Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2z3x; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.1 Å)
- Summary
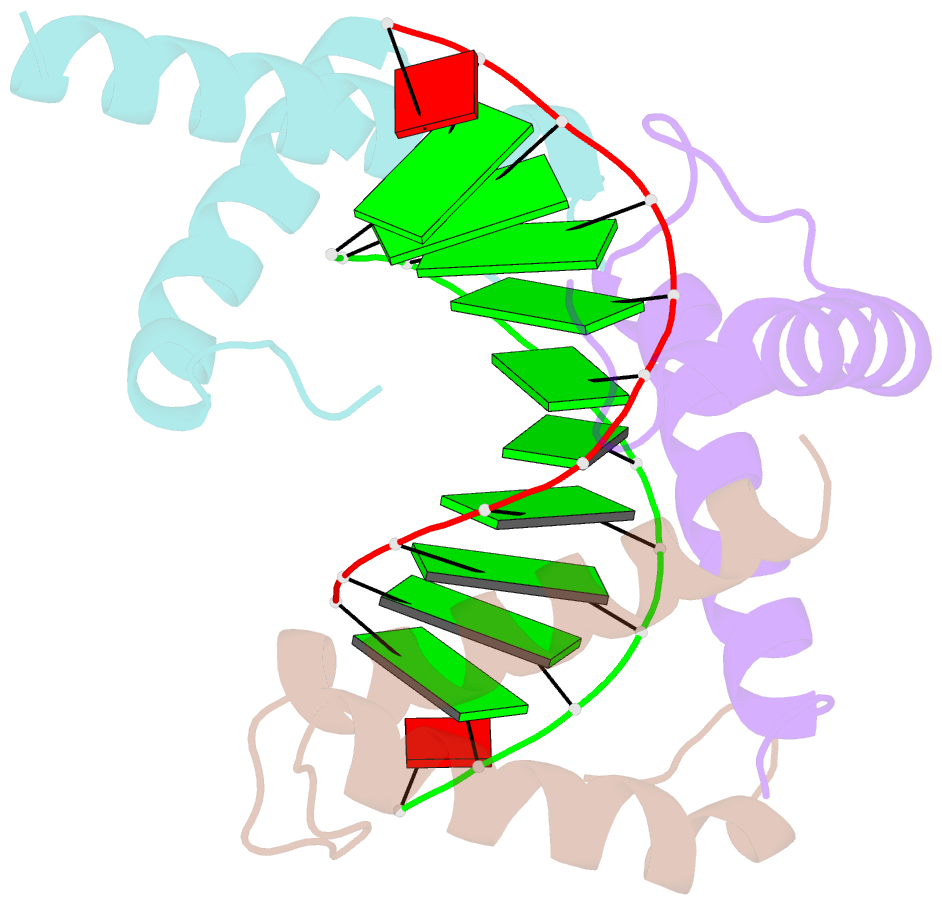
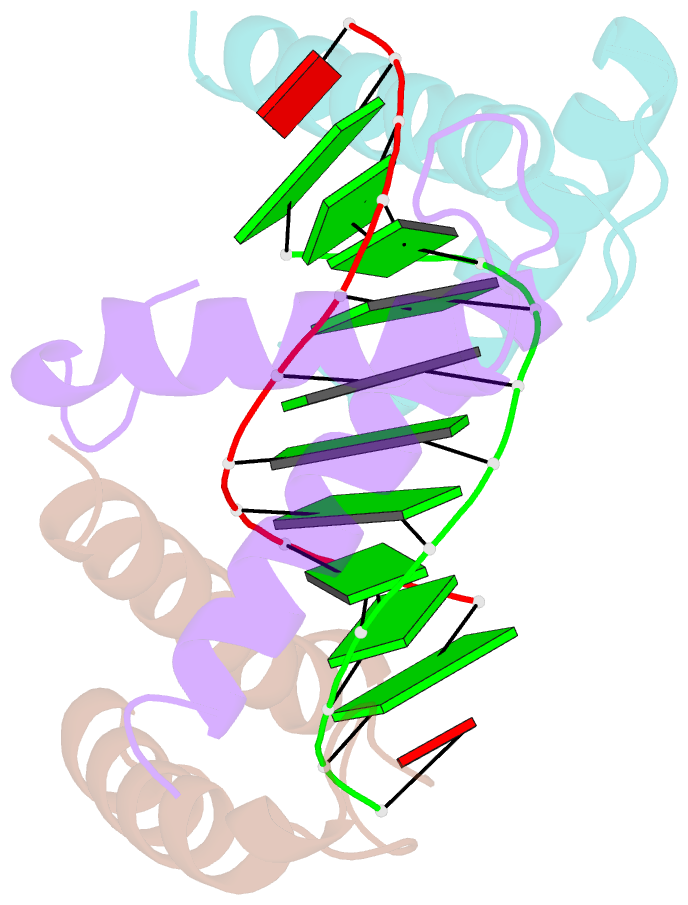
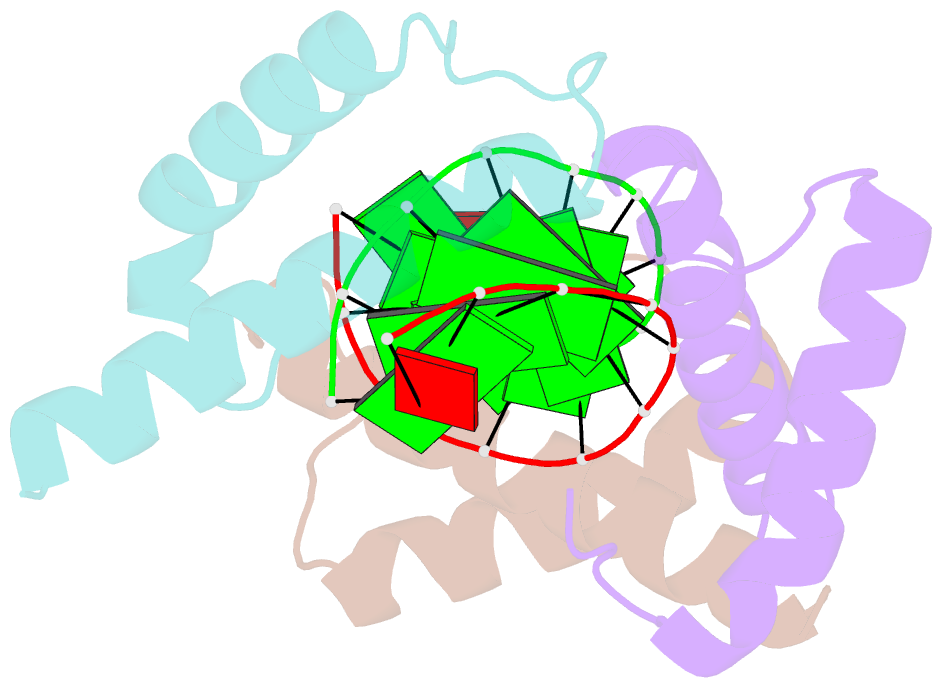
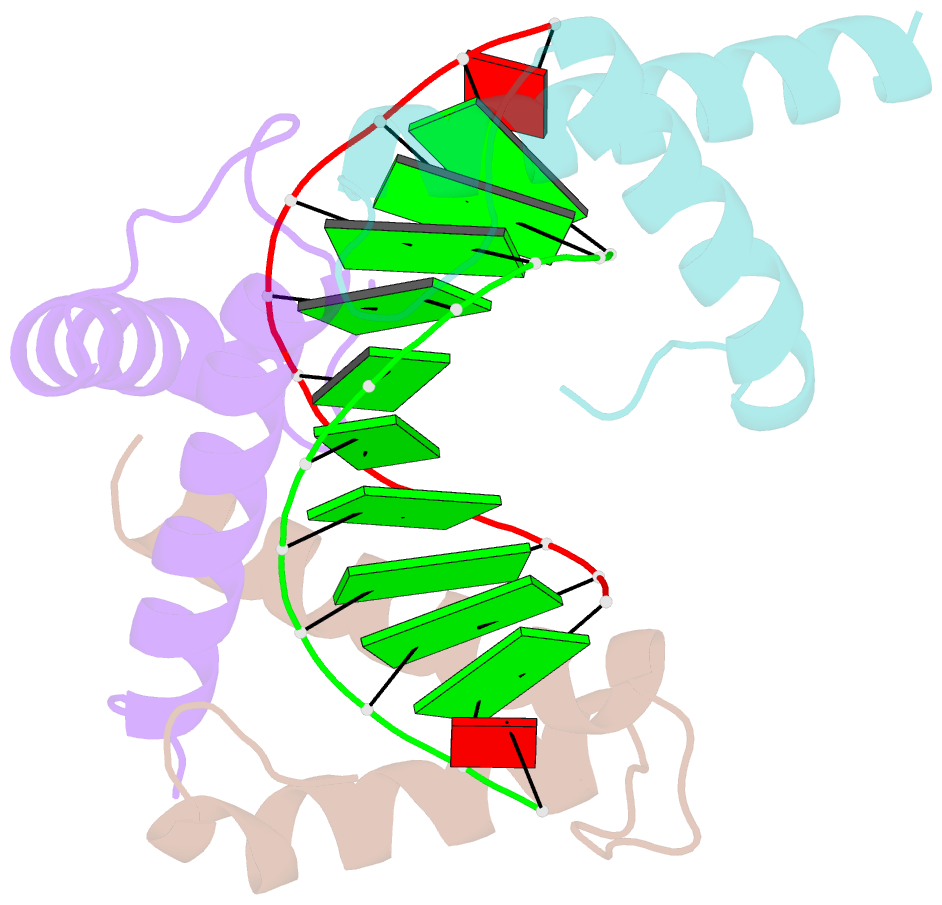
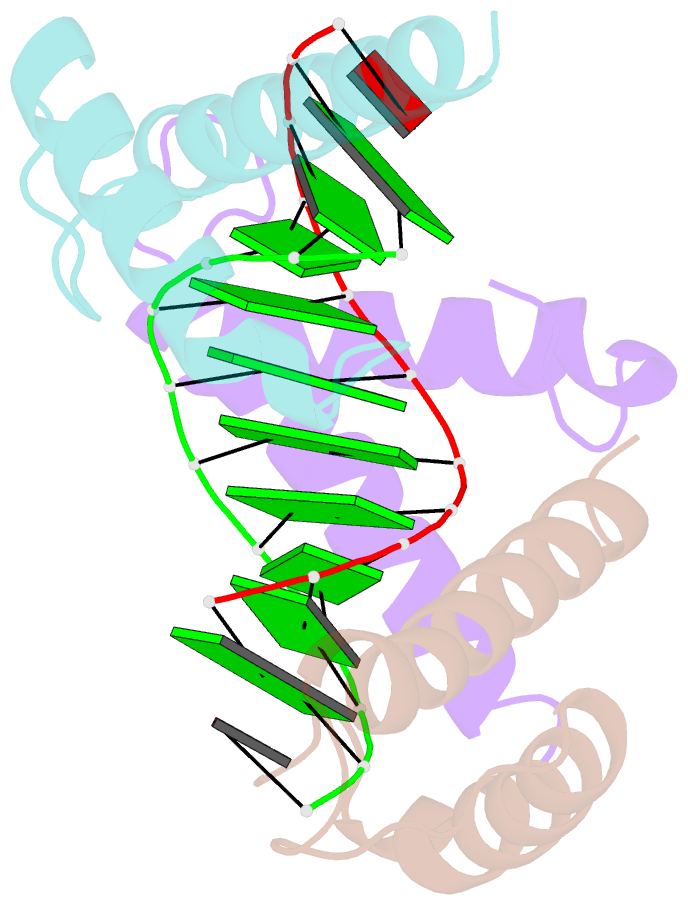
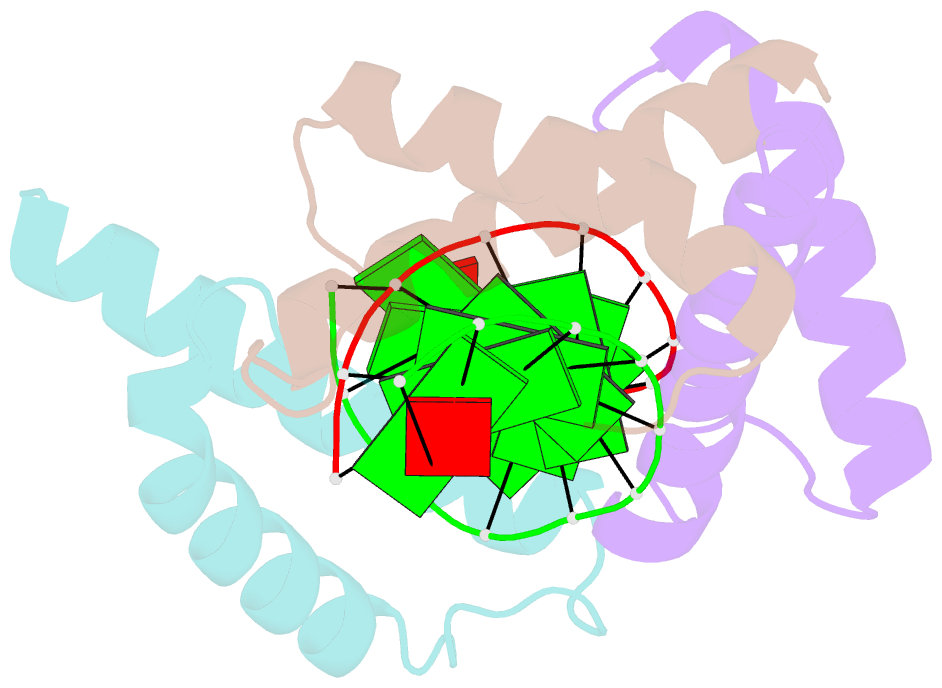
- Structure of a protein-DNA complex essential for DNA protection in spore of bacillus species
- Reference
- Lee KS, Bumbaca D, Kosman J, Setlow P, Jedrzejas MJ (2008): "Structure of a protein-DNA complex essential for DNA protection in spores of Bacillus species." Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 105, 2806-2811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708244105.
- Abstract
- The DNA-binding alpha/beta-type small acid-soluble proteins (SASPs) are a major factor in the resistance and long-term survival of spores of Bacillus species by protecting spore DNA against damage due to desiccation, heat, toxic chemicals, enzymes, and UV radiation. We now report the crystal structure at 2.1 A resolution of an alpha/beta-type SASP bound to a 10-bp DNA duplex. In the complex, the alpha/beta-type SASP adopt a helix-turn-helix motif, interact with DNA through minor groove contacts, bind to approximately 6 bp of DNA as a dimer, and the DNA is in an A-B type conformation. The structure of the complex provides important insights into the molecular details of both DNA and alpha/beta-type SASP protection in the complex and thus also in spores.