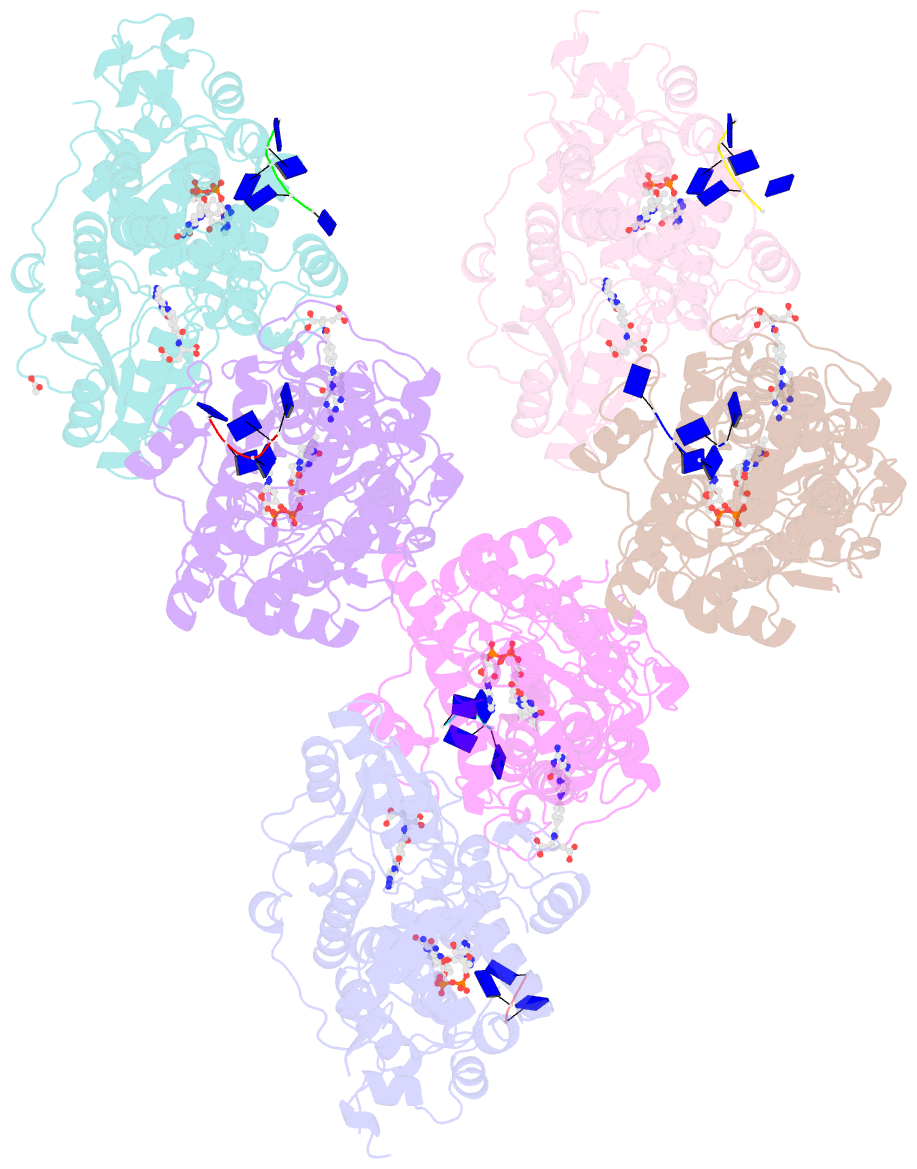
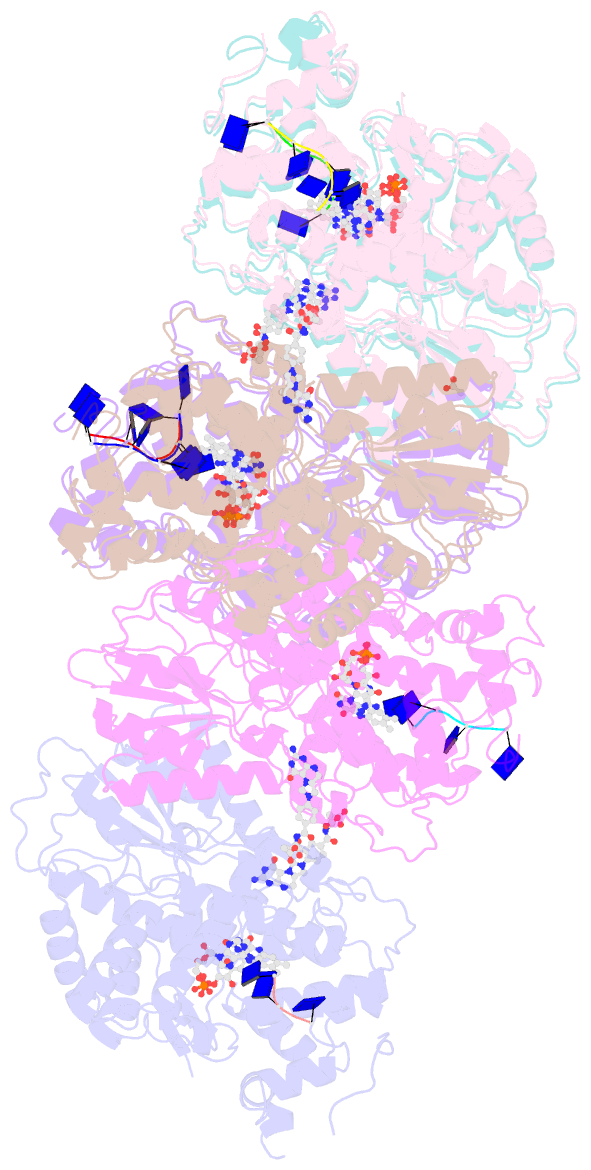
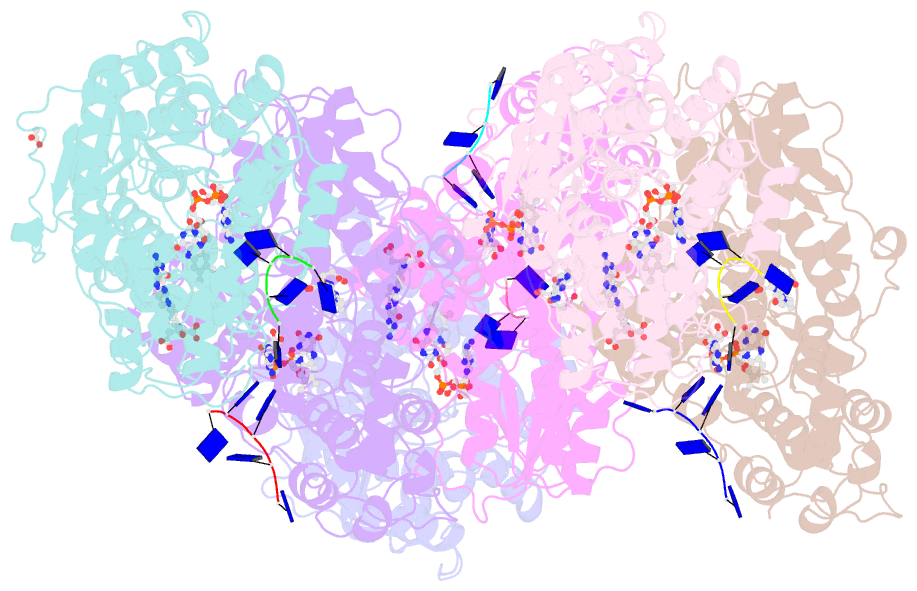
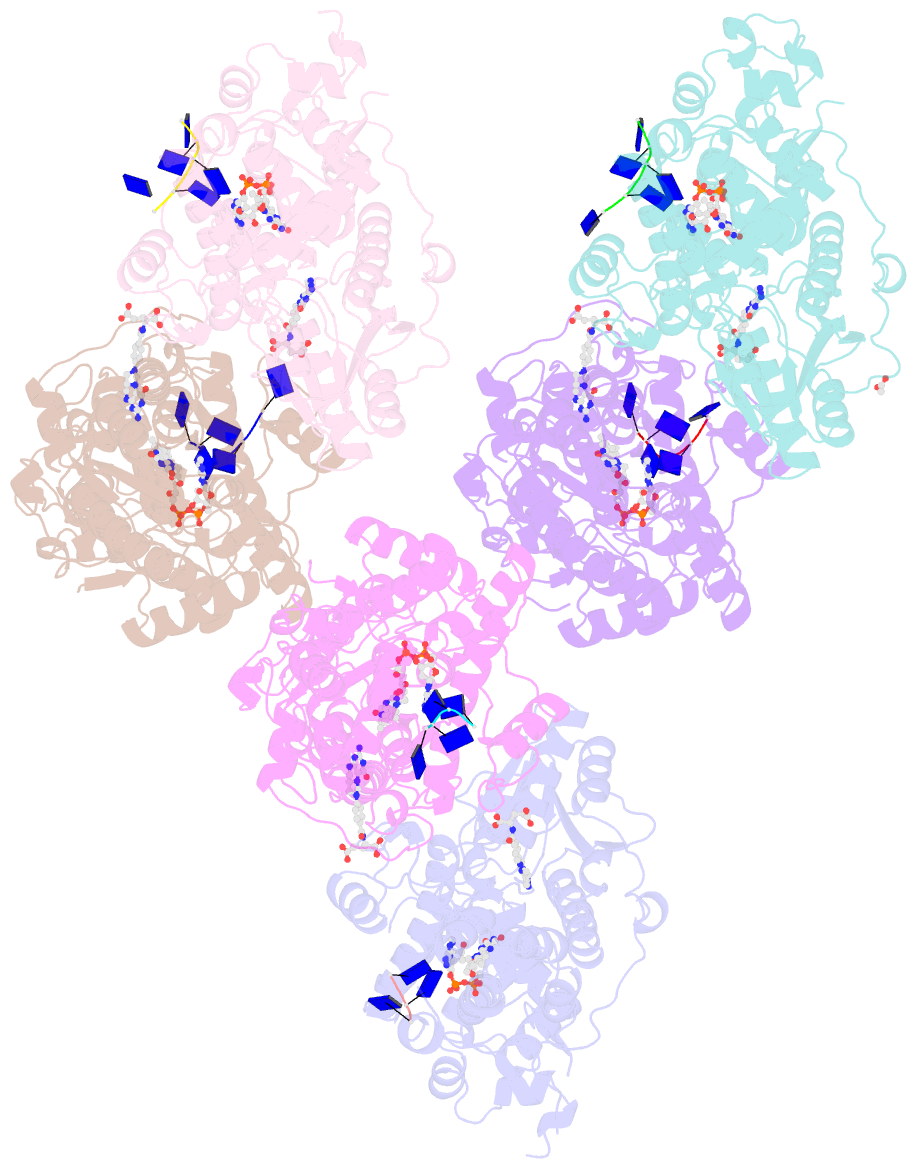
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2vtb; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- lyase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.01 Å)
- Summary
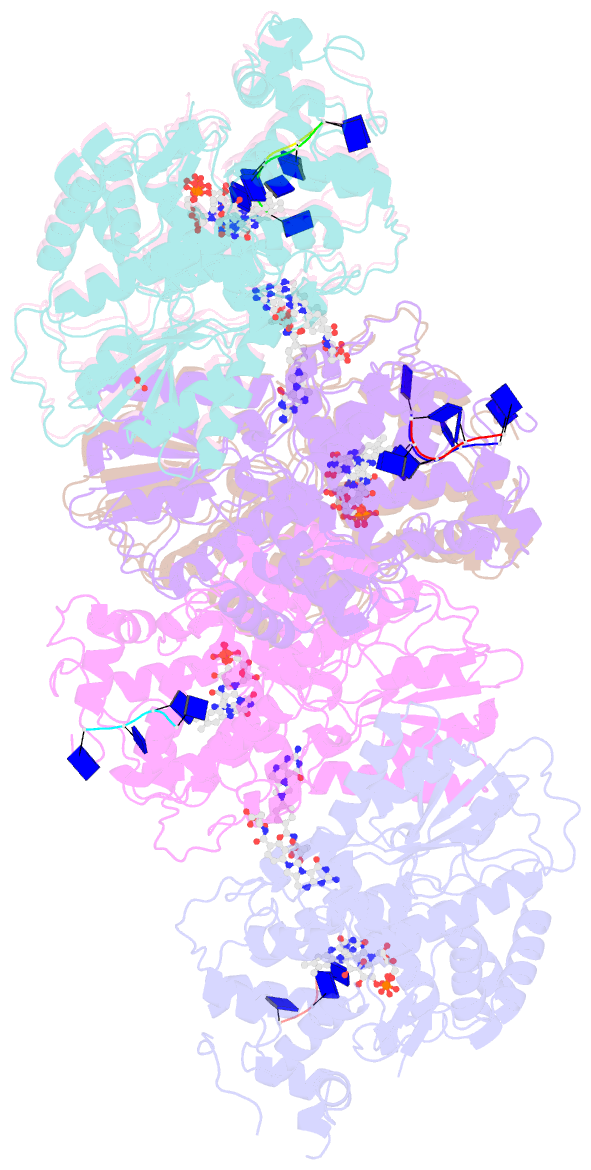
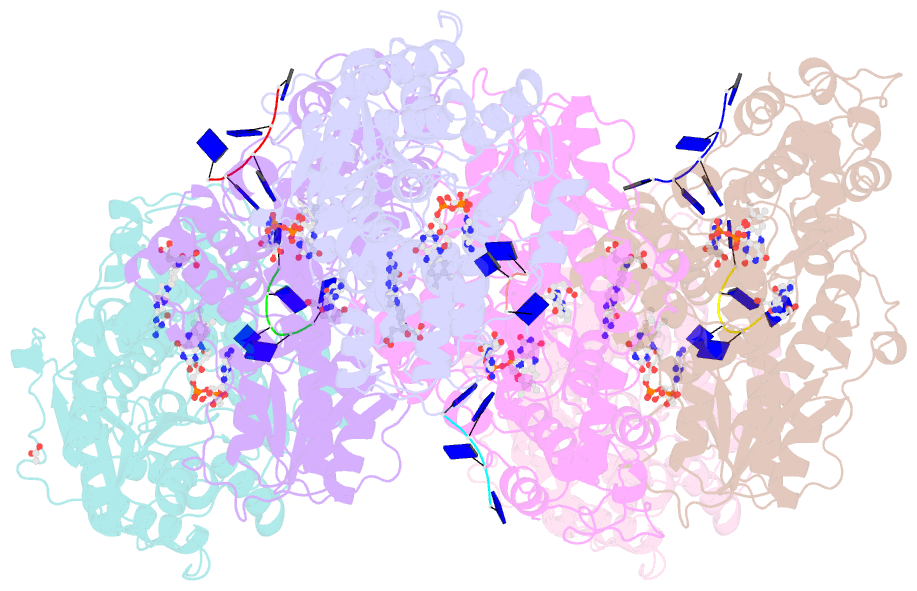
- Structure of cryptochrome 3 - DNA complex
- Reference
- Pokorny R, Klar T, Hennecke U, Carell T, Batschauer A, Essen L-O (2008): "Recognition and Repair of Uv Lesions in Loop Structures of Duplex DNA by Dash-Type Cryptochrome." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 105, 21023. doi: 10.1073/PNAS.0805830106.
- Abstract
- DNA photolyases and cryptochromes (cry) form a family of flavoproteins that use light energy in the blue/UV-A region for the repair of UV-induced DNA lesions or for signaling, respectively. Very recently, it was shown that members of the DASH cryptochrome subclade repair specifically cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) in UV-damaged single-stranded DNA. Here, we report the crystal structure of Arabidopsis cryptochrome 3 with an in-situ-repaired CPD substrate in single-stranded DNA. The structure shows a binding mode similar to that of conventional DNA photolyases. Furthermore, CPD lesions in double-stranded DNA are bound and repaired with similar efficiency as in single-stranded DNA if the CPD lesion is present in a loop structure. Together, these data reveal that DASH cryptochromes catalyze light-driven DNA repair like conventional photolyases but lack an efficient flipping mechanism for interaction with CPD lesions within duplex DNA.