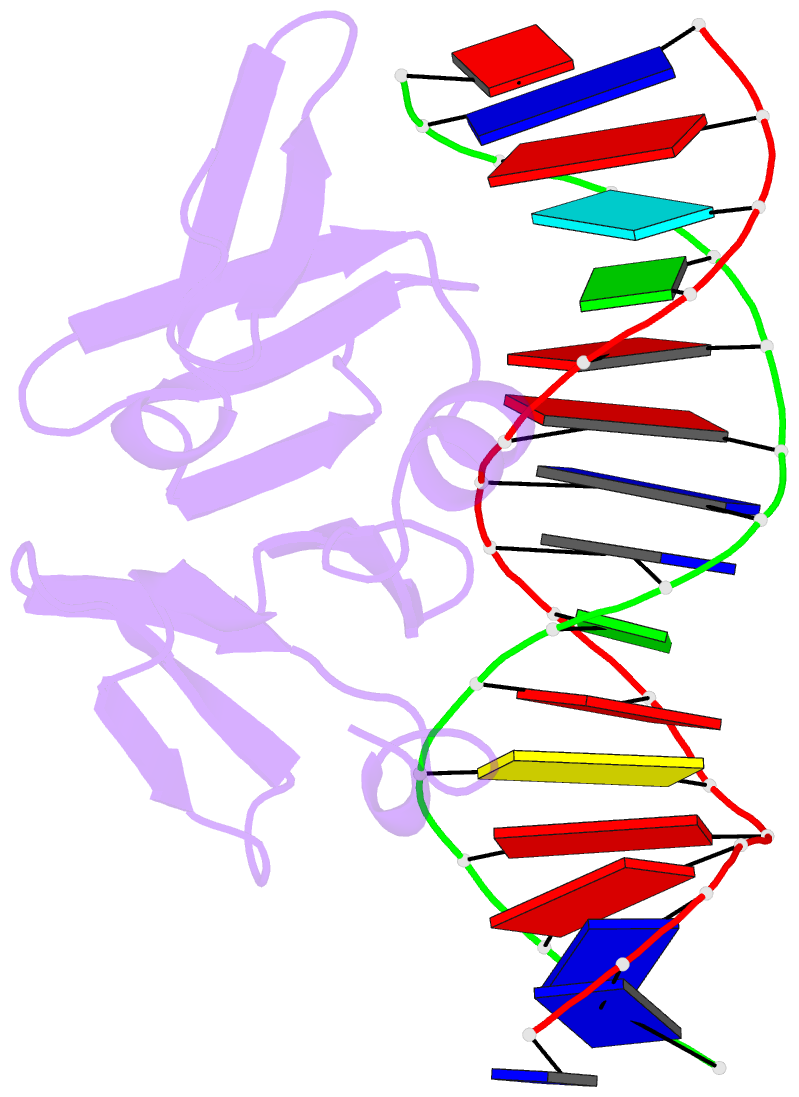
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3bs1; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription regulator
- Method
- X-ray (1.6 Å)
- Summary
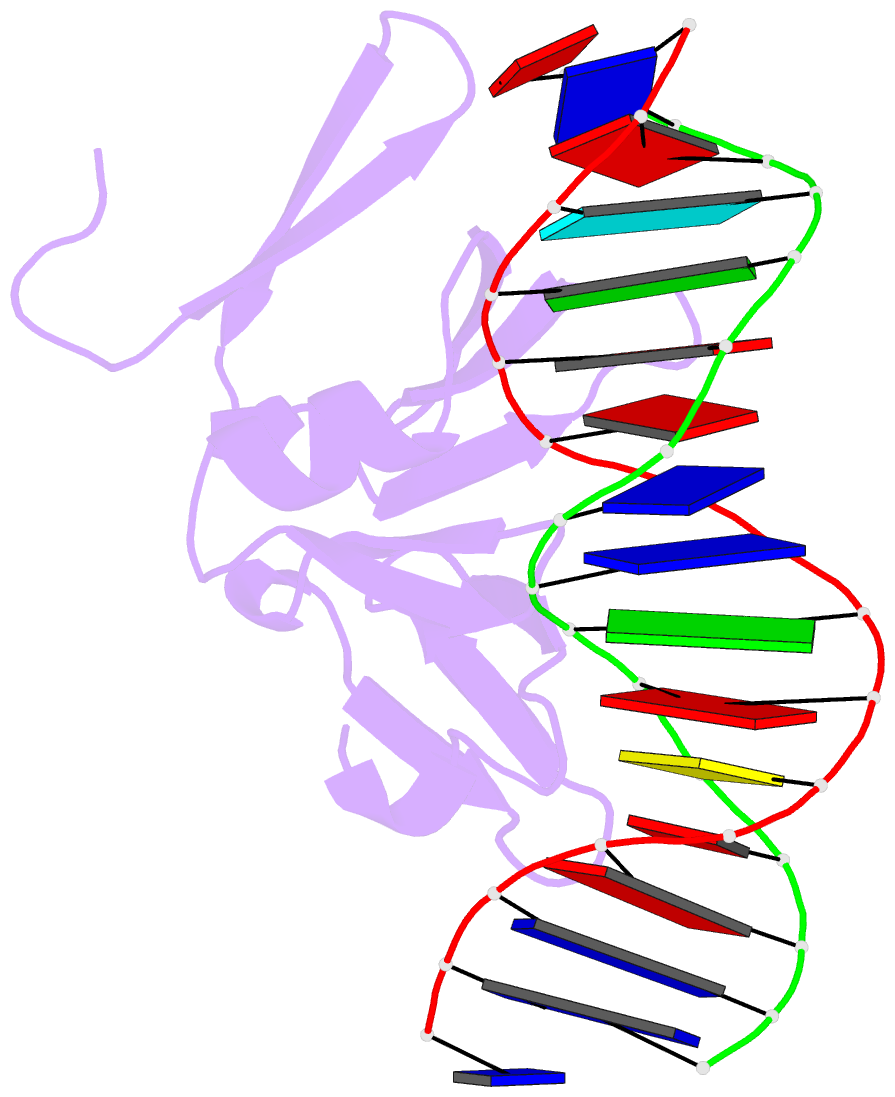
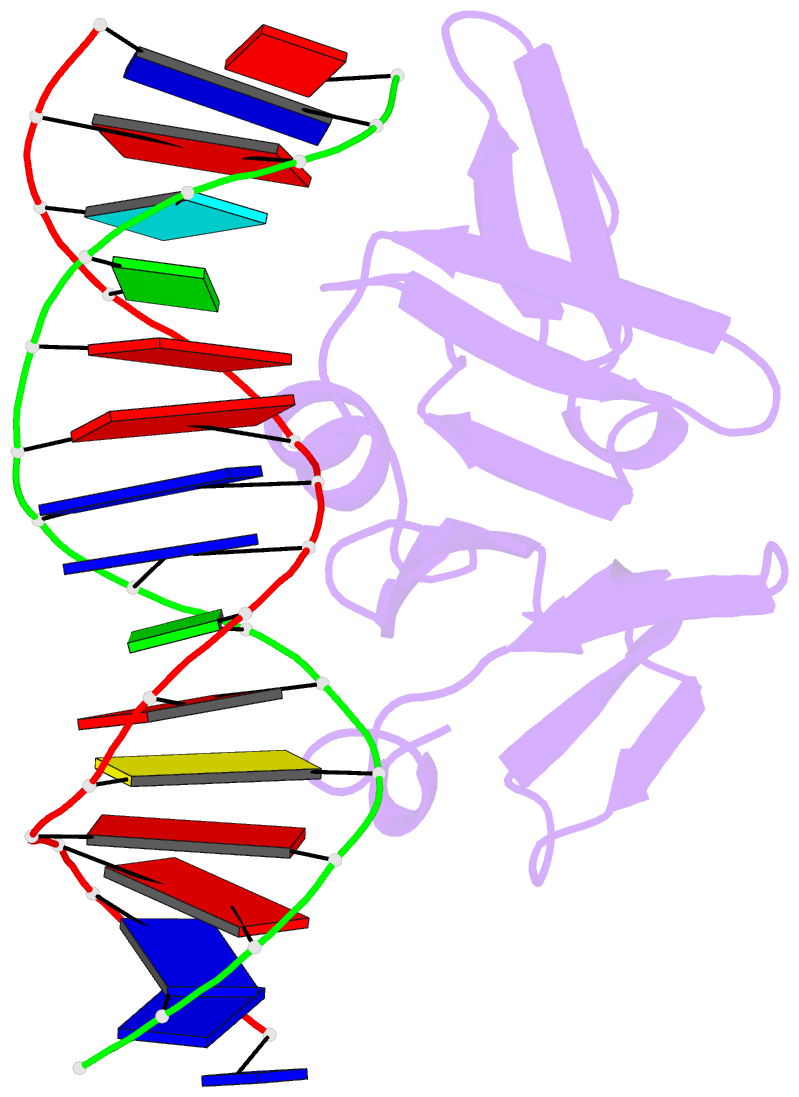
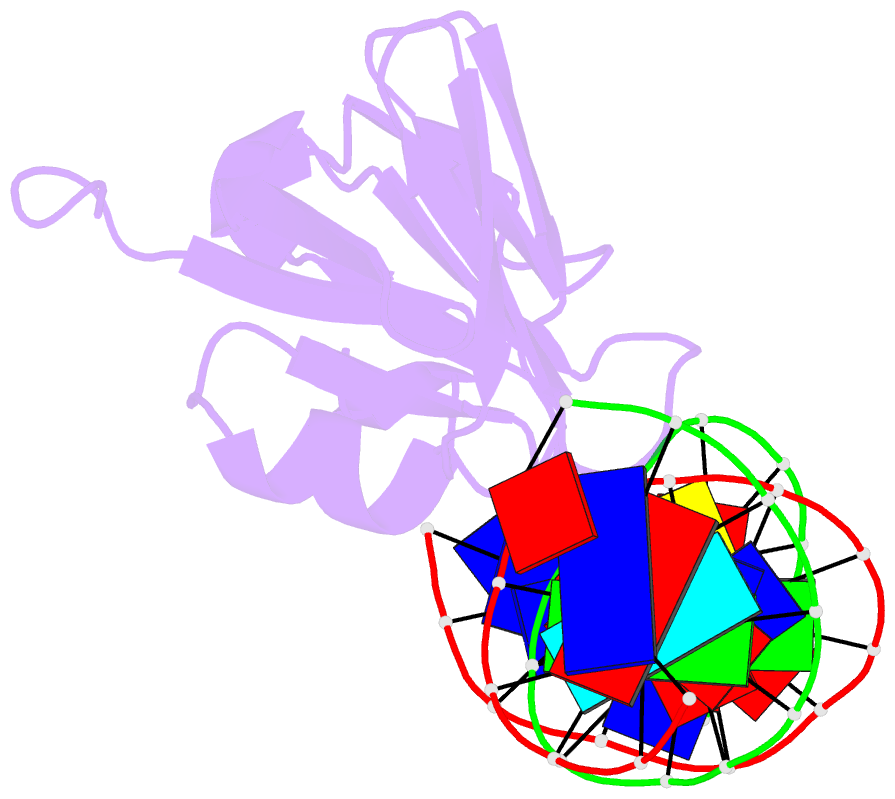
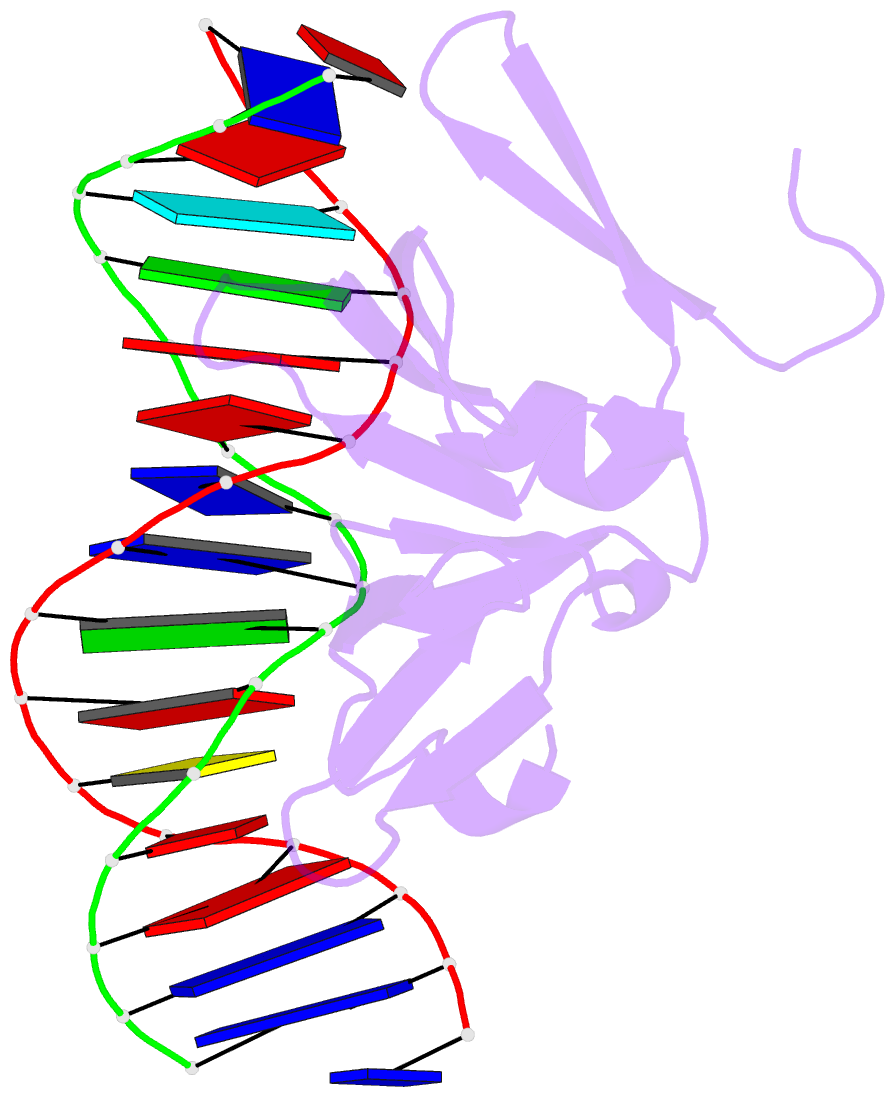
- Structure of the staphylococcus aureus agra lyttr domain bound to DNA reveals a beta fold with a novel mode of binding
- Reference
- Sidote DJ, Barbieri CM, Wu T, Stock AM (2008): "Structure of the Staphylococcus aureus AgrA LytTR Domain Bound to DNA Reveals a Beta Fold with an Unusual Mode of Binding." Structure, 16, 727-735. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2008.02.011.
- Abstract
- The LytTR domain is a DNA-binding motif found within the AlgR/AgrA/LytR family of transcription factors that regulate virulence factor and toxin gene expression in pathogenic bacteria. This previously uncharacterized domain lacks sequence similarity with proteins of known structure. The crystal structure of the DNA-binding domain of Staphylococcus aureus AgrA complexed with a DNA pentadecamer duplex has been determined at 1.6 A resolution. The structure establishes a 10-stranded beta fold for the LytTR domain and reveals its mode of interaction with DNA. Residues within loop regions of AgrA contact two successive major grooves and the intervening minor groove on one face of the oligonucleotide duplex, inducing a substantial bend in the DNA. Loss of DNA binding upon substitution of key interacting residues in AgrA supports the observed binding mode. This mode of protein-DNA interaction provides a potential target for future antimicrobial drug design.