Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2rra; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
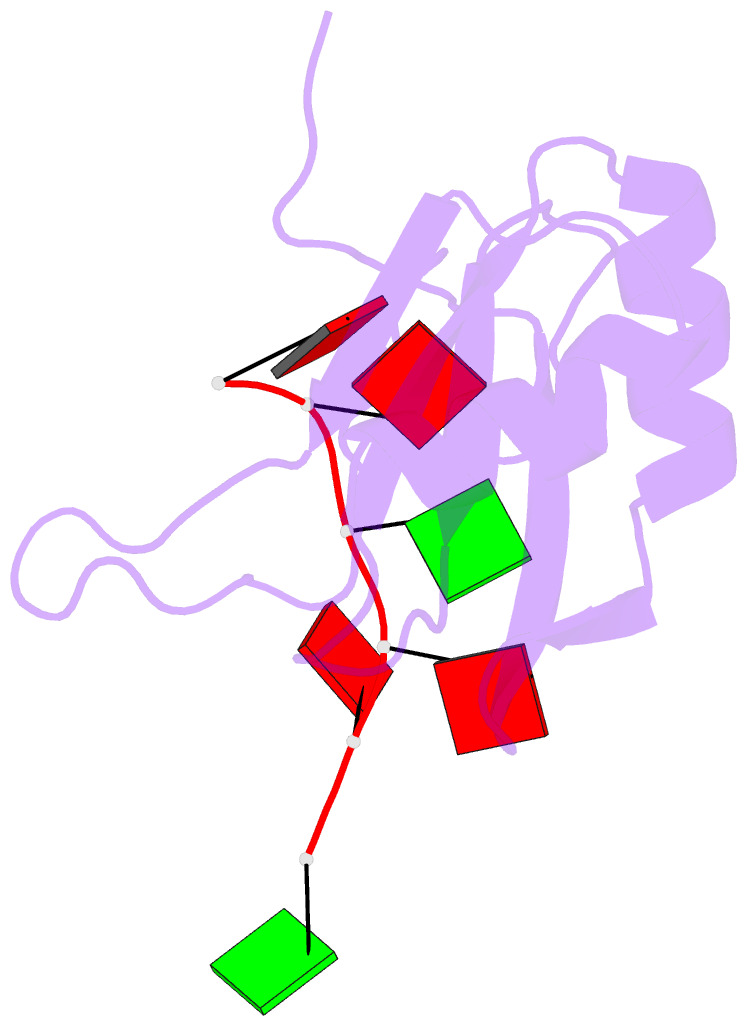
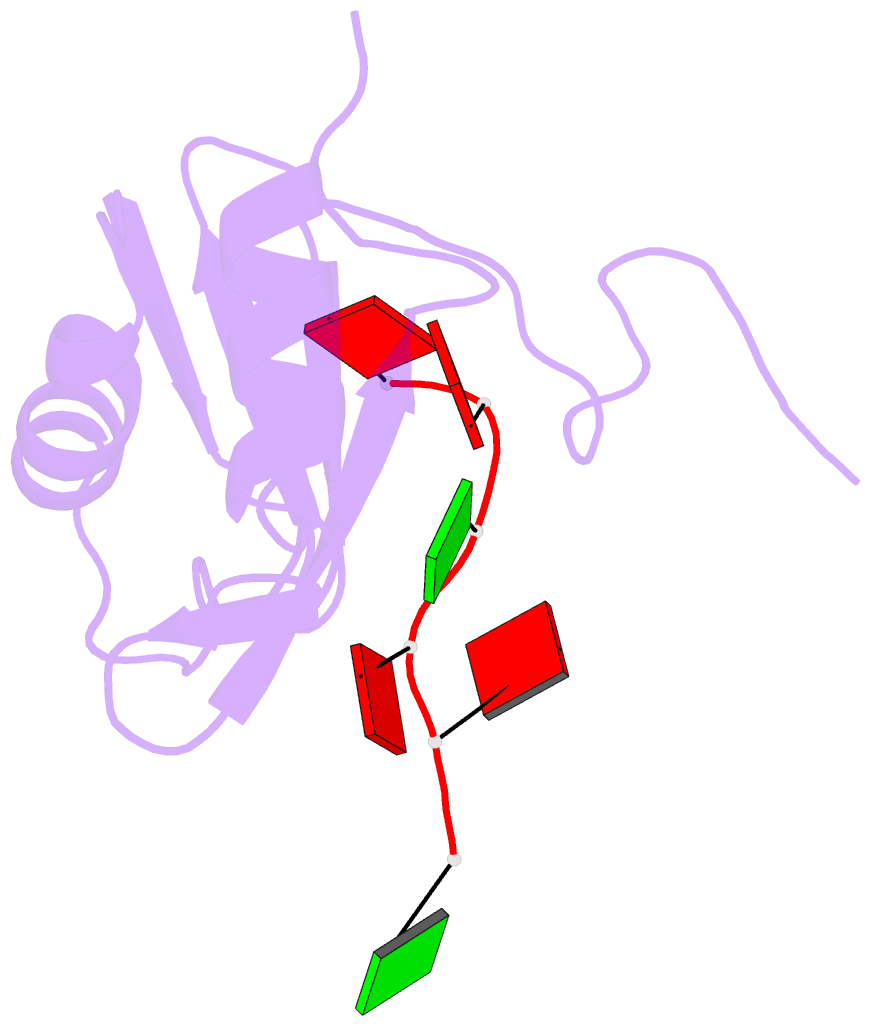
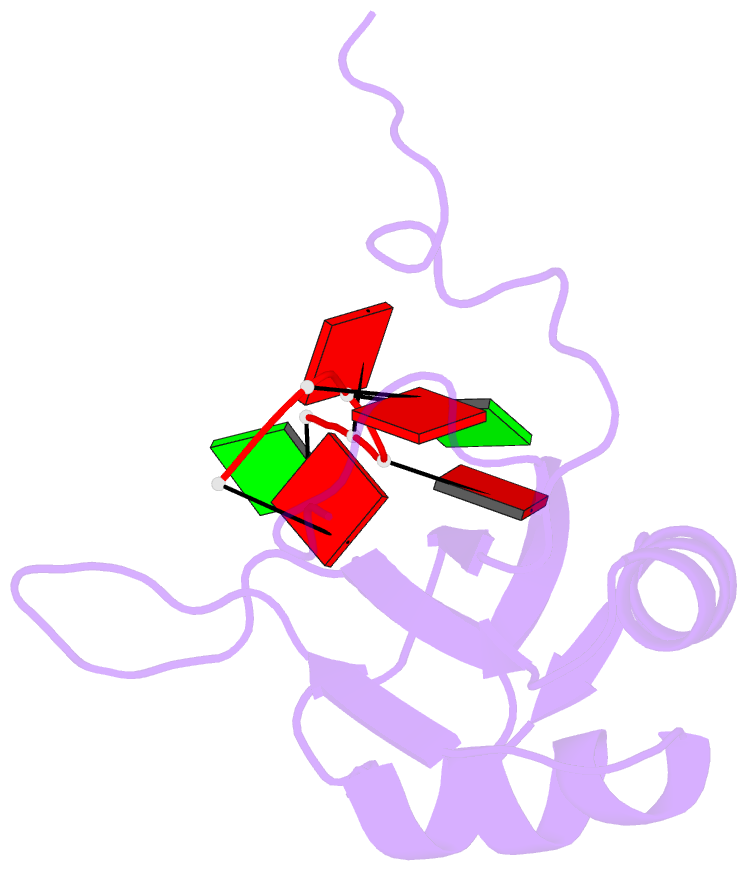
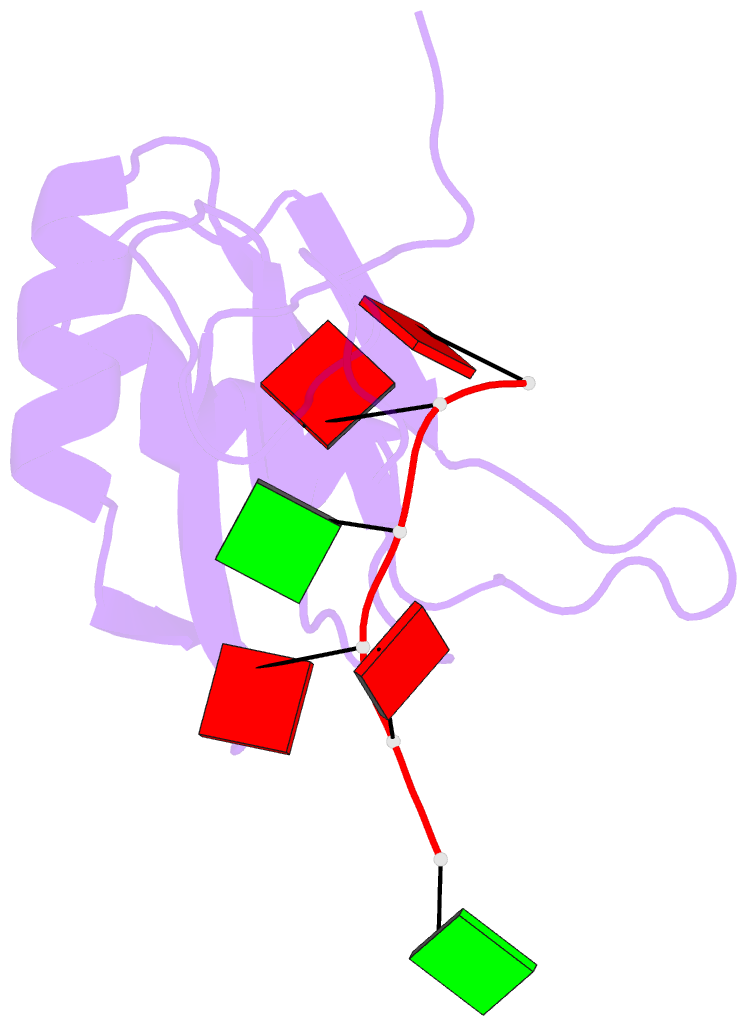
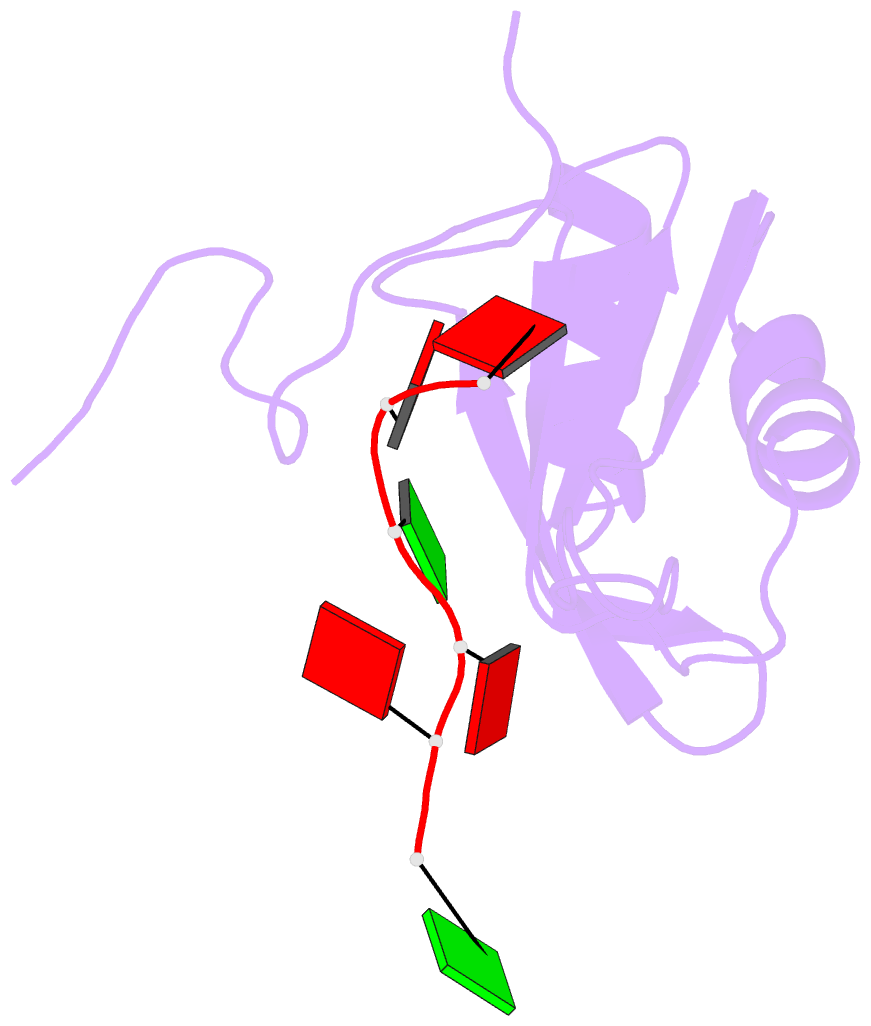
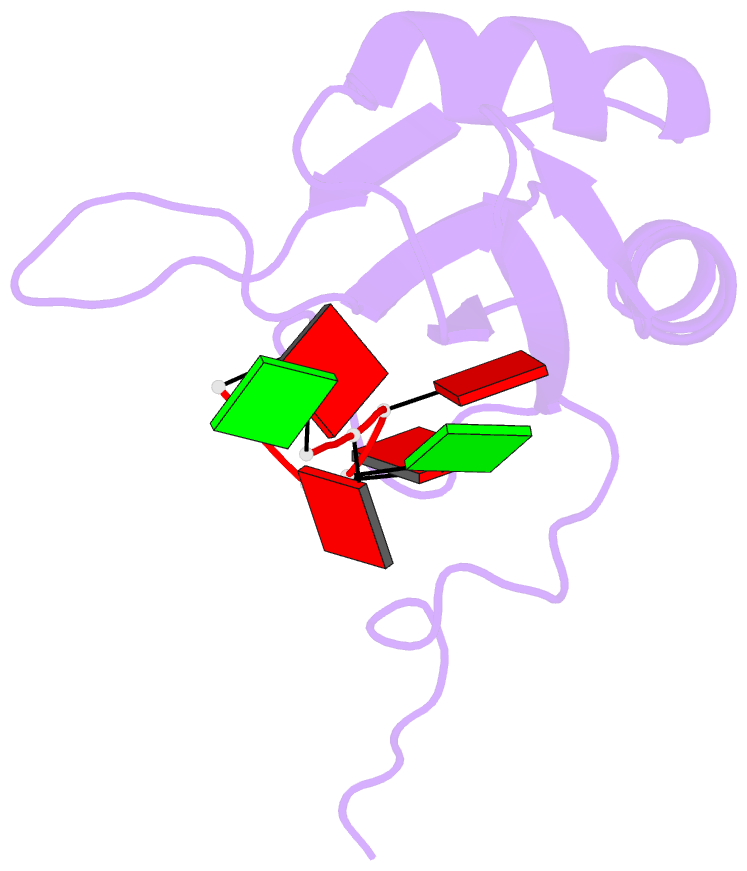
- Solution structure of RNA binding domain in human tra2 beta protein in complex with RNA (gaagaa)
- Reference
- Tsuda K, Someya T, Kuwasako K, Takahashi M, He F, Unzai S, Inoue M, Harada T, Watanabe S, Terada T, Kobayashi N, Shirouzu M, Kigawa T, Tanaka A, Sugano S, Guntert P, Yokoyama S, Muto Y (2011): "Structural basis for the dual RNA-recognition modes of human Tra2-beta RRM." Nucleic Acids Res., 39, 1538-1553. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq854.
- Abstract
- Human Transformer2-β (hTra2-β) is an important member of the serine/arginine-rich protein family, and contains one RNA recognition motif (RRM). It controls the alternative splicing of several pre-mRNAs, including those of the calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), the survival motor neuron 1 (SMN1) protein and the tau protein. Accordingly, the RRM of hTra2-β specifically binds to two types of RNA sequences [the CAA and (GAA)(2) sequences]. We determined the solution structure of the hTra2-β RRM (spanning residues Asn110-Thr201), which not only has a canonical RRM fold, but also an unusual alignment of the aromatic amino acids on the β-sheet surface. We then solved the complex structure of the hTra2-β RRM with the (GAA)(2) sequence, and found that the AGAA tetra-nucleotide was specifically recognized through hydrogen-bond formation with several amino acids on the N- and C-terminal extensions, as well as stacking interactions mediated by the unusually aligned aromatic rings on the β-sheet surface. Further NMR experiments revealed that the hTra2-β RRM recognizes the CAA sequence when it is integrated in the stem-loop structure. This study indicates that the hTra2-β RRM recognizes two types of RNA sequences in different RNA binding modes.