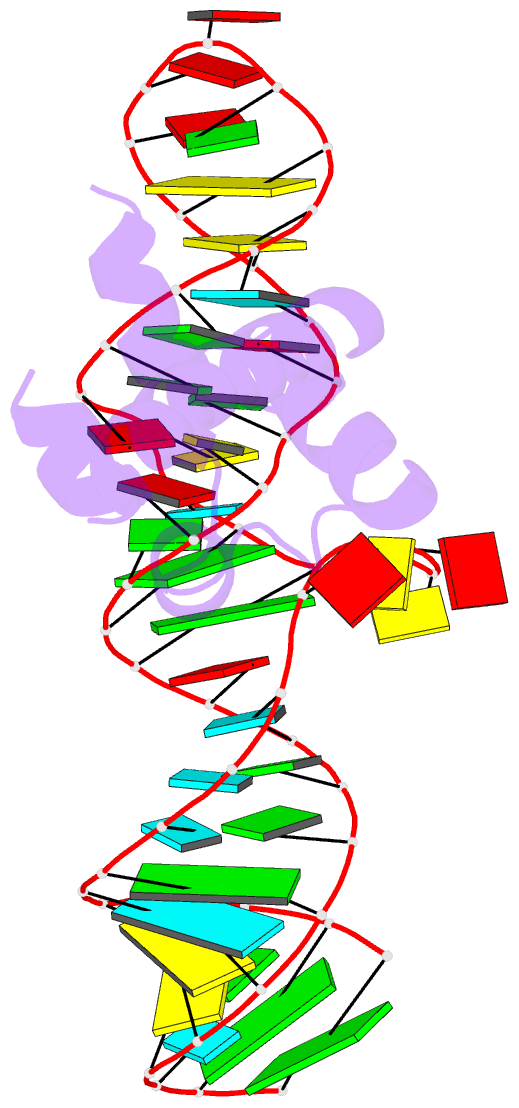
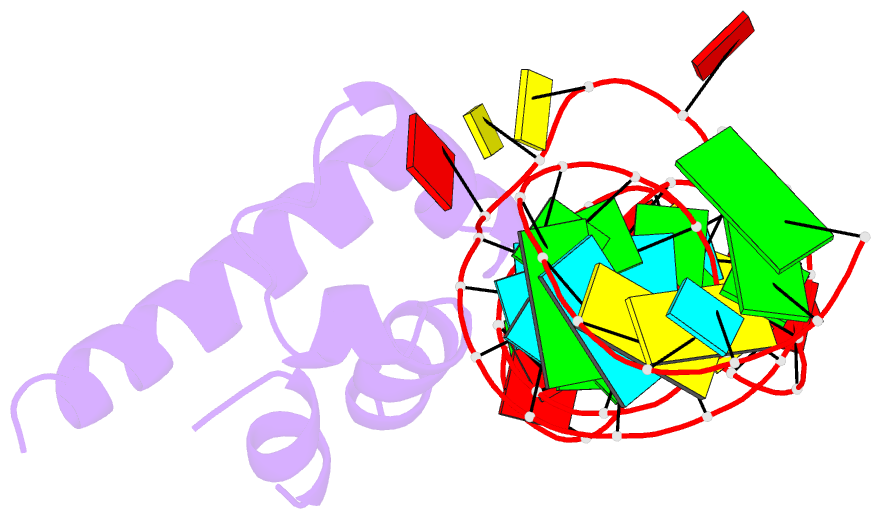
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2pxq; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- signaling protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
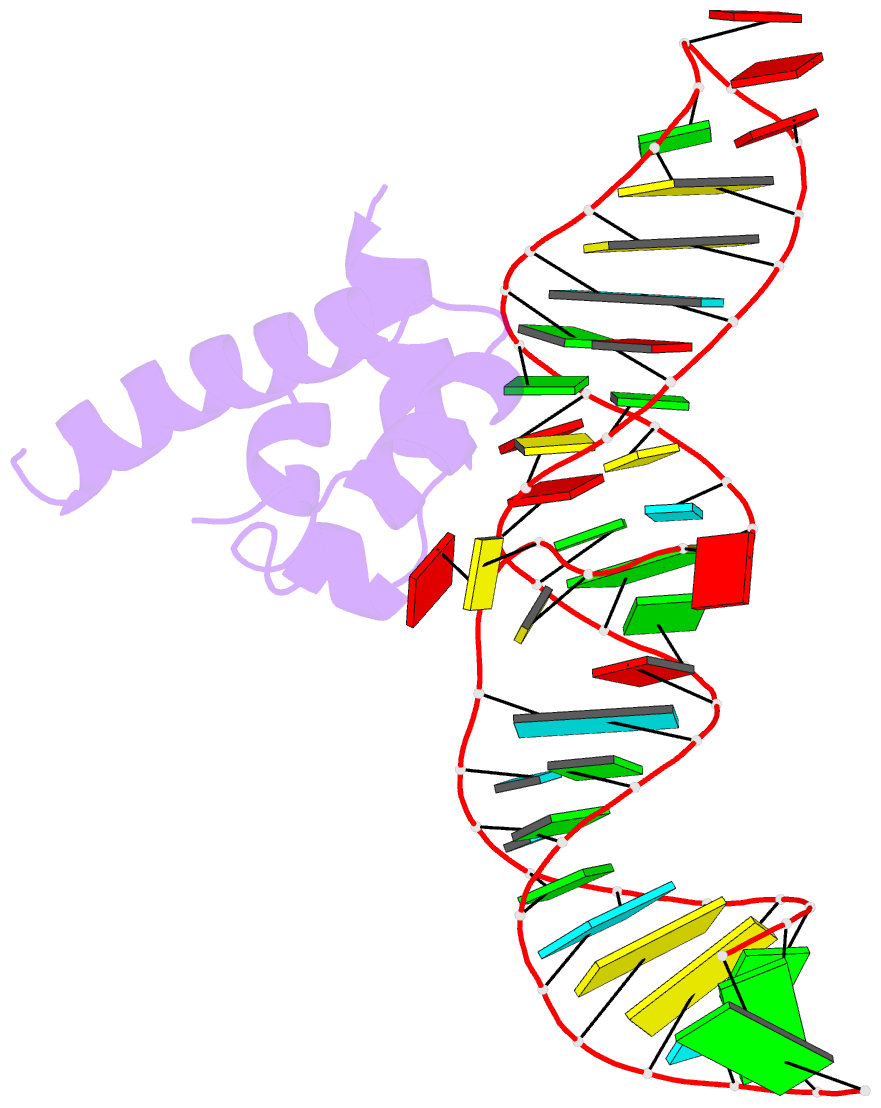
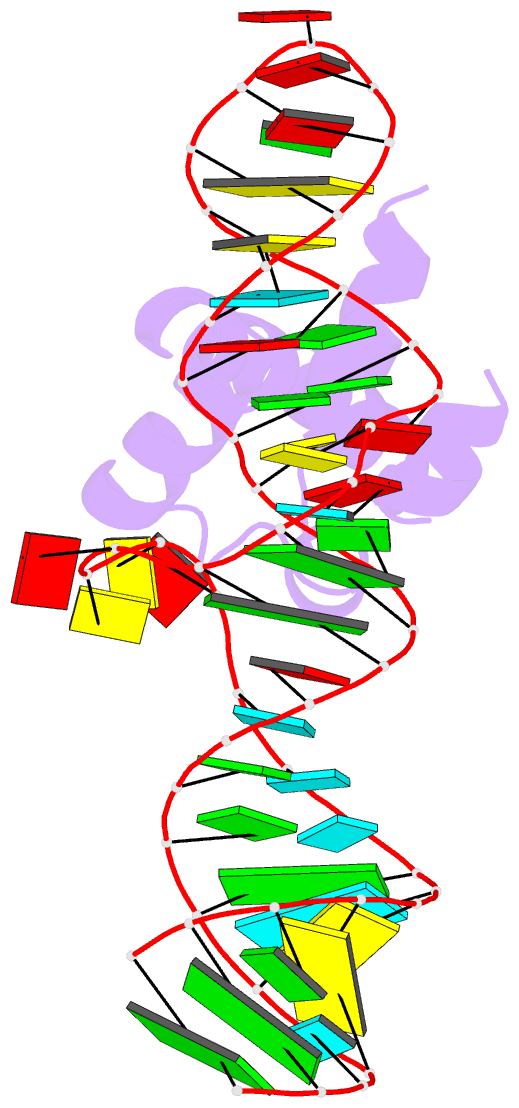
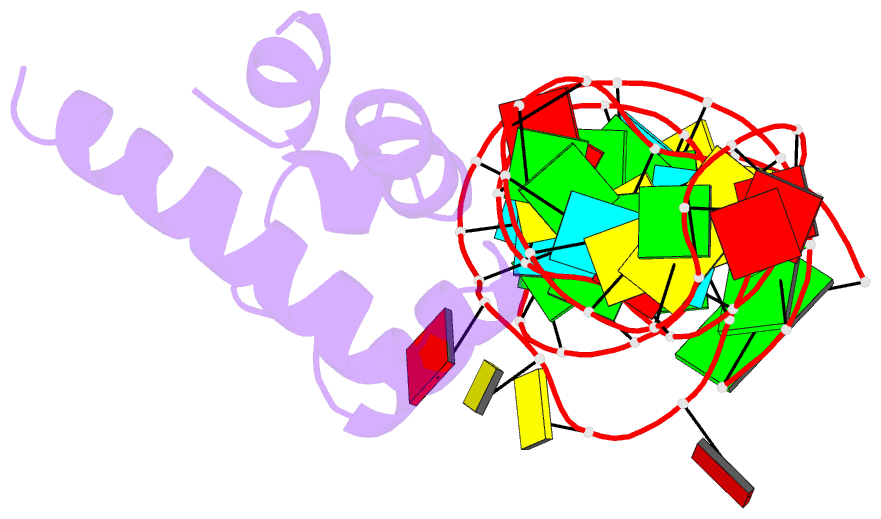
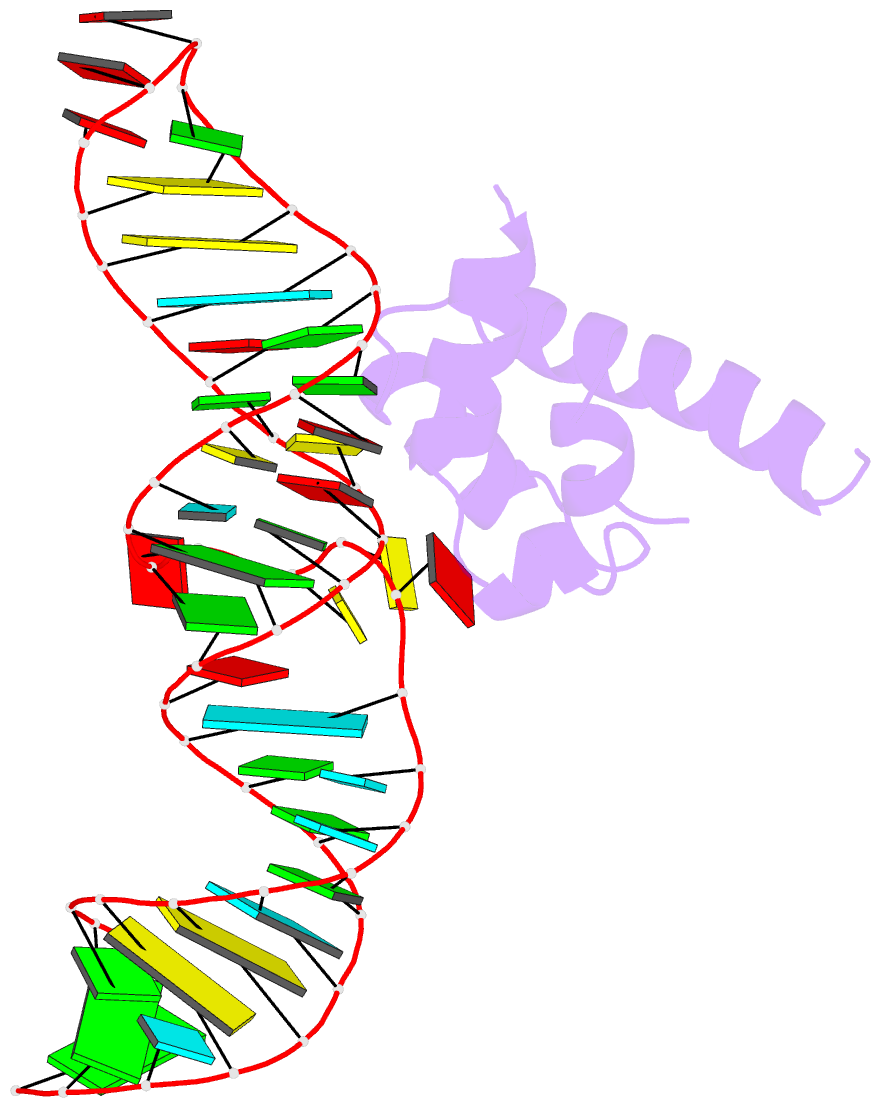
- Variant 14 of ribonucleoprotein core of the e. coli signal recognition particle
- Reference
- Keel AY, Rambo RP, Batey RT, Kieft JS (2007): "A General Strategy to Solve the Phase Problem in RNA Crystallography." Structure, 15, 761-772. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.06.003.
- Abstract
- X-ray crystallography of biologically important RNA molecules has been hampered by technical challenges, including finding heavy-atom derivatives to obtain high-quality experimental phase information. Existing techniques have drawbacks, limiting the rate at which important new structures are solved. To address this, we have developed a reliable means to localize heavy atoms specifically to virtually any RNA. By solving the crystal structures of thirteen variants of the G*U wobble pair cation binding motif, we have identified a version that when inserted into an RNA helix introduces a high-occupancy cation binding site suitable for phasing. This "directed soaking" strategy can be integrated fully into existing RNA crystallography methods, potentially increasing the rate at which important structures are solved and facilitating routine solving of structures using Cu-Kalpha radiation. This method already has been used to solve several crystal structures.