Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3bt7; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.43 Å)
- Summary
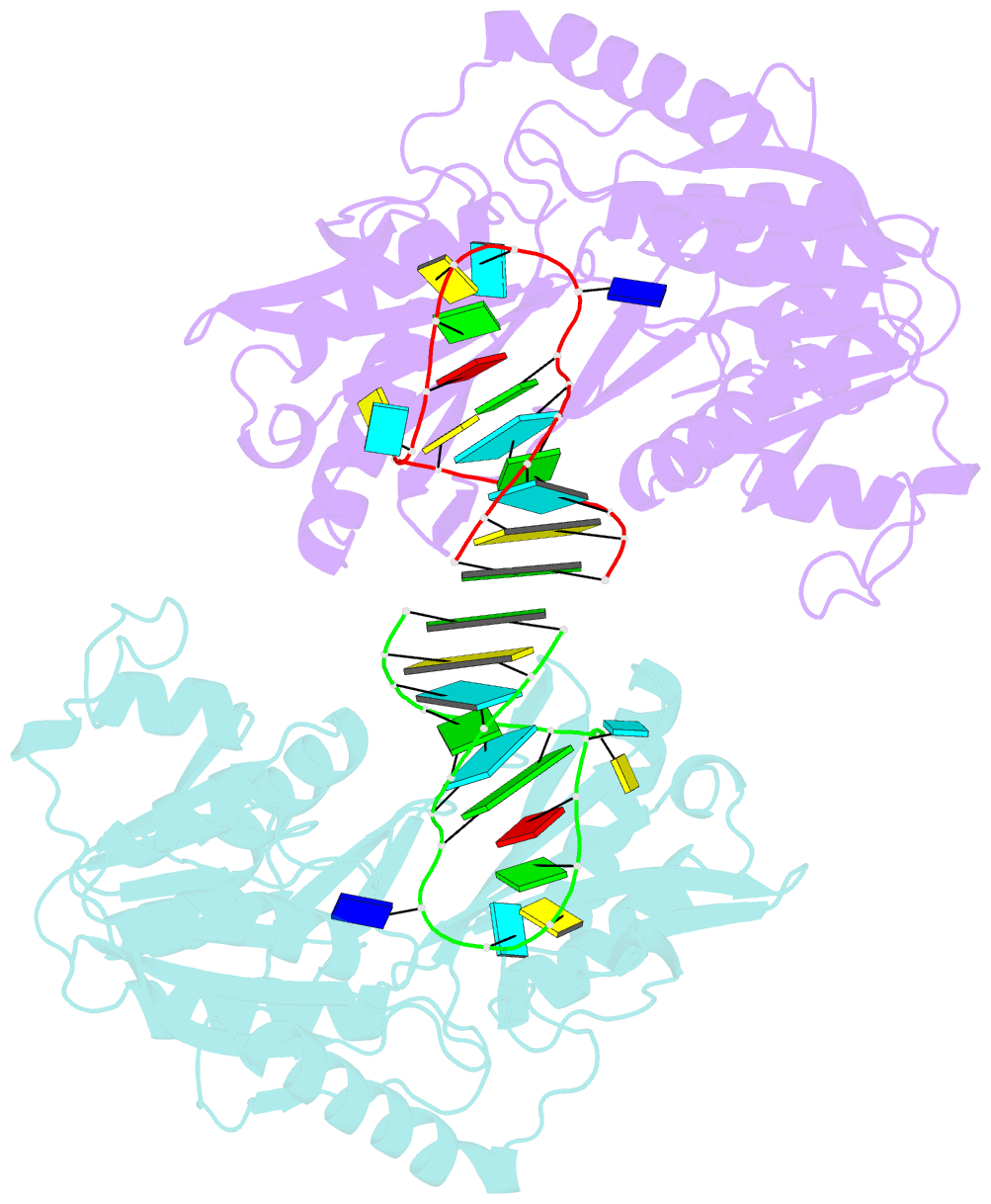
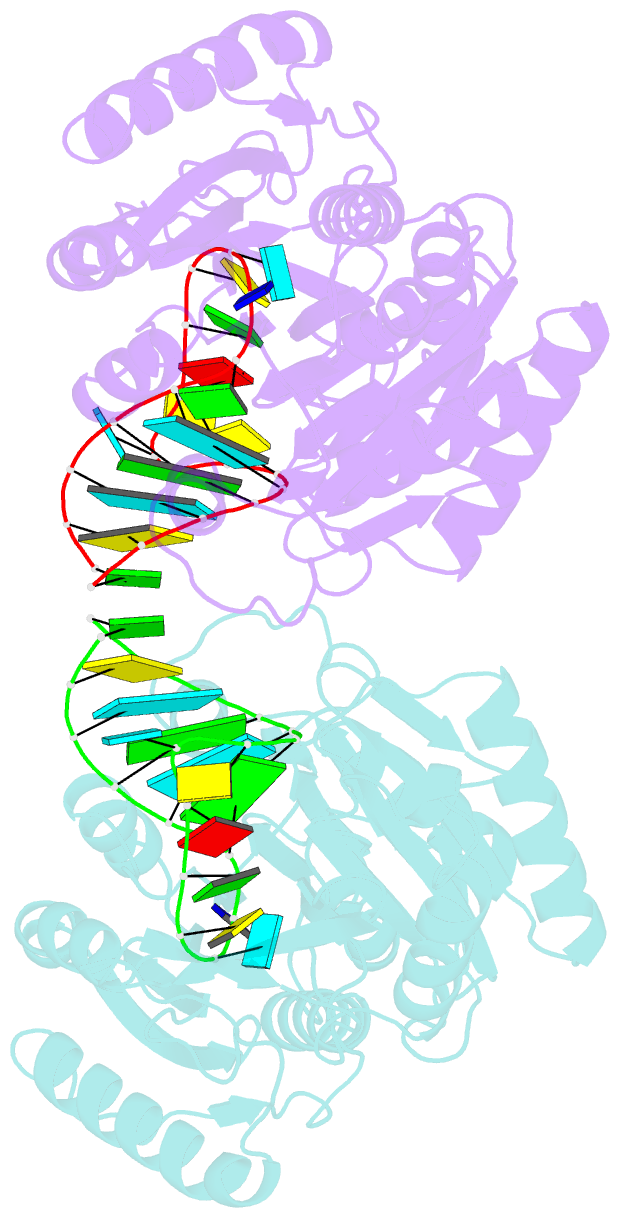
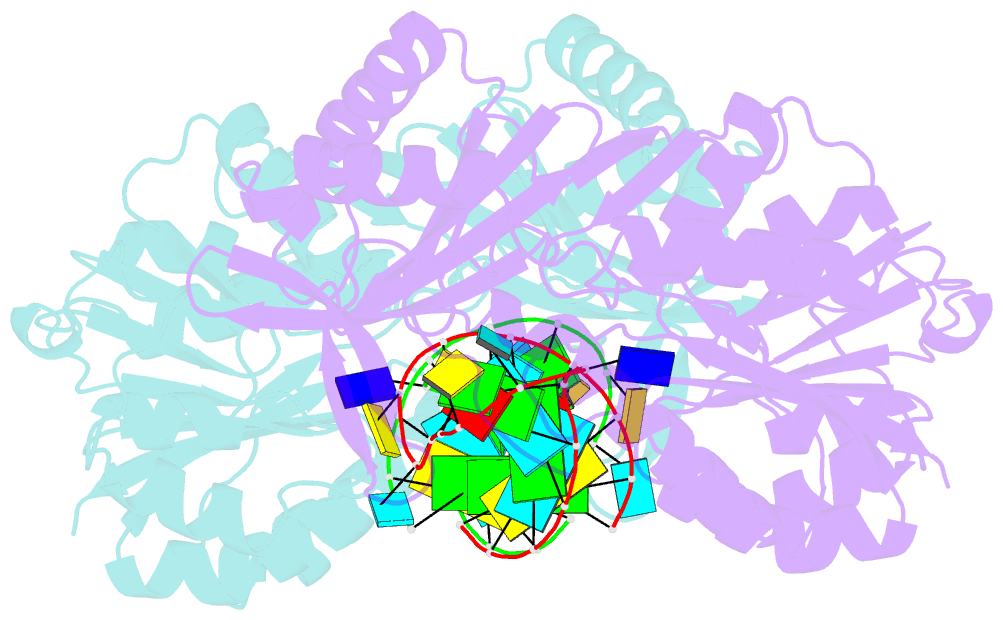
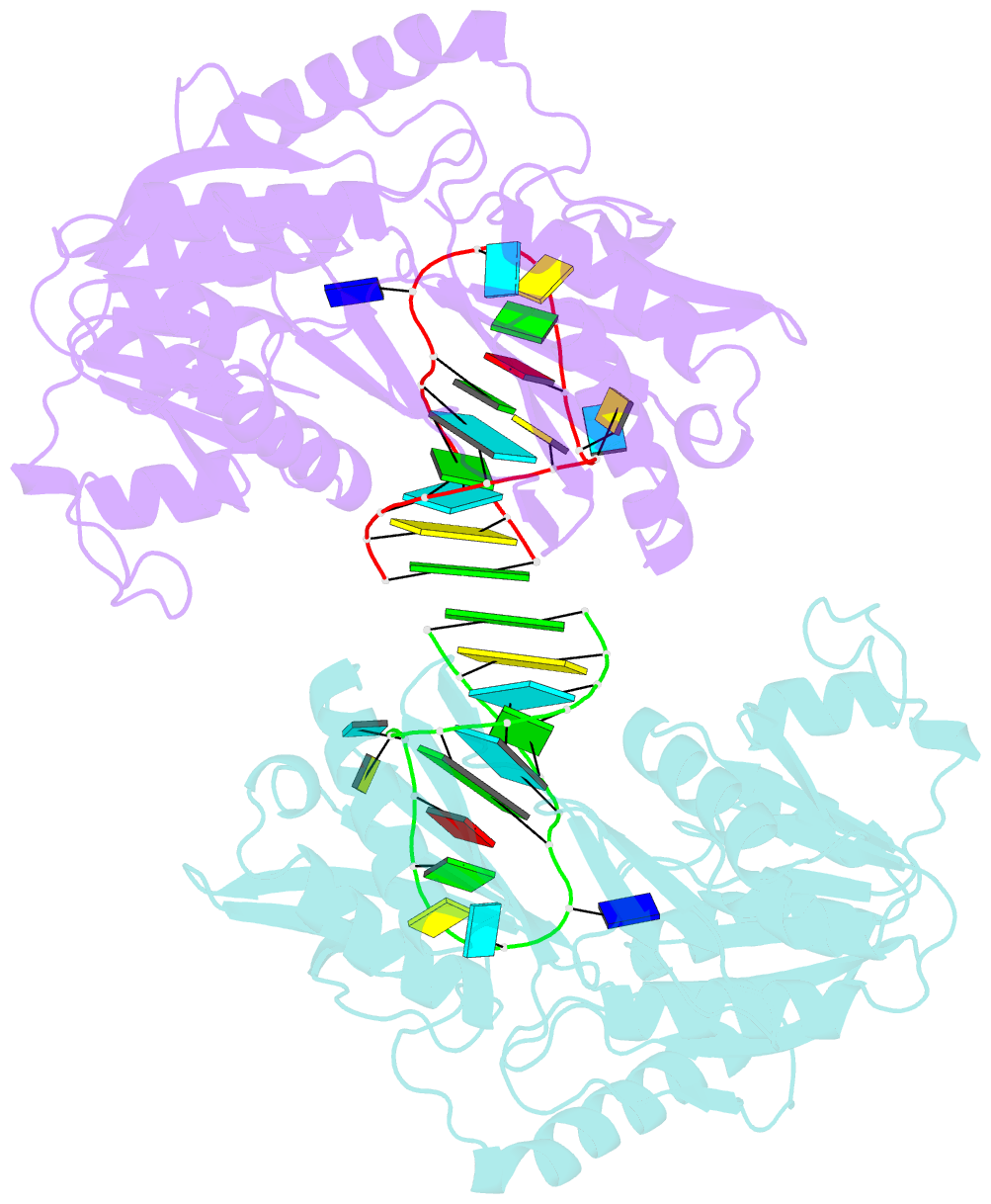
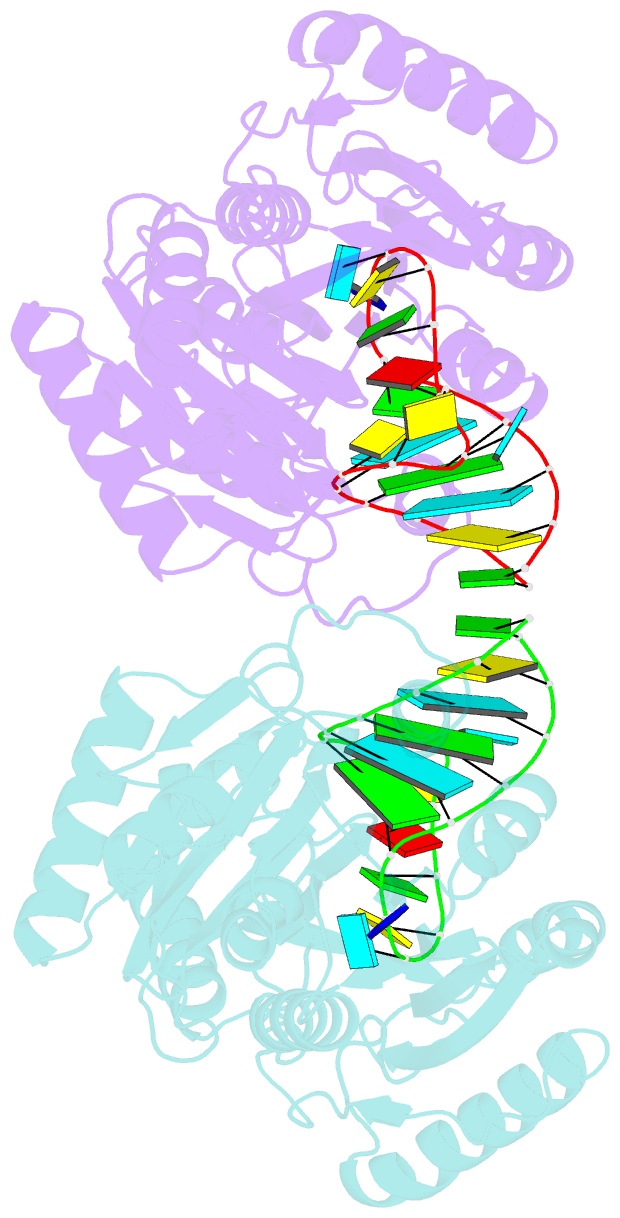
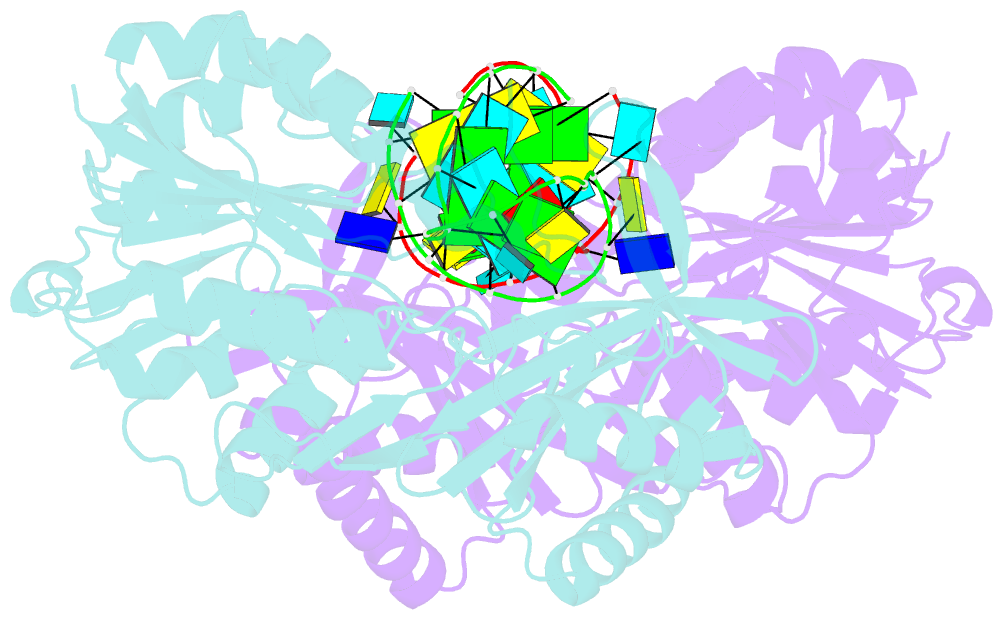
- Structure of e. coli 5-methyluridine methyltransferase trma in complex with 19 nucleotide t-arm analogue
- Reference
- Alian A, Lee TT, Griner SL, Stroud RM, Finer-Moore J (2008): "Structure of a TrmA-RNA complex: A consensus RNA fold contributes to substrate selectivity and catalysis in m5U methyltransferases." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.Usa, 105, 6876-6881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802247105.
- Abstract
- TrmA catalyzes S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet)-dependent methylation of U54 in most tRNAs. We solved the structure of the Escherichia coli 5-methyluridine (m(5)U) 54 tRNA methyltransferase (MTase) TrmA in a covalent complex with a 19-nt T arm analog to 2.4-A resolution. Mutation of the TrmA catalytic base Glu-358 to Gln arrested catalysis and allowed isolation of the covalent TrmA-RNA complex for crystallization. The protein-RNA interface includes 6 nt of the T loop and two proximal base pairs of the stem. U54 is flipped out of the loop into the active site. A58 occupies the space of the everted U54 and is part of a collinear base stack G53-A58-G57-C56-U55. The RNA fold is different from T loop conformations in unbound tRNA or T arm analogs, but nearly identical to the fold of the RNA loop bound at the active site of the m(5)U MTase RumA. In both enzymes, this consensus fold presents the target U and the following two bases to a conserved binding groove on the protein. Outside of this fold, the RumA and TrmA substrates have completely different structures and protein interfaces. Loop residues other than the target U54 make more than half of their hydrogen bonds to the protein via sugar-phosphate moieties, accounting, in part, for the broad consensus sequence for TrmA substrates.