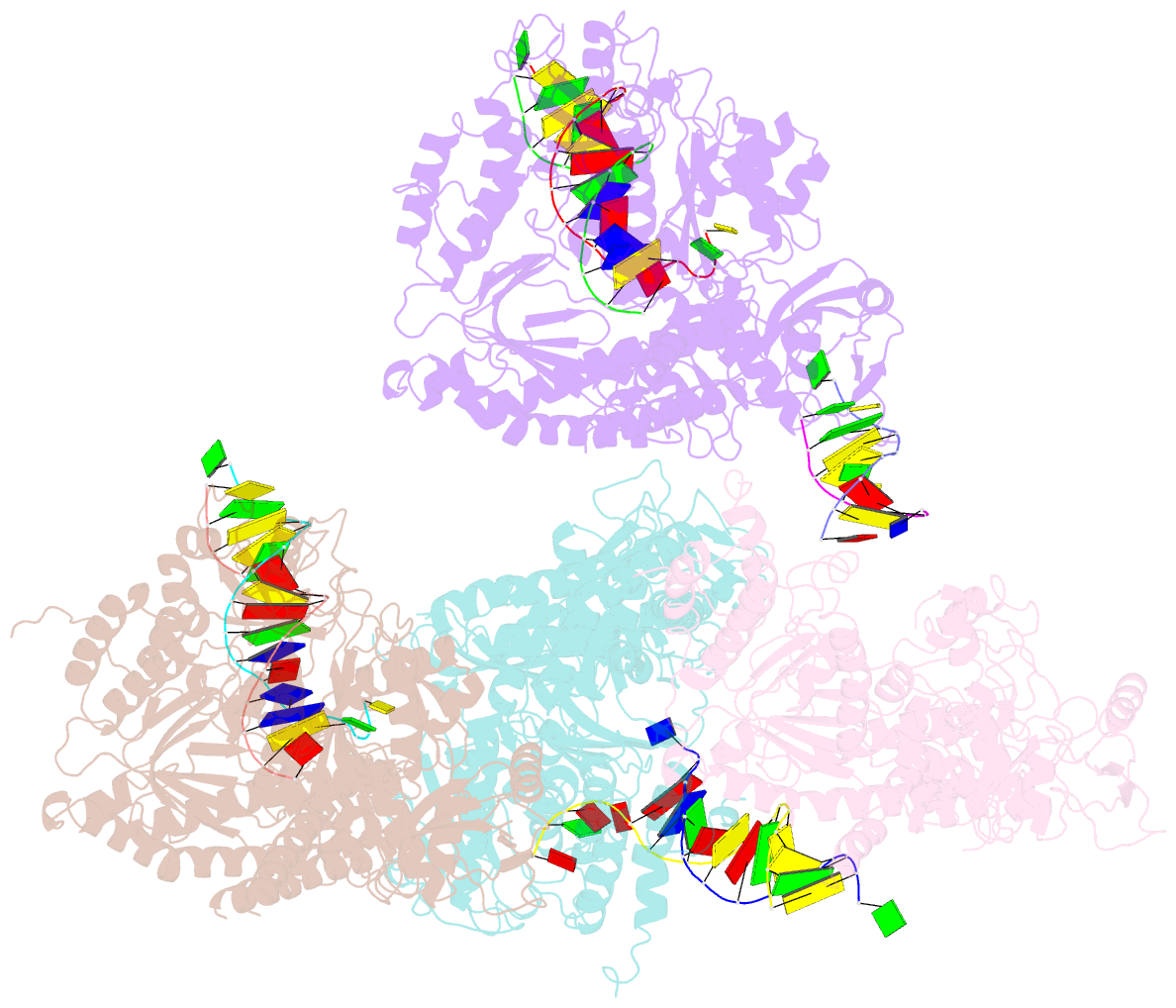
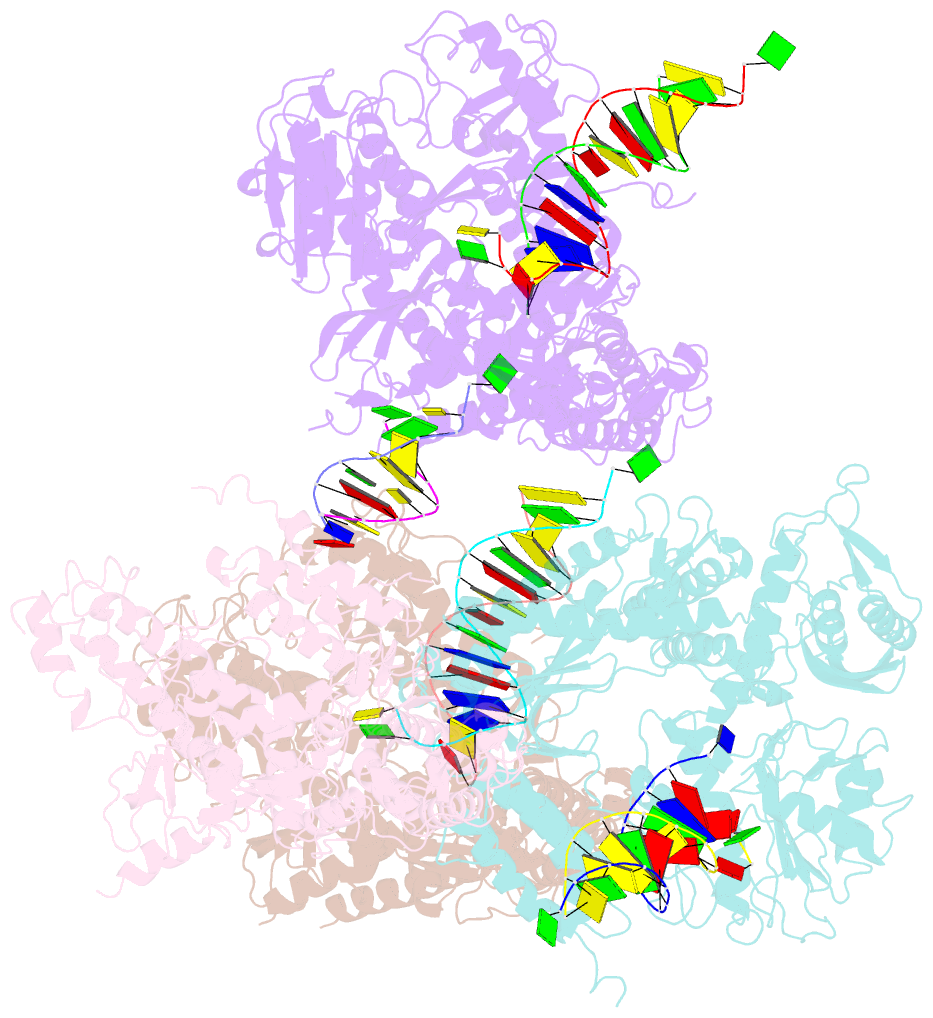
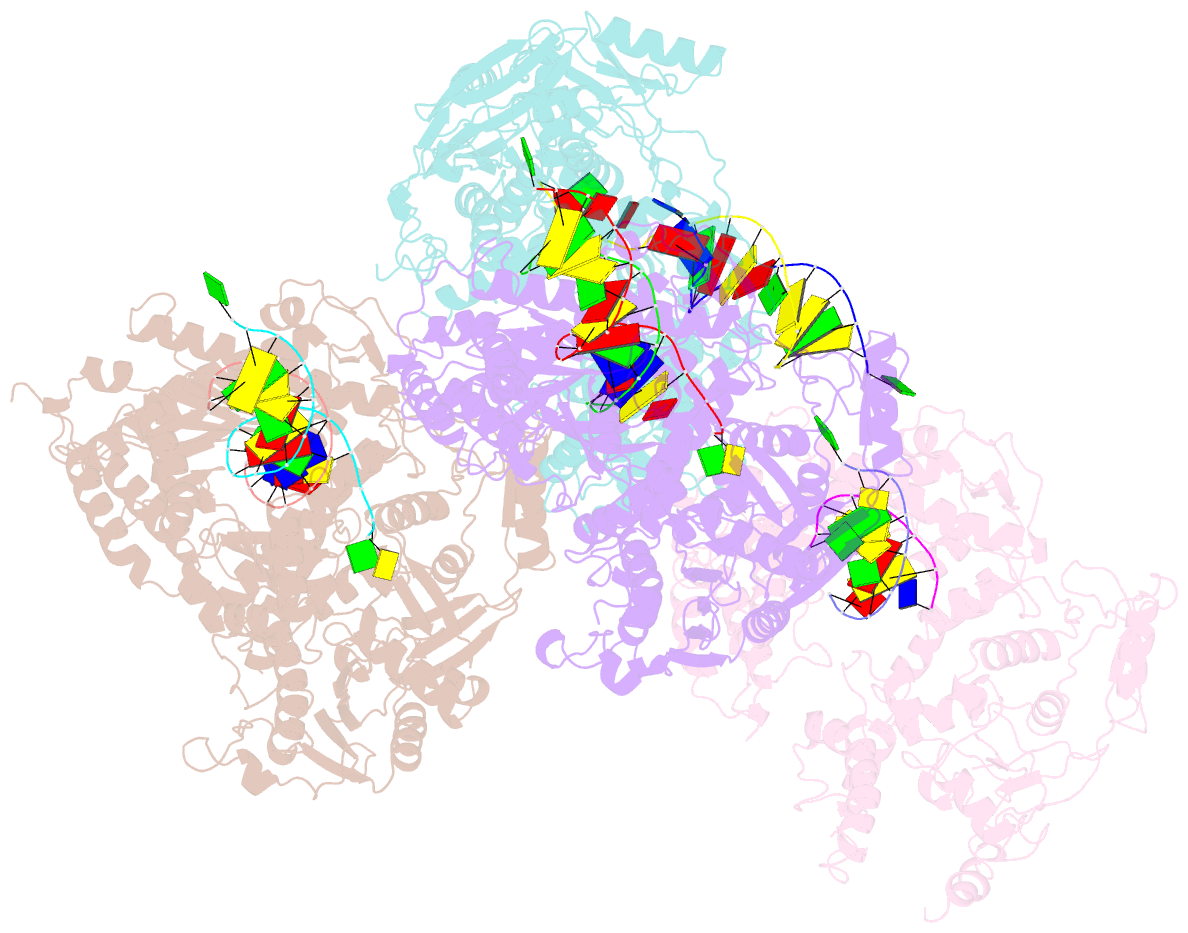
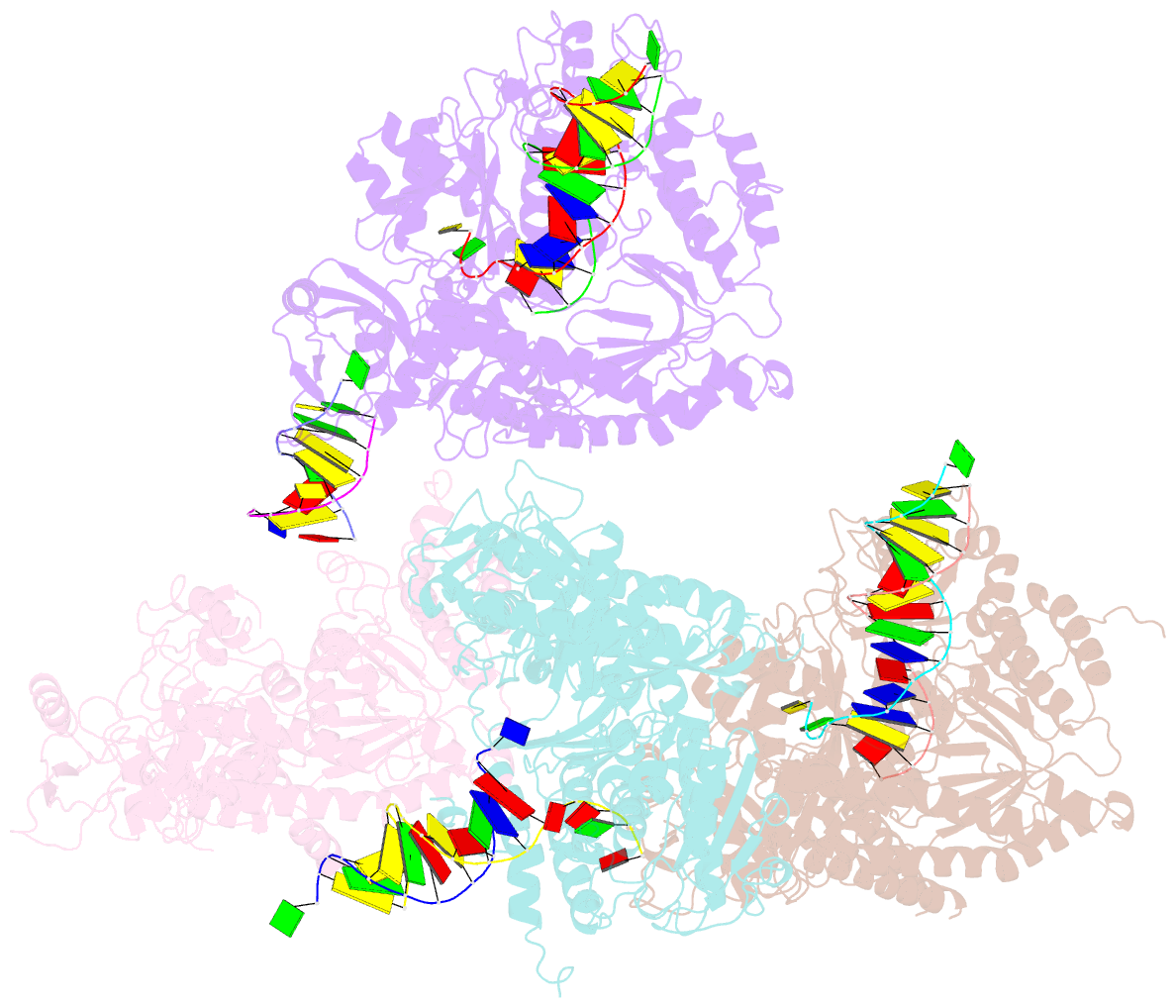
- Crystal structure of rb69 gp43 in complex with DNA containing an abasic site analog
- Reference
- Hogg M, Wallace SS, Doublie S (2004): "Crystallographic snapshots of a replicative DNA polymerase encountering an abasic site." Embo J., 23, 1483-1493. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.760015.
- Abstract
- Abasic sites are common DNA lesions, which are strong blocks to replicative polymerases and are potentially mutagenic when bypassed. We report here the 2.8 A structure of the bacteriophage RB69 replicative DNA polymerase attempting to process an abasic site analog. Four different complexes were captured in the crystal asymmetric unit: two have DNA in the polymerase active site whereas the other two molecules are in the exonuclease mode. When compared to complexes with undamaged DNA, the DNA surrounding the abasic site reveals distinct changes suggesting why the lesion is so poorly bypassed: the DNA in the polymerase active site has not translocated and is therefore stalled, precluding extension. All four molecules exhibit conformations that differ from the previously published structures. The polymerase incorporates dAMP across the lesion under crystallization conditions, indicating that the different conformations observed in the crystal may be part of the active site switching reaction pathway.