Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2q2t; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ligase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.3 Å)
- Summary
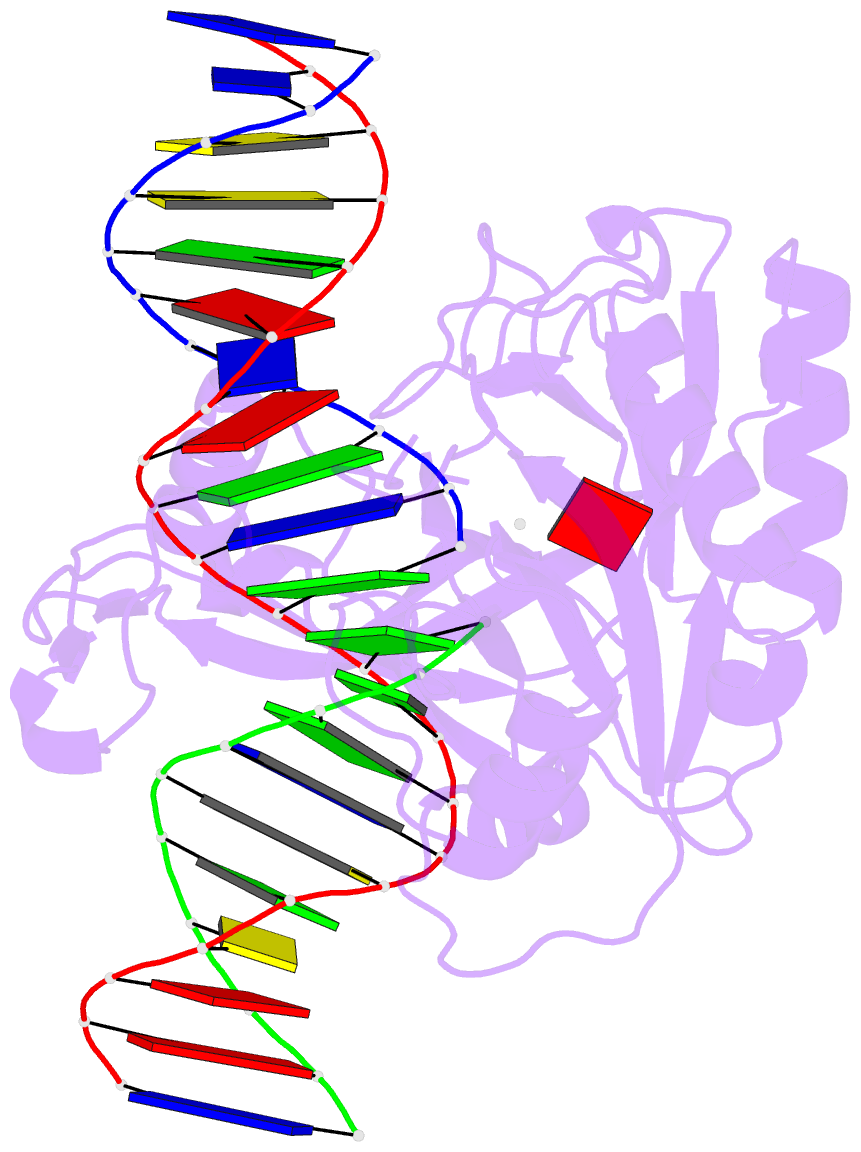
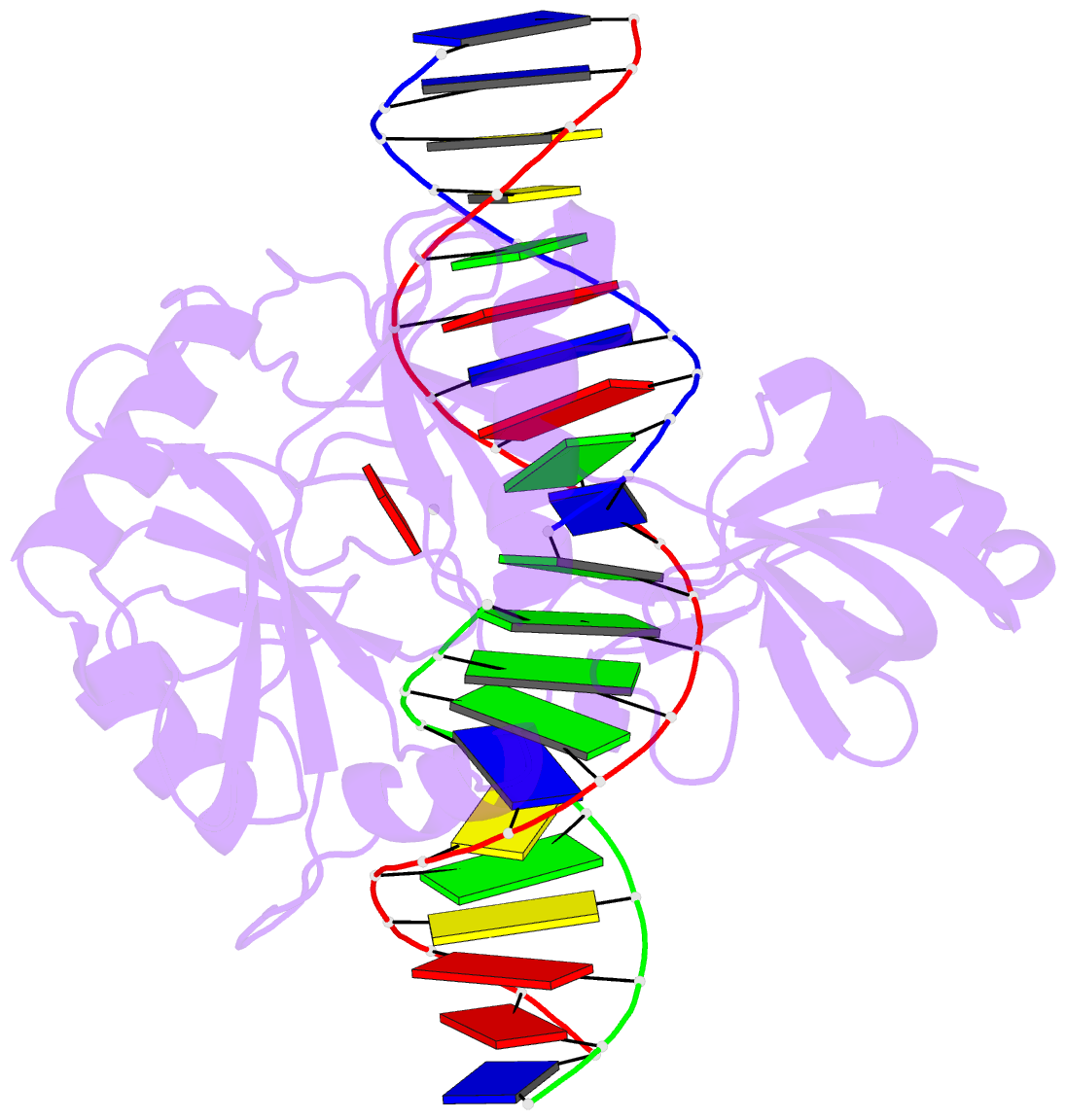
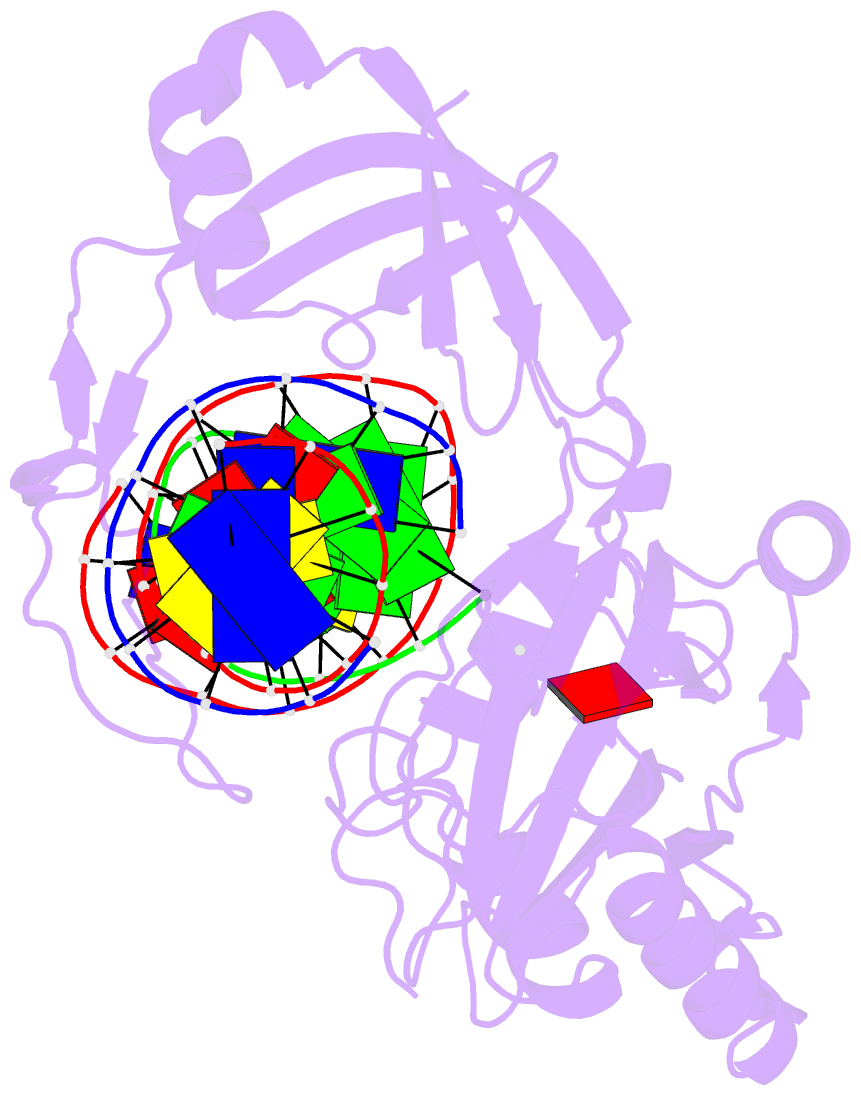
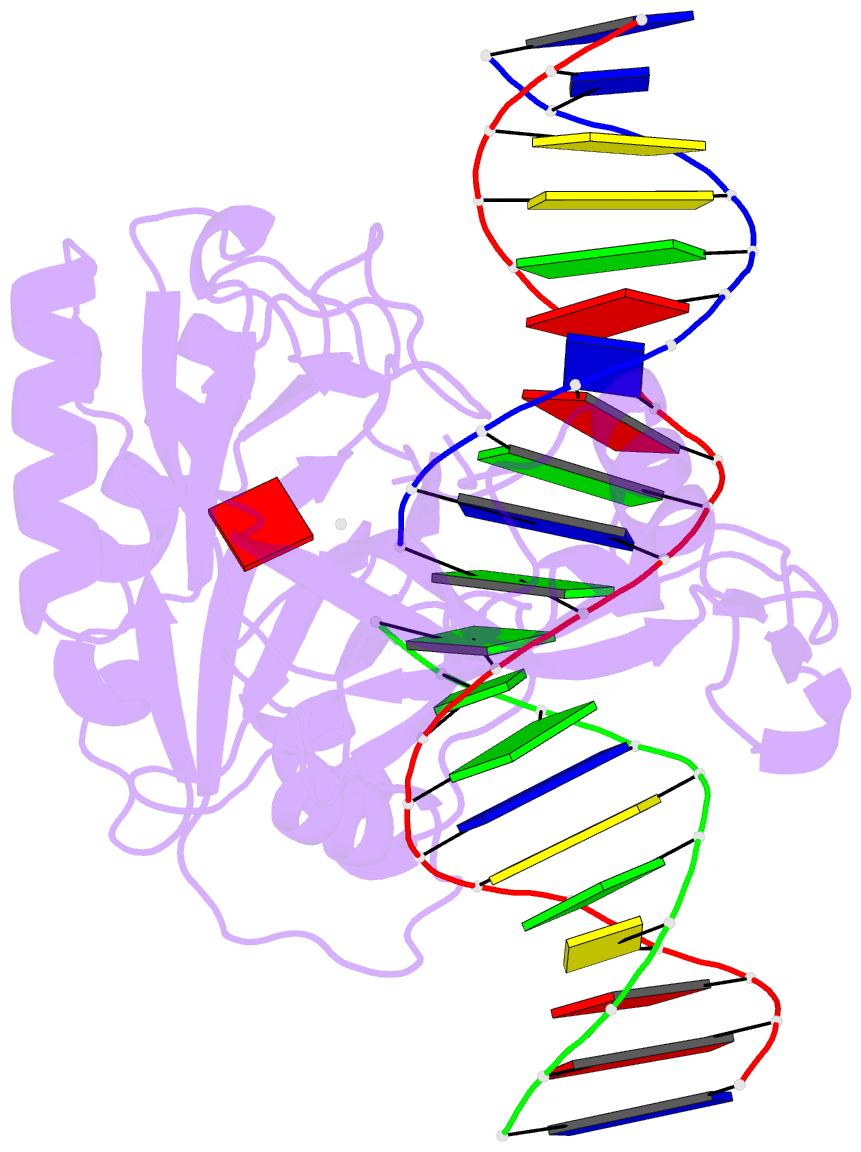
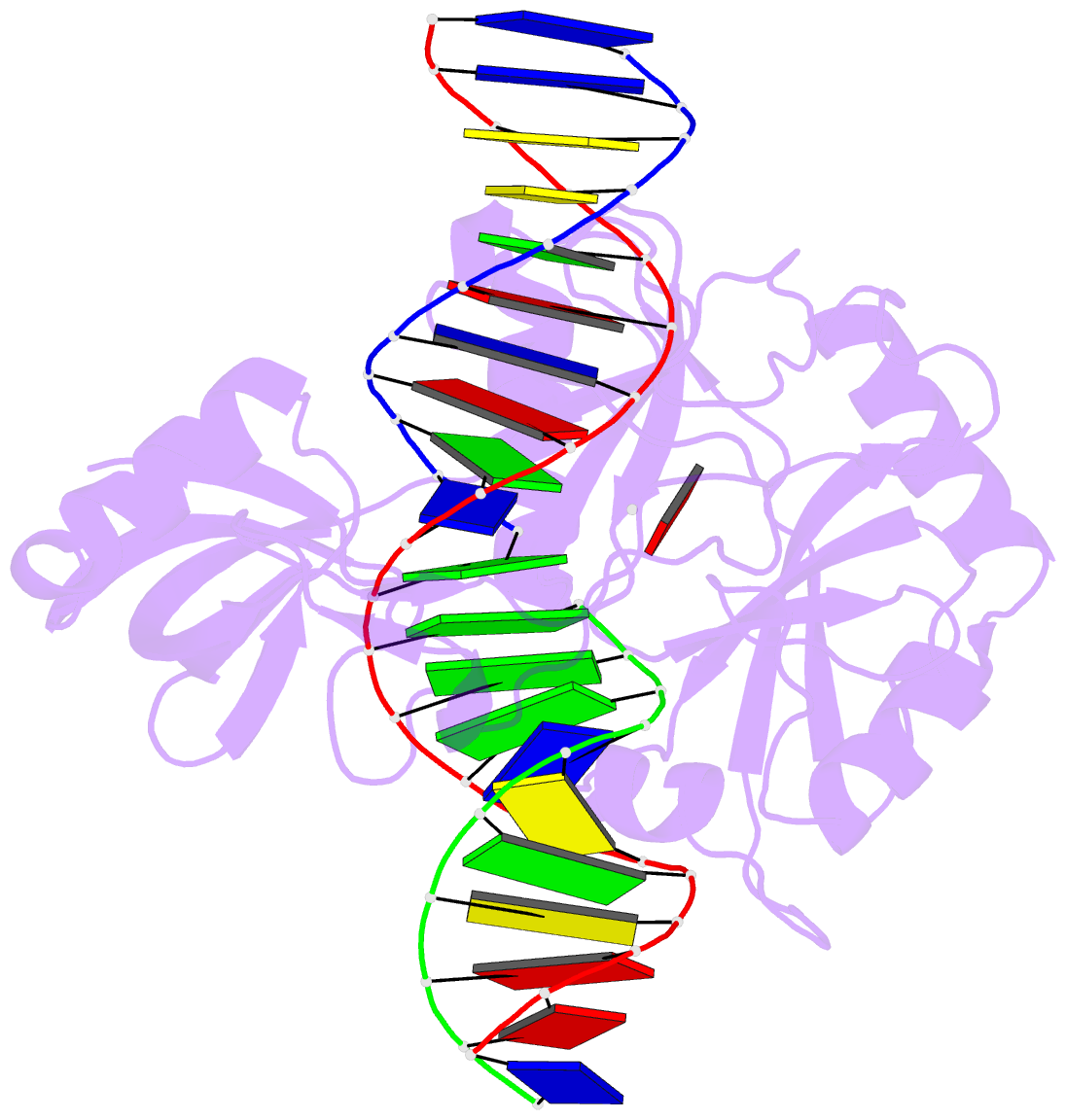
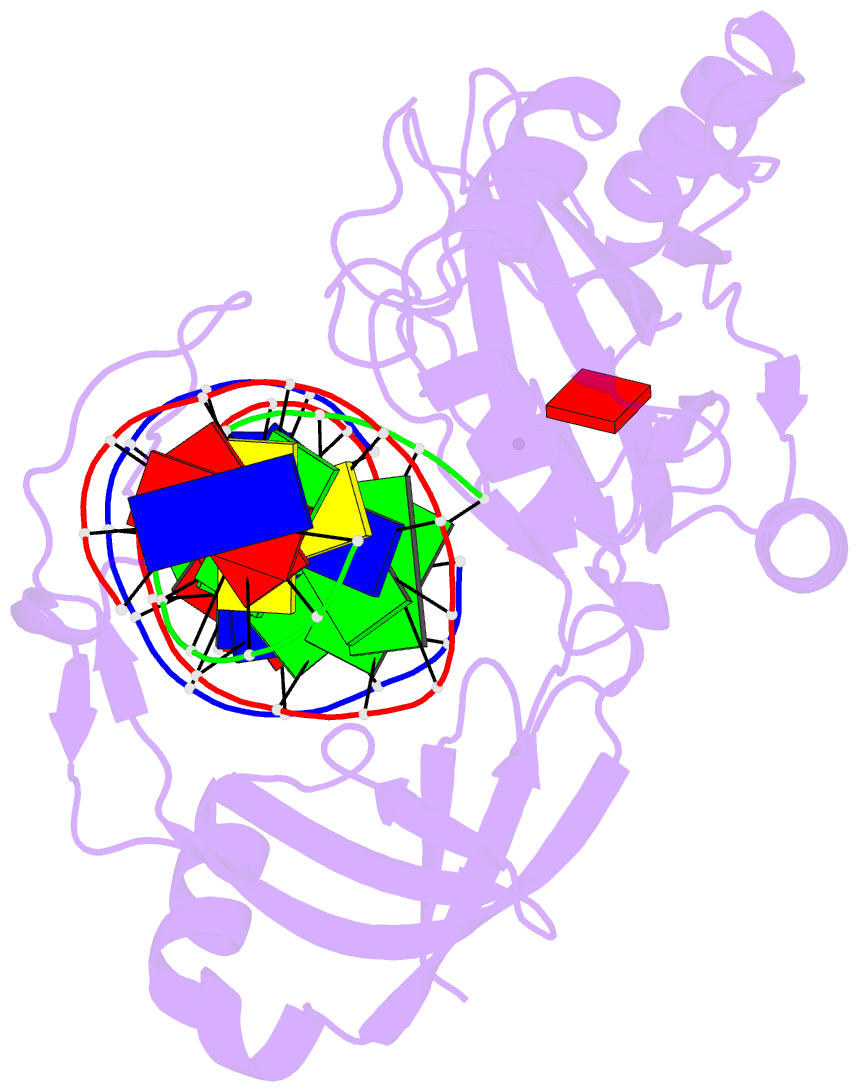
- Structure of chlorella virus DNA ligase-adenylate bound to a 5' phosphorylated nick
- Reference
- Nair PA, Nandakumar J, Smith P, Odell M, Lima CD, Shuman S (2007): "Structural basis for nick recognition by a minimal pluripotent DNA ligase." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 14, 770-778. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1266.
- Abstract
- Chlorella virus DNA ligase, the smallest eukaryotic ligase known, has pluripotent biological activity and an intrinsic nick-sensing function, despite having none of the accessory domains found in cellular ligases. A 2.3-A crystal structure of the Chlorella virus ligase-AMP intermediate bound to duplex DNA containing a 3'-OH-5'-PO4 nick reveals a new mode of DNA envelopment, in which a short surface loop emanating from the OB domain forms a beta-hairpin 'latch' that inserts into the DNA major groove flanking the nick. A network of interactions with the 3'-OH and 5'-PO4 termini in the active site illuminates the DNA adenylylation mechanism and the crucial roles of AMP in nick sensing and catalysis. Addition of a divalent cation triggered nick sealing in crystallo, establishing that the nick complex is a bona fide intermediate in the DNA repair pathway.