Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3bsx; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.32 Å)
- Summary
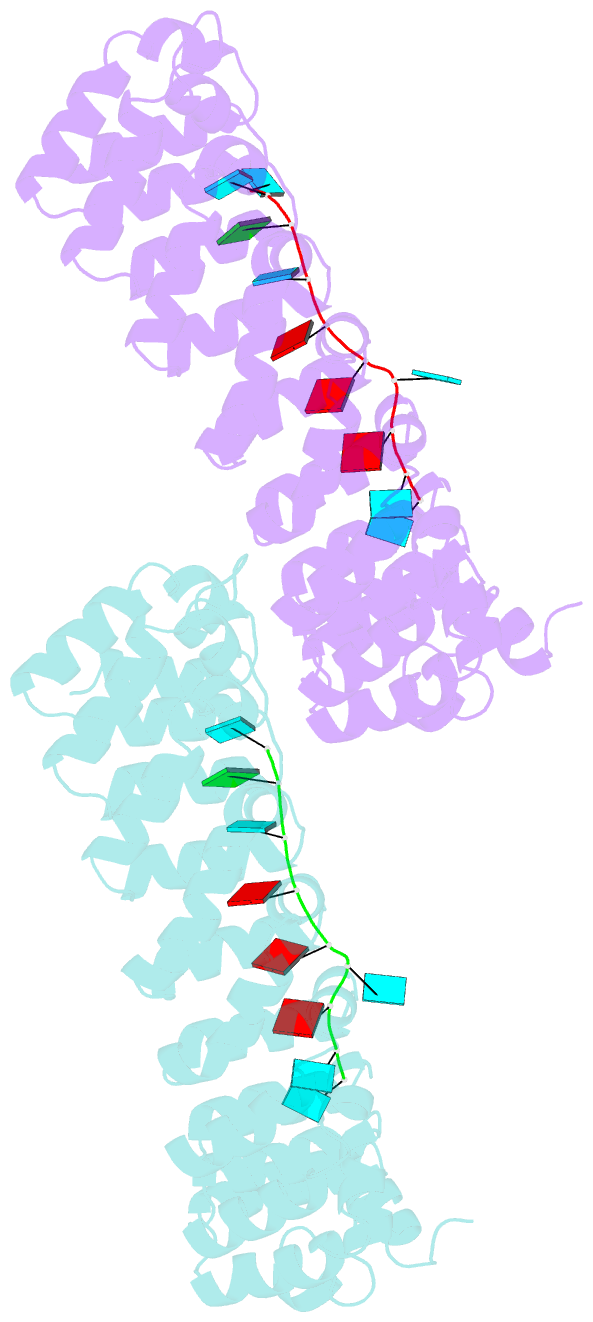
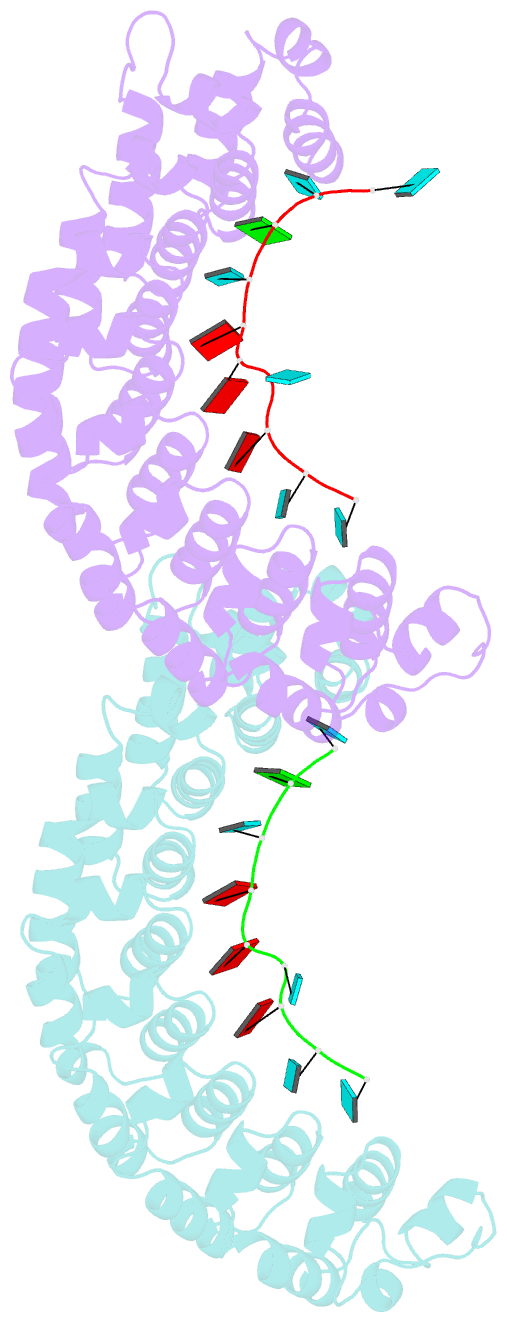
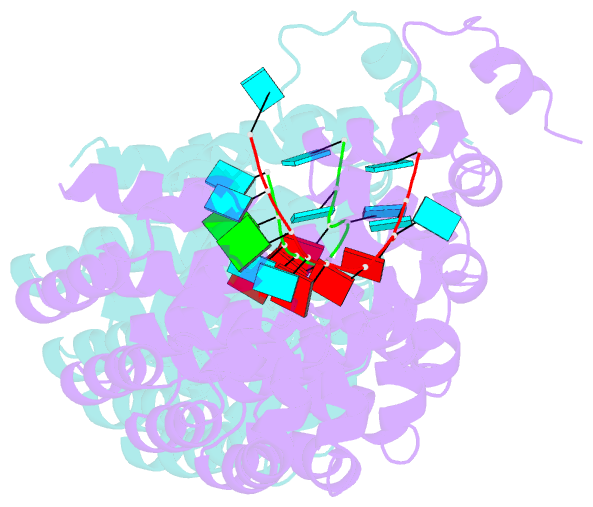
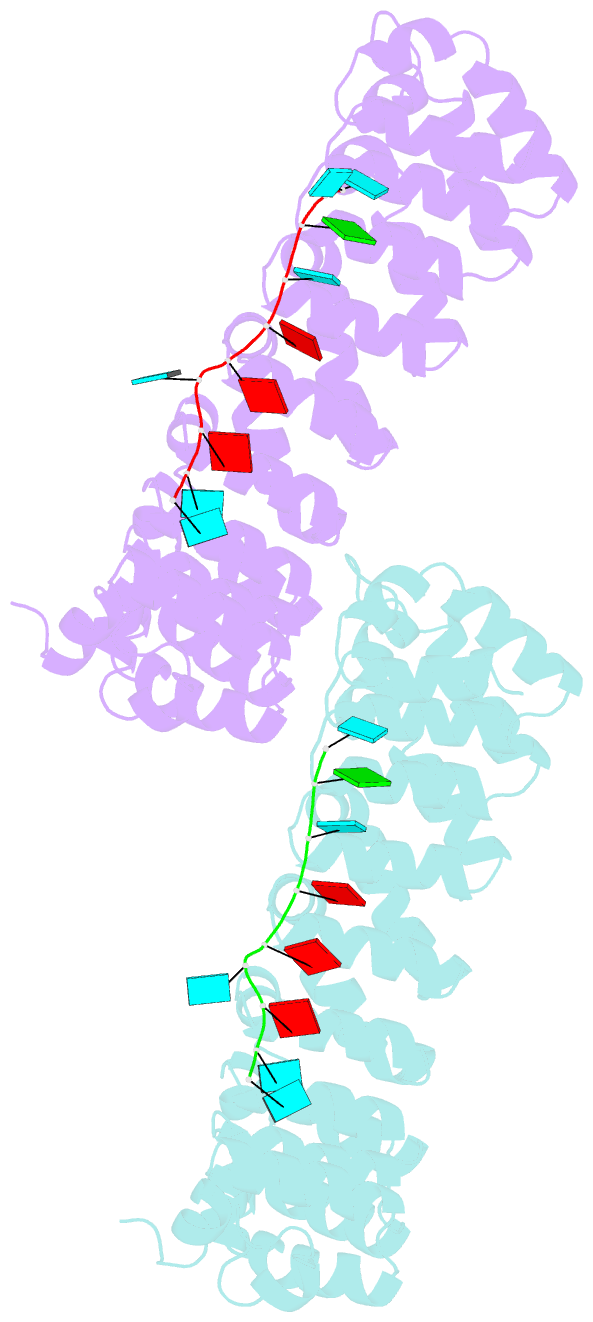
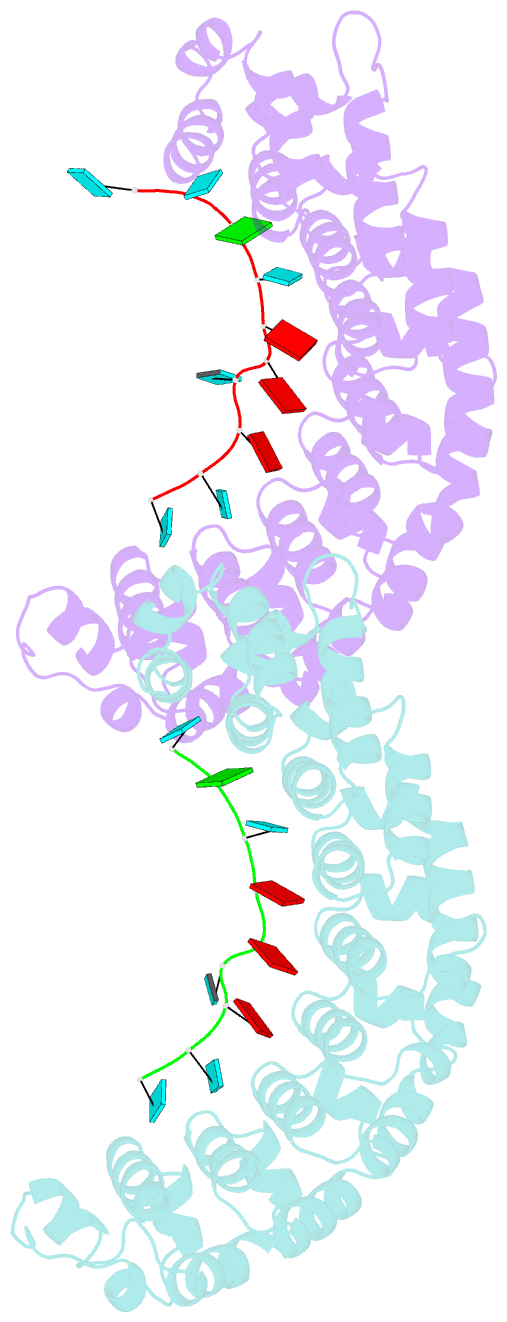
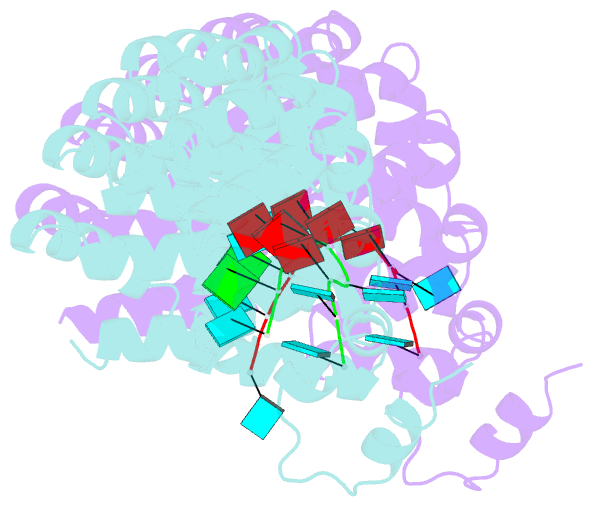
- Crystal structure of human pumilio 1 in complex with puf5 RNA
- Reference
- Gupta YK, Nair DT, Wharton RP, Aggarwal AK (2008): "Structures of human Pumilio with noncognate RNAs reveal molecular mechanisms for binding promiscuity." Structure, 16, 549-557. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2008.01.006.
- Abstract
- Pumilio is a founder member of the evolutionarily conserved Puf family of RNA-binding proteins that control a number of physiological processes in eukaryotes. A structure of human Pumilio (hPum) Puf domain bound to a Drosophila regulatory sequence showed that each Puf repeat recognizes a single nucleotide. Puf domains in general bind promiscuously to a large set of degenerate sequences, but the structural basis for this promiscuity has been unclear. Here, we describe the structures of hPum Puf domain complexed to two noncognate RNAs, CycB(reverse) and Puf5. In each complex, one of the nucleotides is ejected from the binding surface, in effect, acting as a "spacer." The complexes also reveal the plasticity of several Puf repeats, which recognize noncanonical nucleotides. Together, these complexes provide a molecular basis for recognition of degenerate binding sites, which significantly increases the number of mRNAs targeted for regulation by Puf proteins in vivo.