Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2xzo; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.395 Å)
- Summary
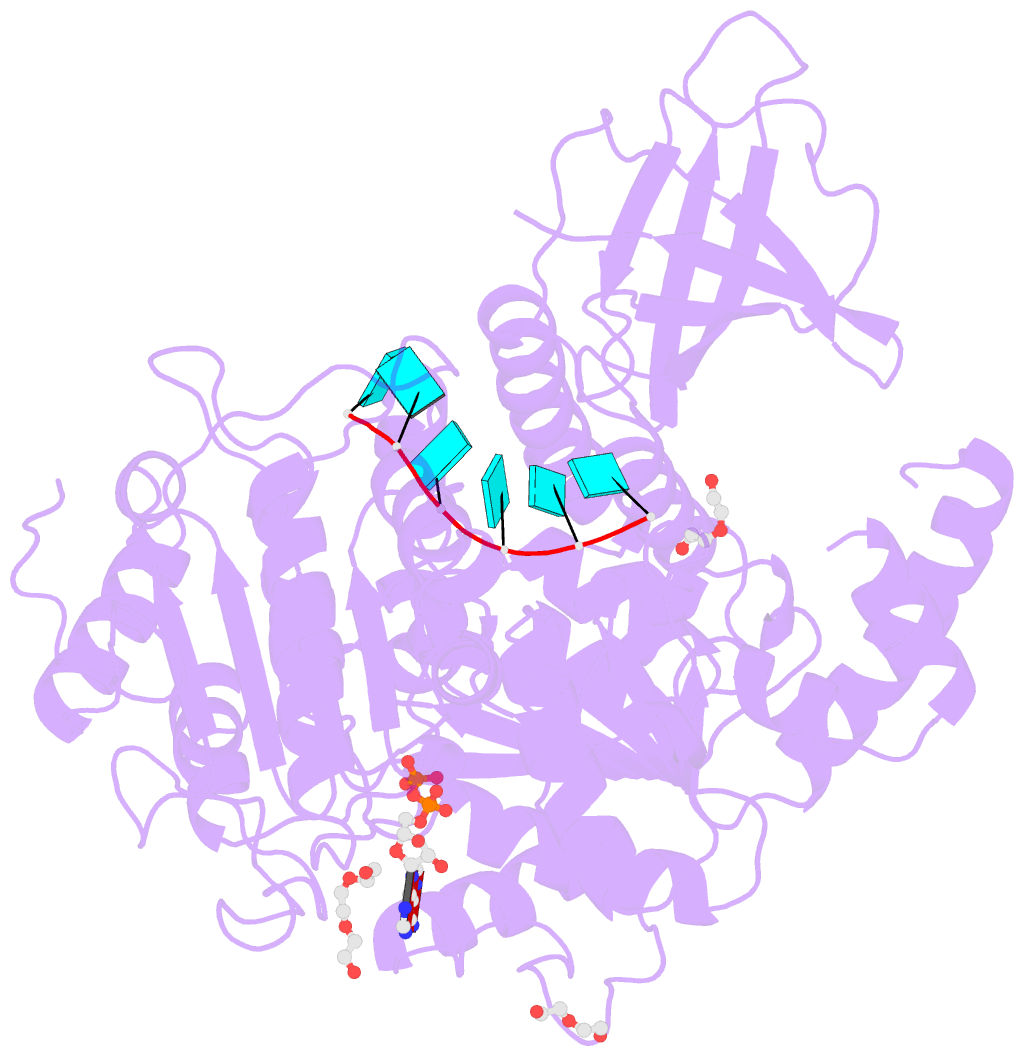
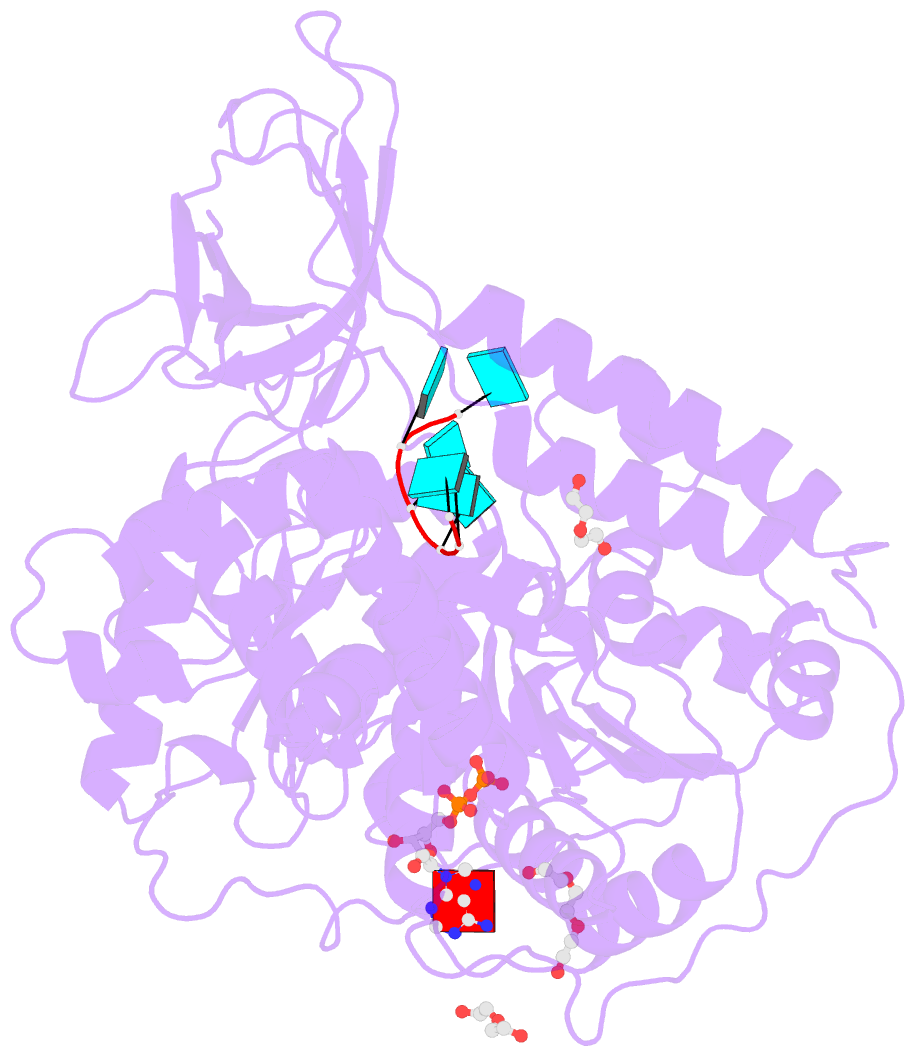
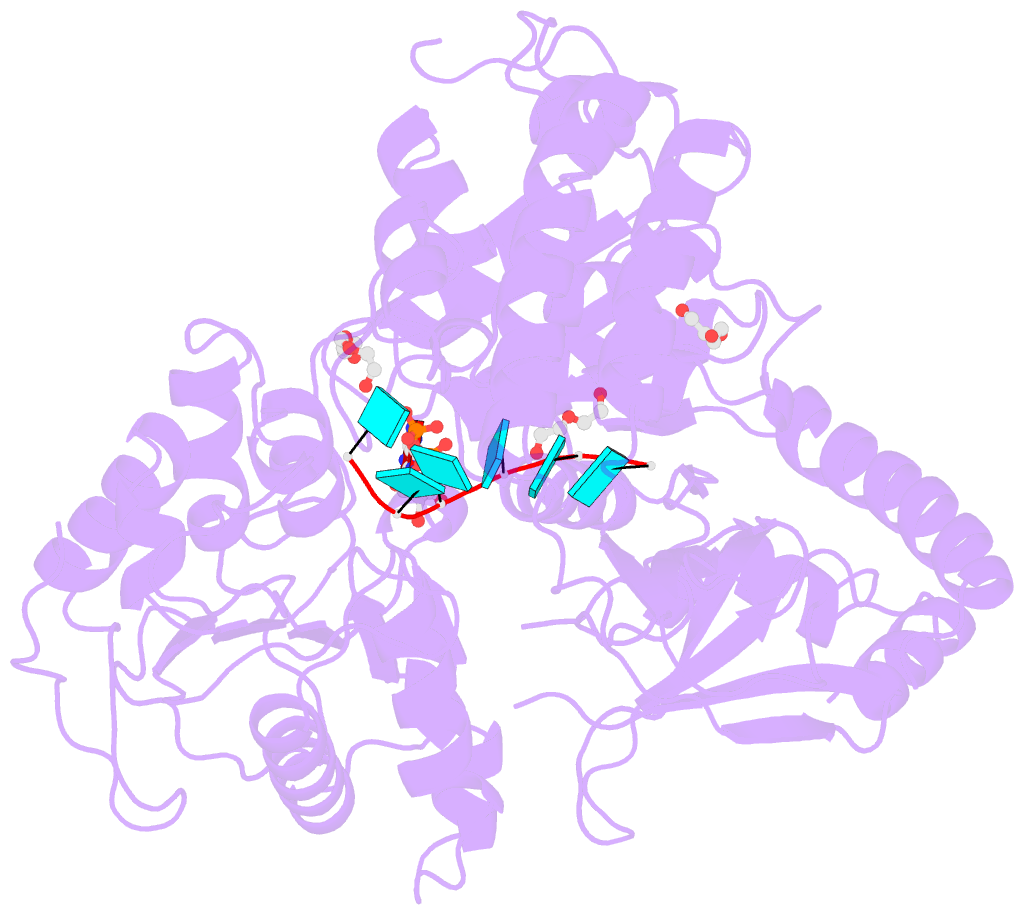
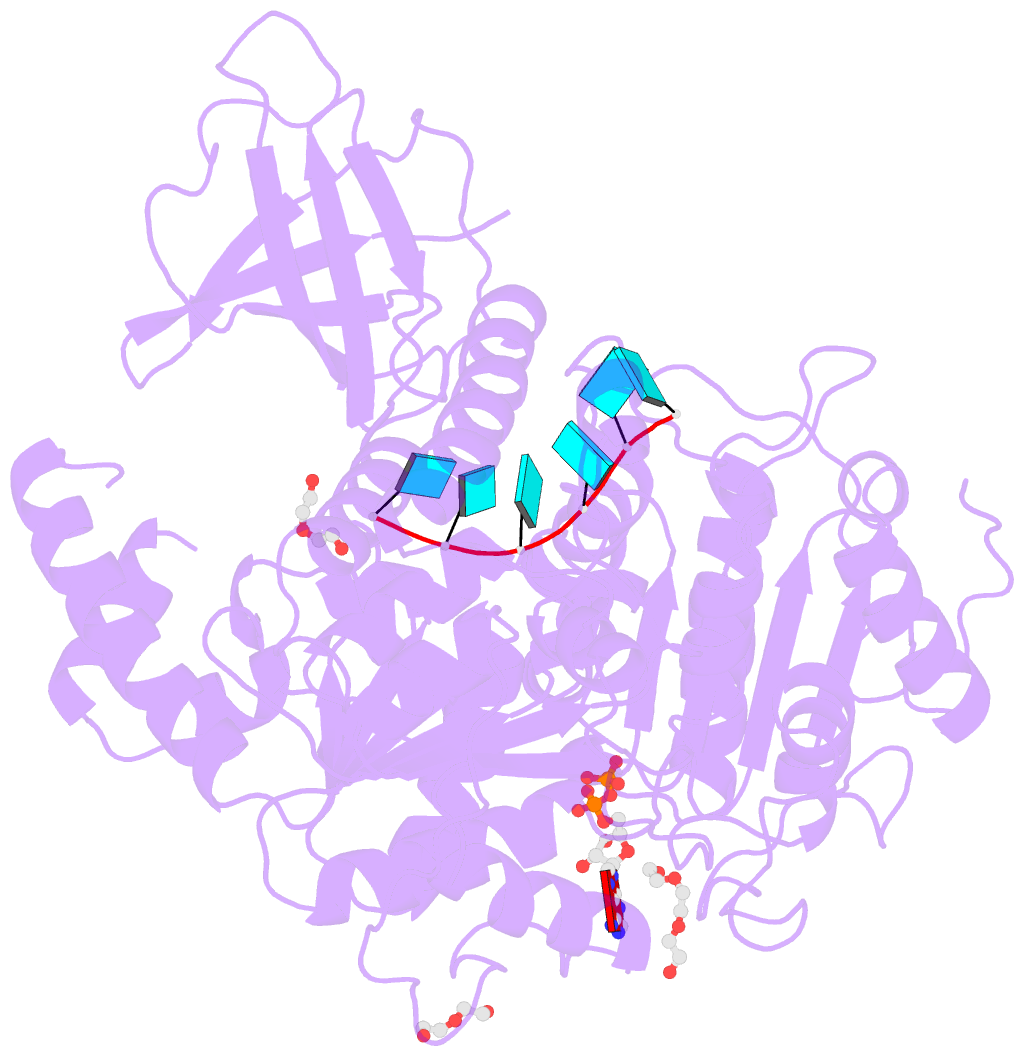
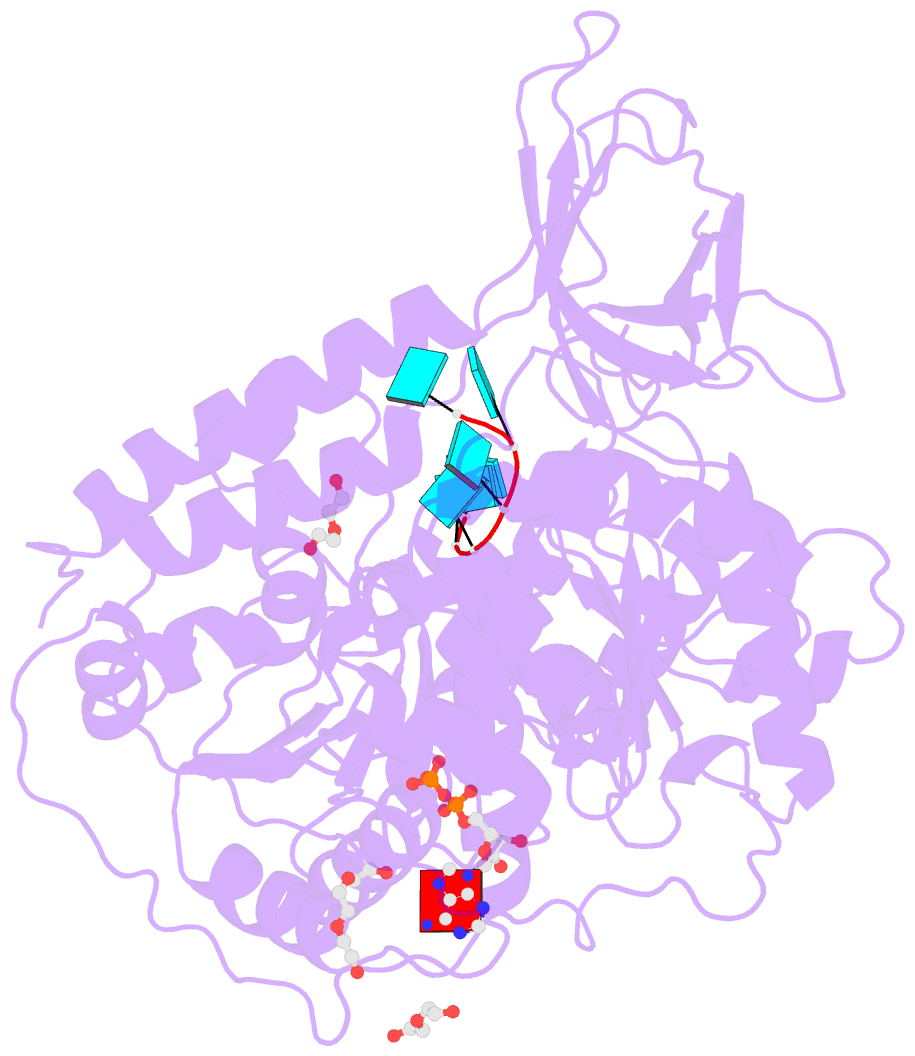
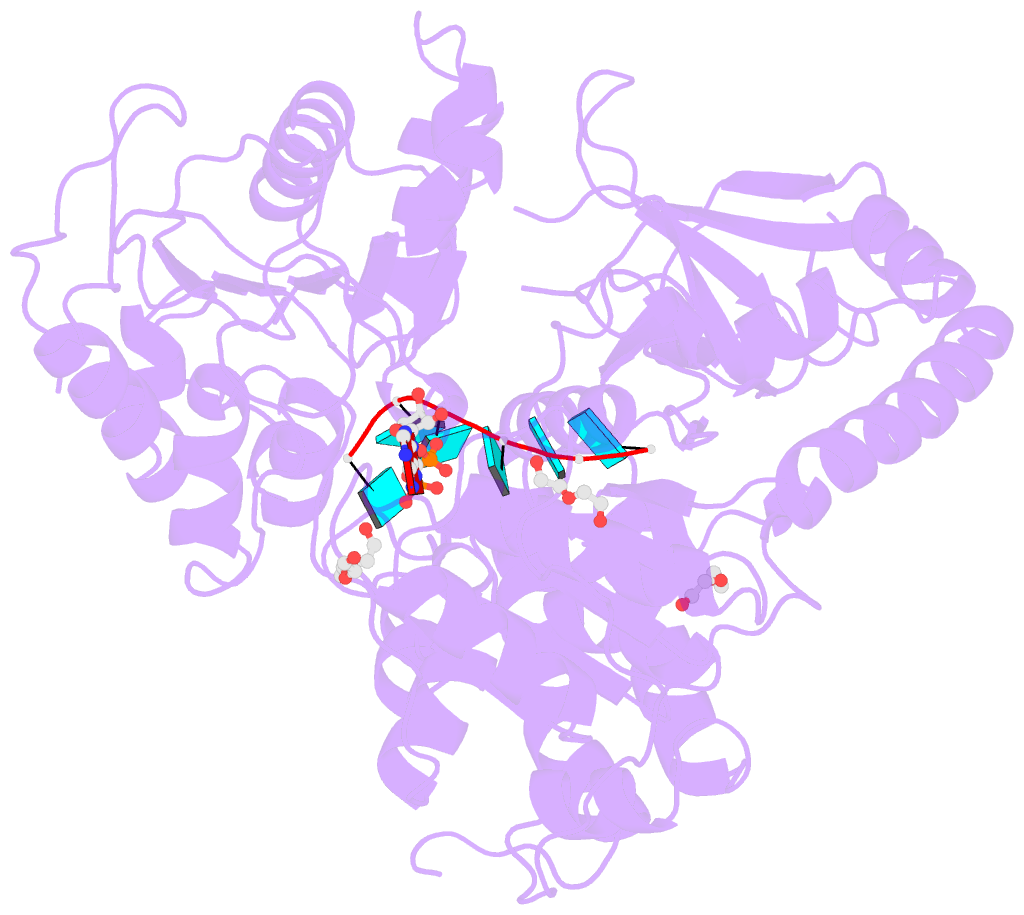
- Upf1 helicase - RNA complex
- Reference
- Chakrabarti S, Jayachandran U, Bonneau F, Fiorini F, Basquin C, Domcke S, Le Hir H, Conti E (2011): "Molecular Mechanisms for the RNA-Dependent ATPase Activity of Upf1 and its Regulation by Upf2." Mol.Cell, 41, 693. doi: 10.1016/J.MOLCEL.2011.02.010.
- Abstract
- Upf1 is a crucial factor in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, the eukaryotic surveillance pathway that degrades mRNAs containing premature stop codons. The essential RNA-dependent ATPase activity of Upf1 is triggered by the formation of the surveillance complex with Upf2-Upf3. We report crystal structures of Upf1 in the presence and absence of the CH domain, captured in the transition state with ADP:AlF₄⁻ and RNA. In isolation, Upf1 clamps onto the RNA, enclosing it in a channel formed by both the catalytic and regulatory domains. Upon binding to Upf2, the regulatory CH domain of Upf1 undergoes a large conformational change, causing the catalytic helicase domain to bind RNA less extensively and triggering its helicase activity. Formation of the surveillance complex thus modifies the RNA binding properties and the catalytic activity of Upf1, causing it to switch from an RNA-clamping mode to an RNA-unwinding mode.