Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2vw9; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.3 Å)
- Summary
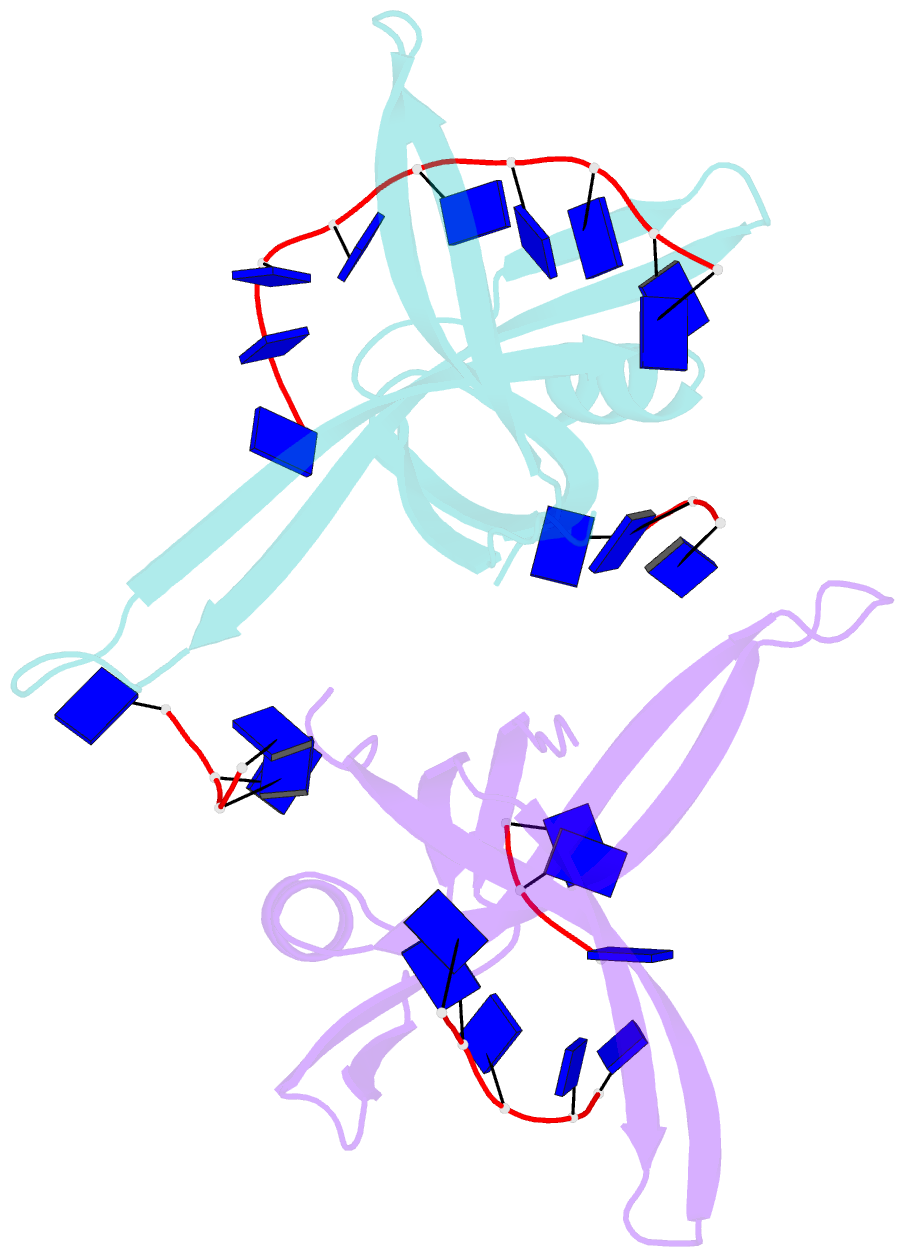
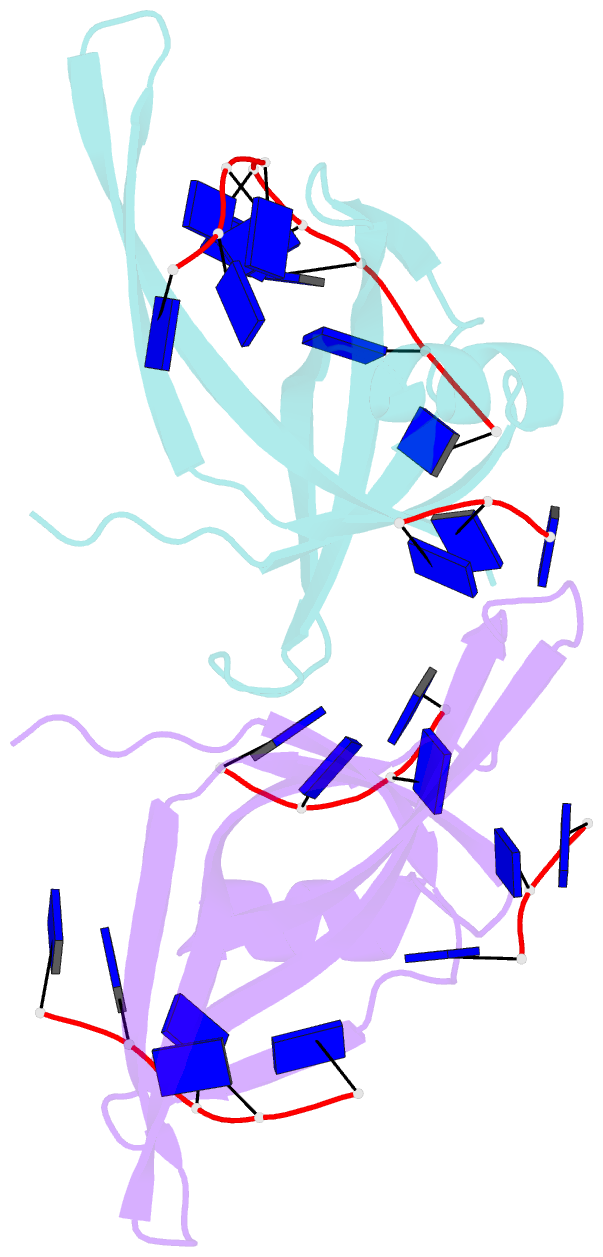
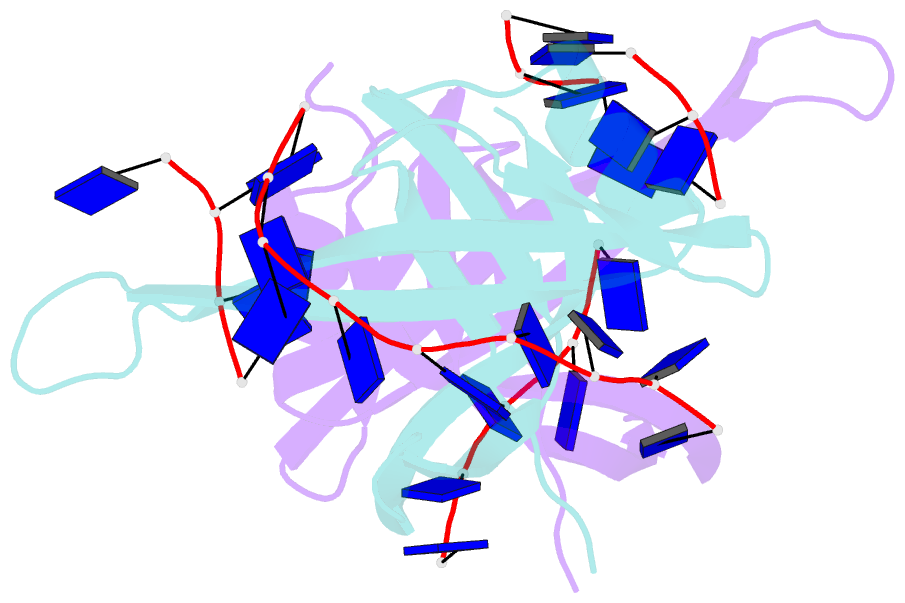
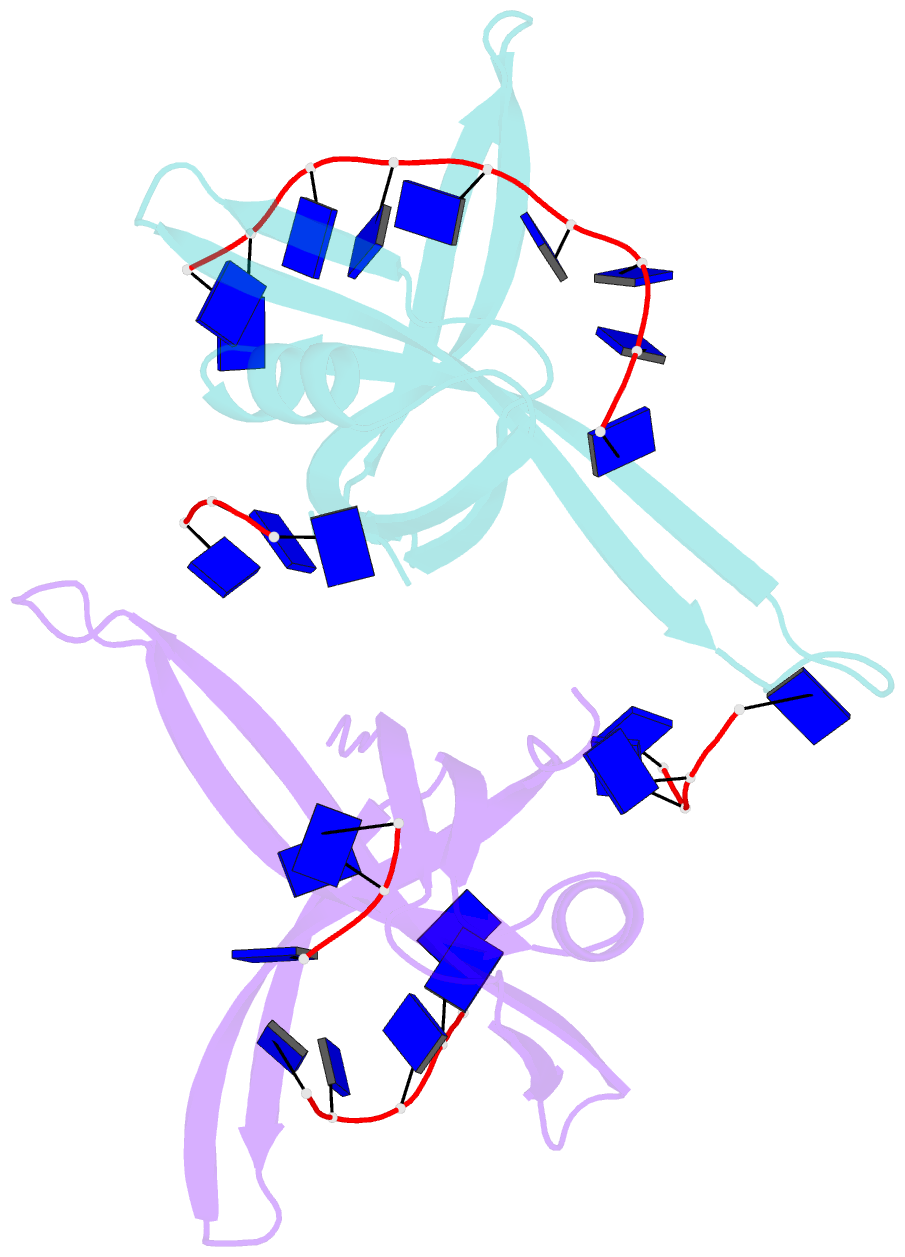
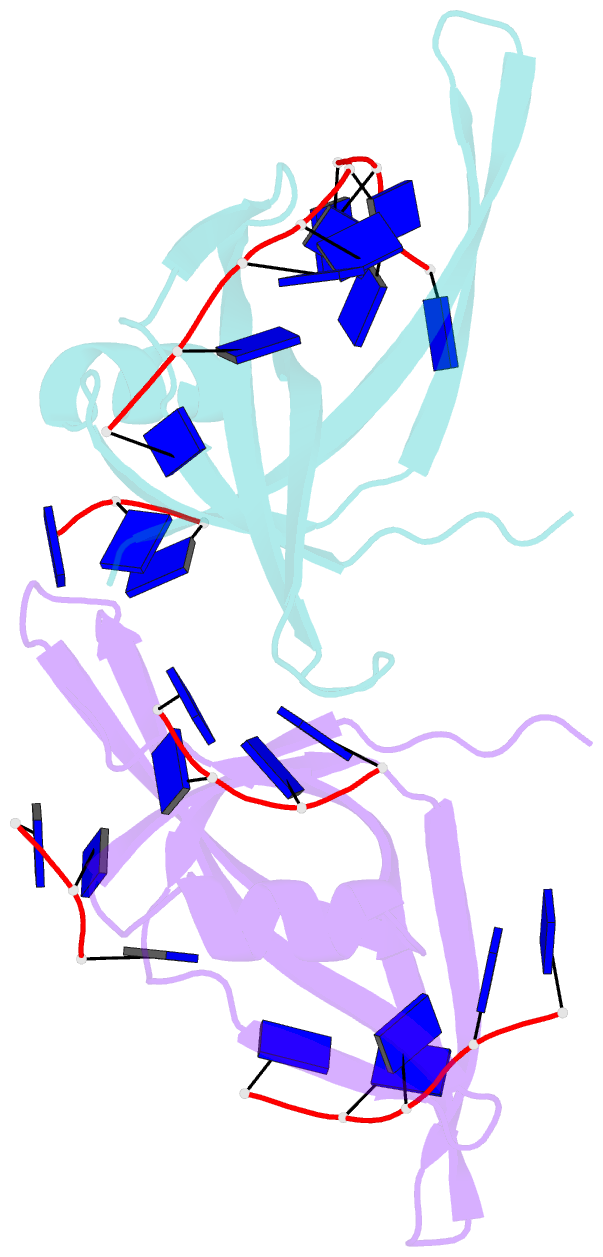
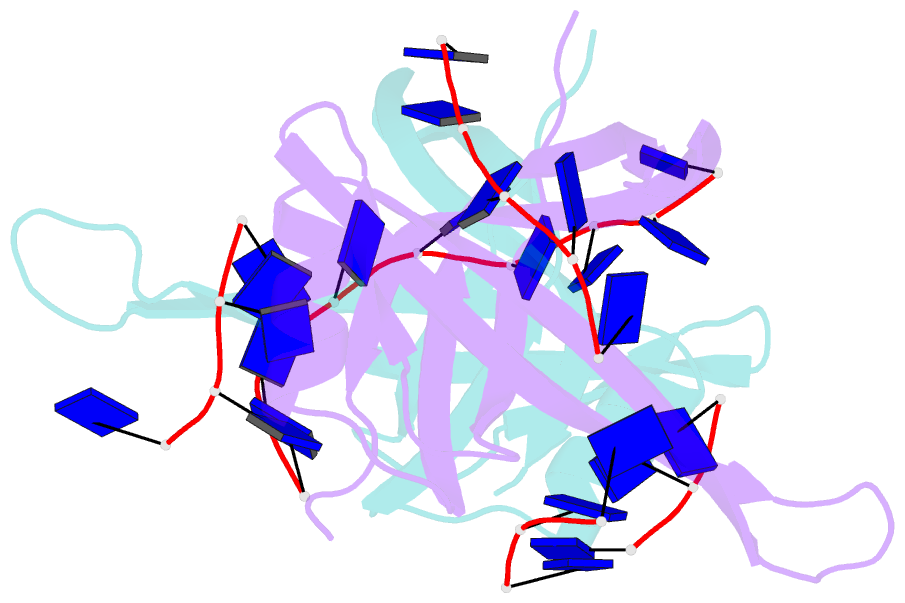
- Single stranded DNA binding protein complex from helicobacter pylori
- Reference
- Chan K-W, Lee Y-J, Wang C-H, Huang H, Sun Y-J (2009): "Single-Stranded DNA-Binding Protein Complex from Helicobacter Pylori Suggests an Ssdna-Binding Surface." J.Mol.Biol., 388, 508. doi: 10.1016/J.JMB.2009.03.022.
- Abstract
- Single-stranded DNA (ssDNA)-binding protein (SSB) plays an important role in DNA replication, recombination, and repair. SSB consists of an N-terminal ssDNA-binding domain with an oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding fold and a flexible C-terminal tail involved in protein-protein interactions. SSB from Helicobacter pylori (HpSSB) was isolated, and the ssDNA-binding characteristics of HpSSB were analyzed by fluorescence titration and electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Tryptophan fluorescence quenching was measured as 61%, and the calculated cooperative affinity was 5.4x10(7) M(-1) with an ssDNA-binding length of 25-30 nt. The crystal structure of the C-terminally truncated protein (HpSSBc) in complex with 35-mer ssDNA [HpSSBc-(dT)(35)] was determined at a resolution of 2.3 A. The HpSSBc monomer folds as an oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding fold with a Y-shaped conformation. The ssDNA wrapped around the HpSSBc tetramer through a continuous binding path comprising five essential aromatic residues and a positively charged surface formed by numerous basic residues.