Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2xkk; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- isomerase-DNA-antibiotic
- Method
- X-ray (3.25 Å)
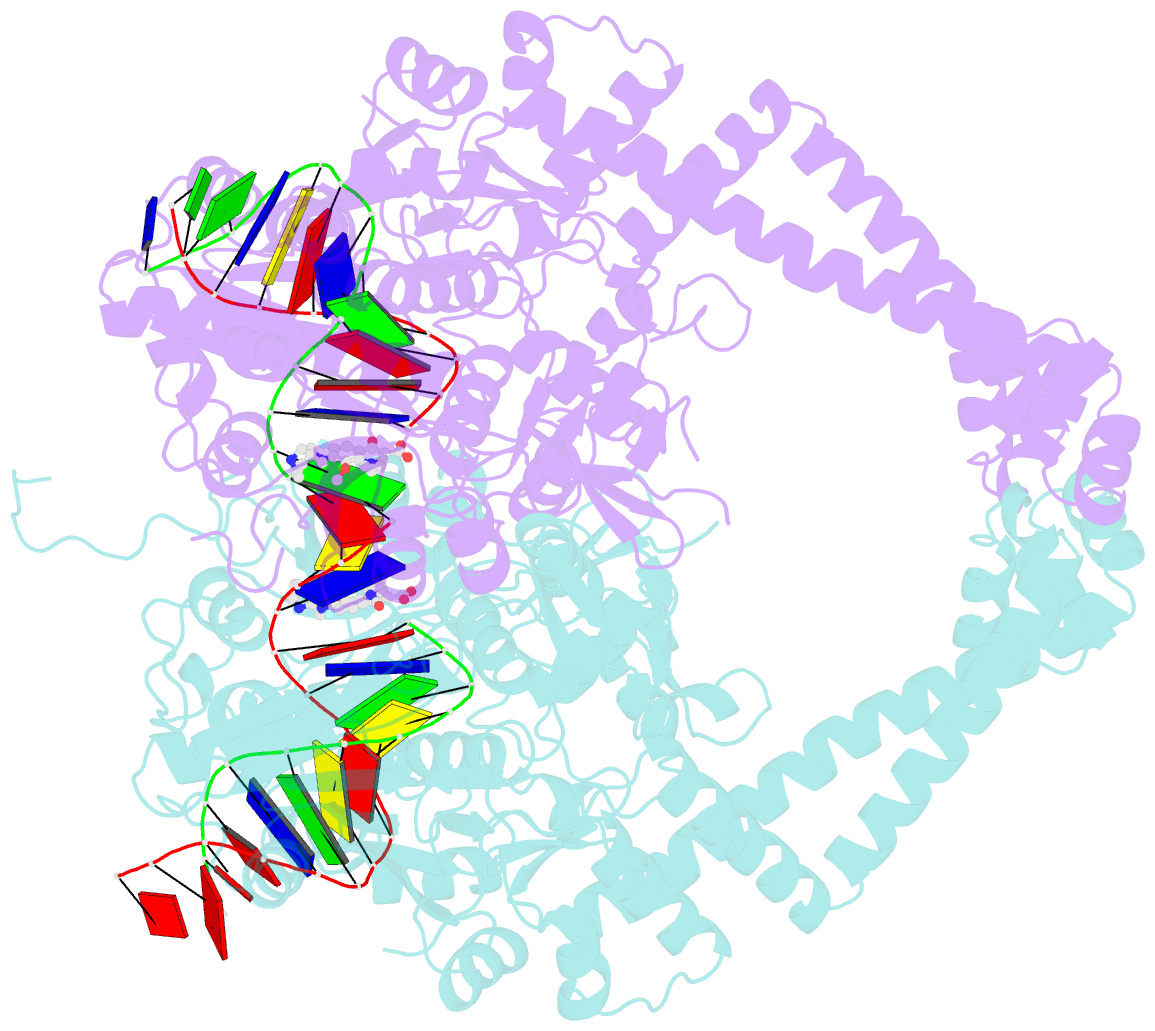
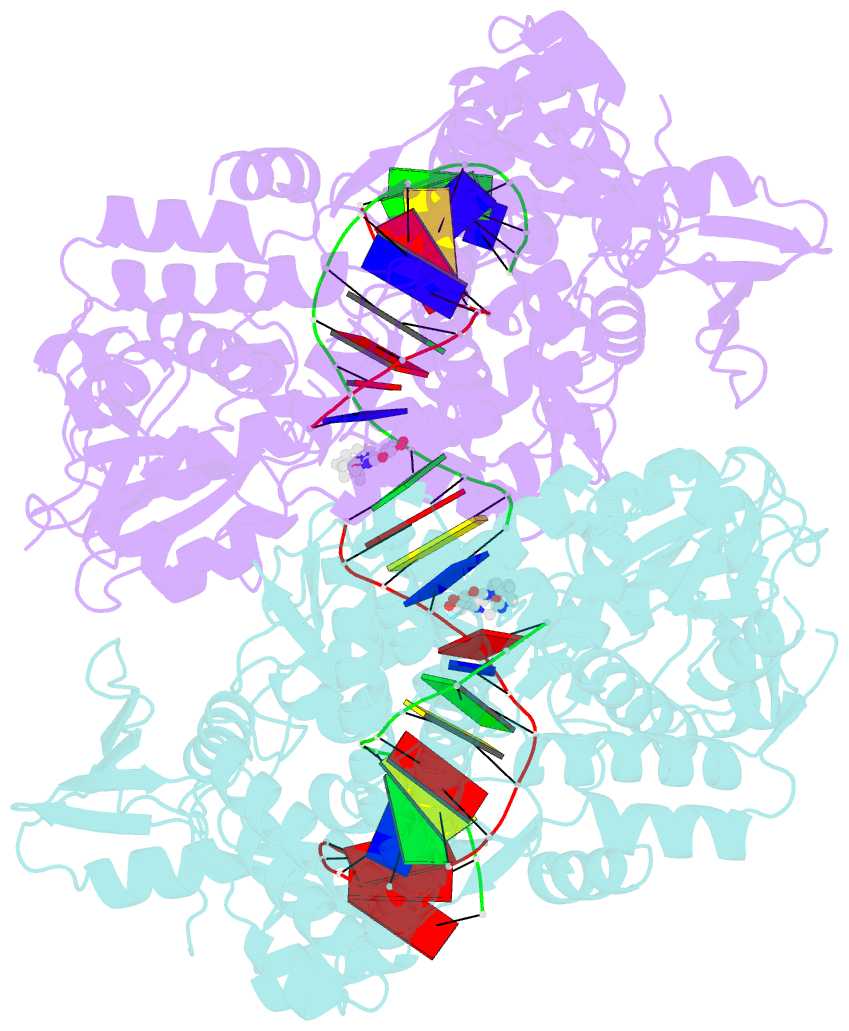
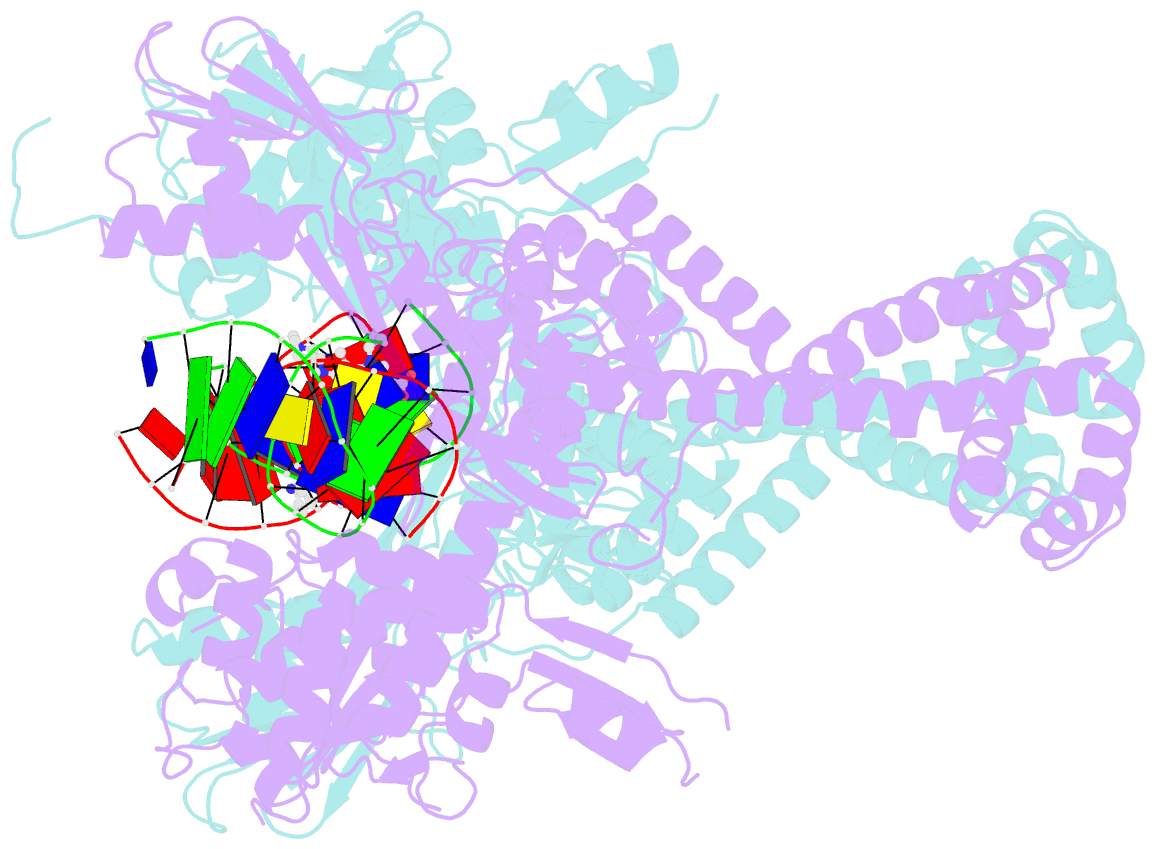
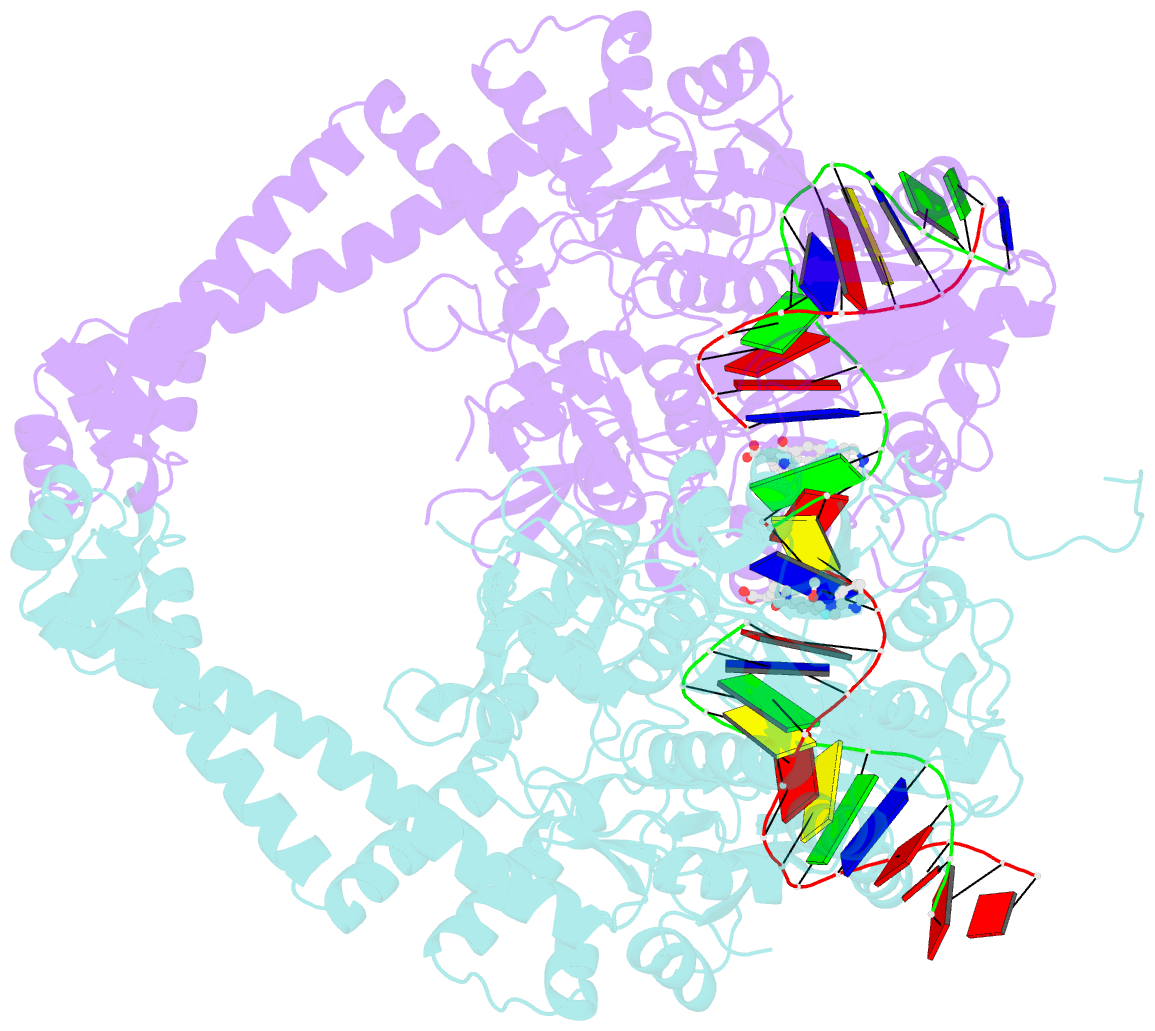
- Summary
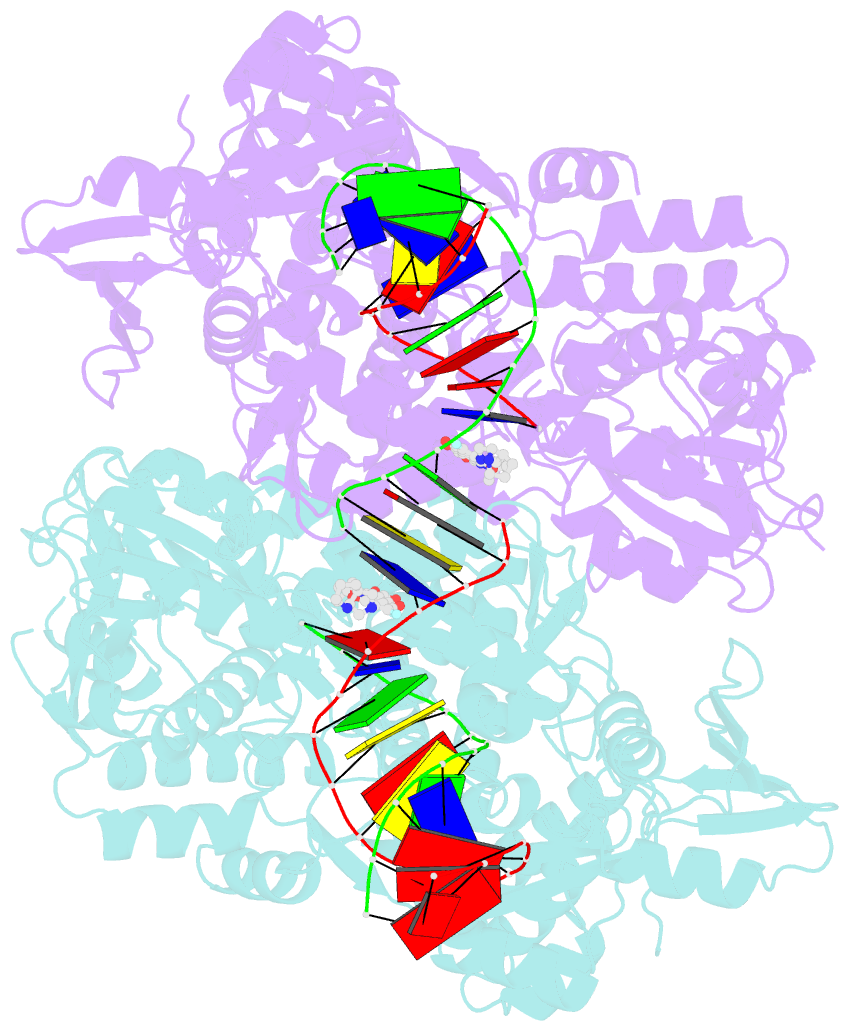
- Crystal structure of moxifloxacin, DNA, and a. baumannii topo iv (pare-parc fusion truncate)
- Reference
- Wohlkonig A, Chan PF, Fosberry AP, Homes P, Huang J, Kranz M, Leydon VR, Miles TJ, Pearson ND, Perera RL, Shillings AJ, Gwynn MN, Bax BD (2010): "Structural Basis of Quinolone Inhibition of Type Iia Topoisomerases and Target-Mediated Resistance." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 17, 1152. doi: 10.1038/NSMB.1892.
- Abstract
- Quinolone antibacterials have been used to treat bacterial infections for over 40 years. A crystal structure of moxifloxacin in complex with Acinetobacter baumannii topoisomerase IV now shows the wedge-shaped quinolone stacking between base pairs at the DNA cleavage site and binding conserved residues in the DNA cleavage domain through chelation of a noncatalytic magnesium ion. This provides a molecular basis for the quinolone inhibition mechanism, resistance mutations and invariant quinolone antibacterial structural features.