Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
3adb;
DSSR-derived features in text and
JSON formats; DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.8 Å)
- Summary
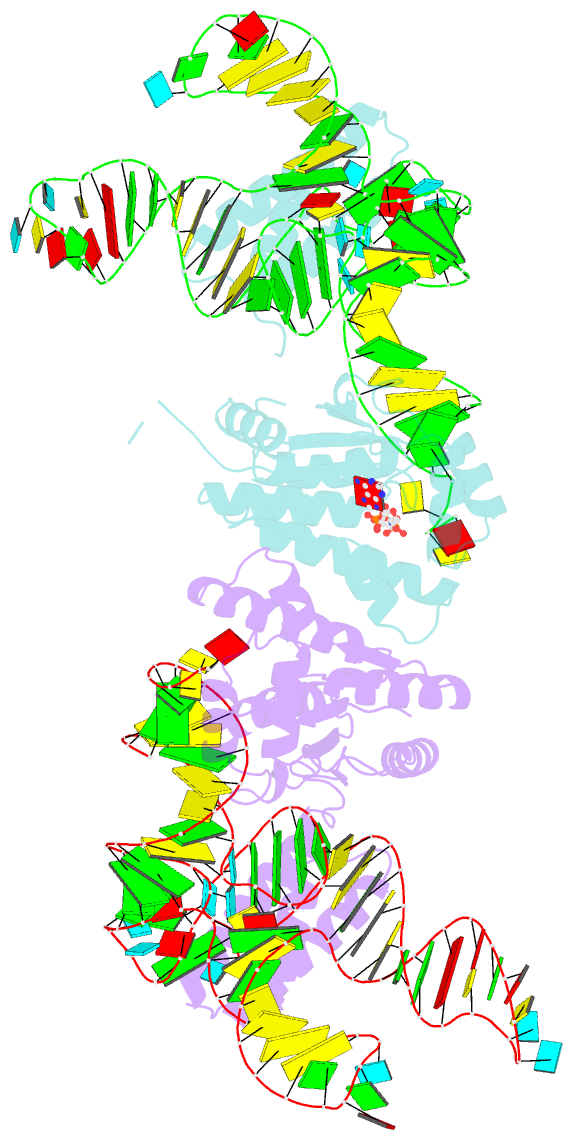
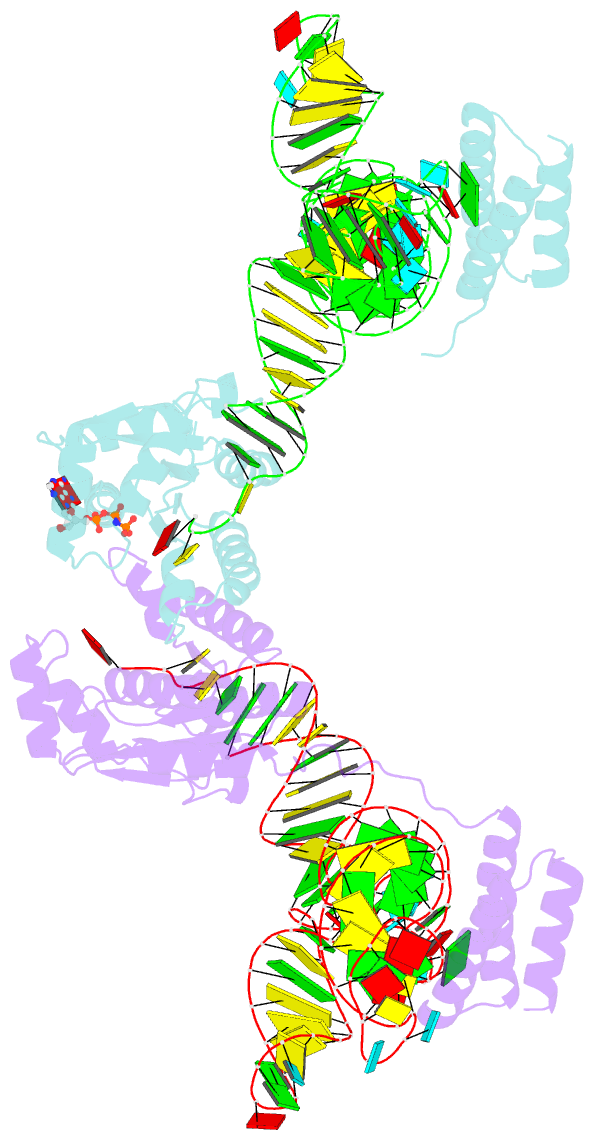
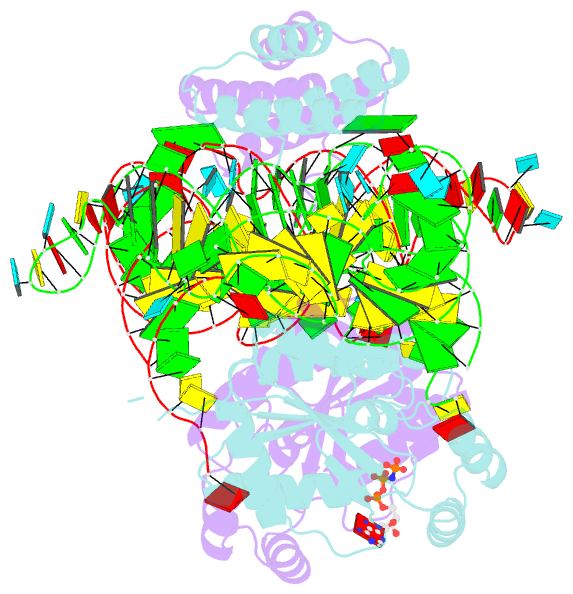
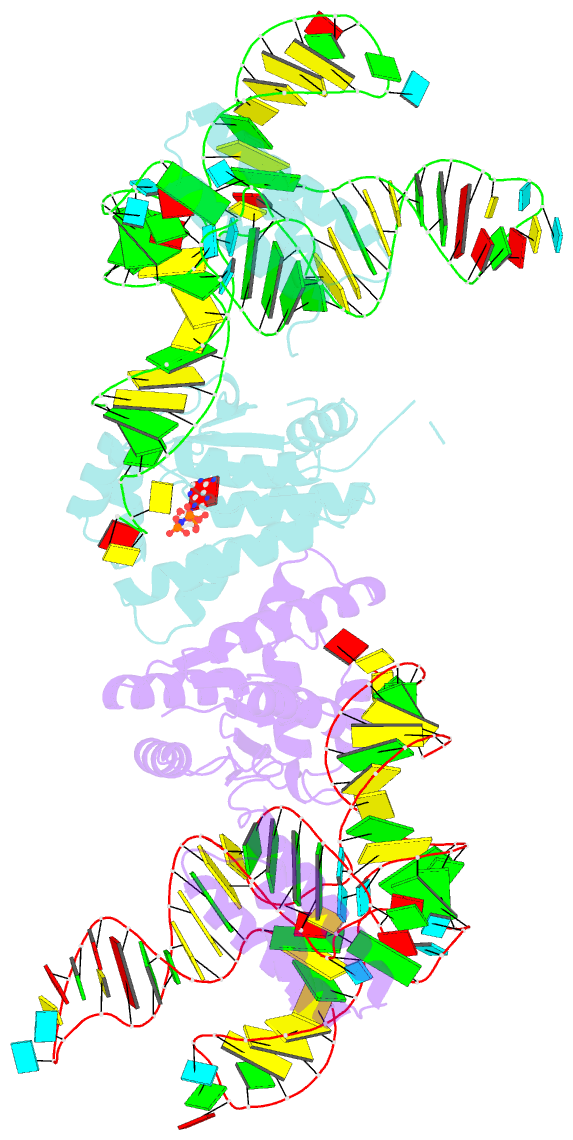
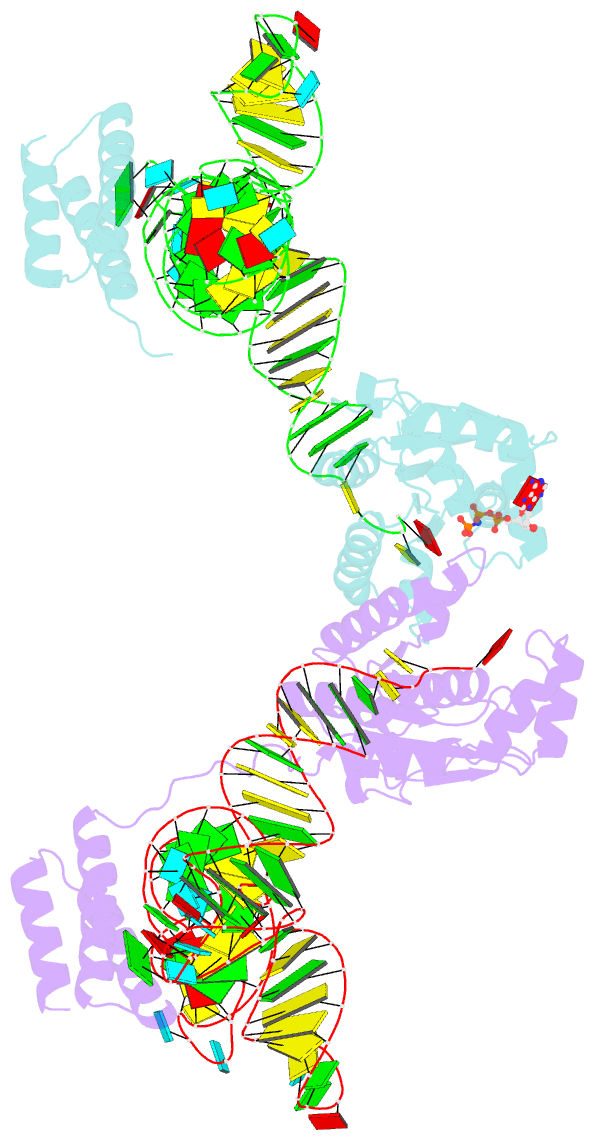
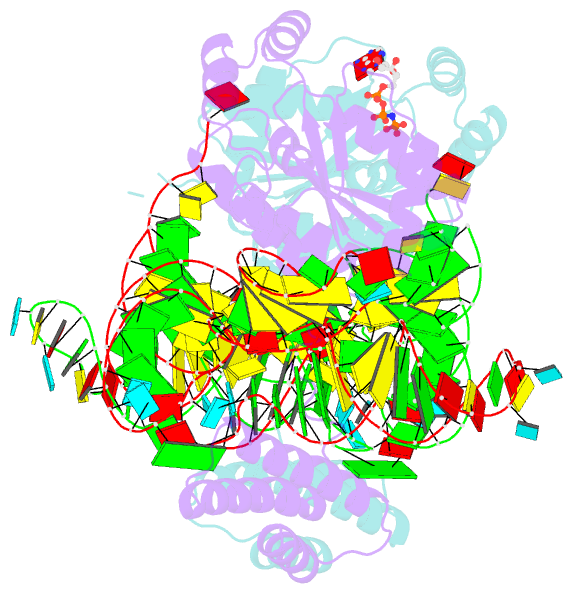
- Crystal structure of o-phosphoseryl-trna kinase
complexed with selenocysteine trna and amppnp (crystal type
1)
- Reference
-
Chiba S, Itoh Y, Sekine S, Yokoyama S (2010): "Structural
Basis for the Major Role of O-Phosphoseryl-tRNA Kinase in
the UGA-Specific Encoding of Selenocysteine."
Mol.Cell, 39, 410-420. doi:
10.1016/j.molcel.2010.07.018.
- Abstract
- The 21(st) amino acid, selenocysteine (Sec), is
assigned to the codon UGA and is biosynthesized on the
selenocysteine-specific tRNA (tRNA(Sec)) with the
corresponding anticodon. In archaea/eukarya, tRNA(Sec) is
ligated with serine by seryl-tRNA synthetase (SerRS), the
seryl moiety is phosphorylated by O-phosphoseryl-tRNA
kinase (PSTK), and the phosphate group is replaced with
selenol by Sep-tRNA:Sec-tRNA synthase. PSTK selectively
phosphorylates seryl-tRNA(Sec), while SerRS serylates both
tRNA(Ser) and tRNA(Sec). In this study, we determined the
crystal structures of the archaeal tRNA(Sec).PSTK complex.
PSTK consists of two independent linker-connected domains,
the N-terminal catalytic domain (NTD) and the C-terminal
domain (CTD). The D-arm.CTD binding occurs independently of
and much more strongly than the acceptor-arm.NTD binding.
PSTK thereby distinguishes the characteristic D arm with
the maximal stem and the minimal loop of tRNA(Sec) from the
canonical D arm of tRNA(Ser), without interacting with the
anticodon. This mechanism is essential for the UGA-specific
encoding of selenocysteine.