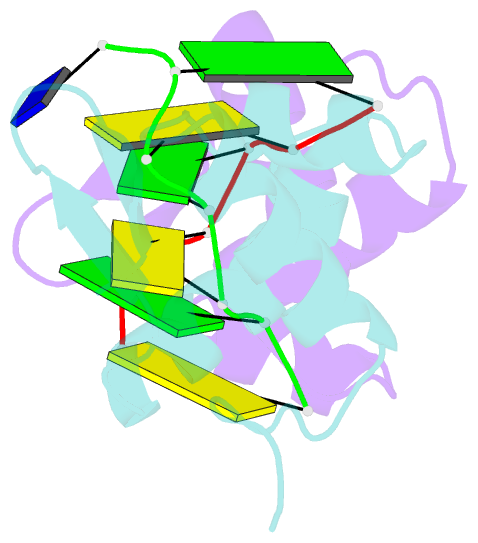
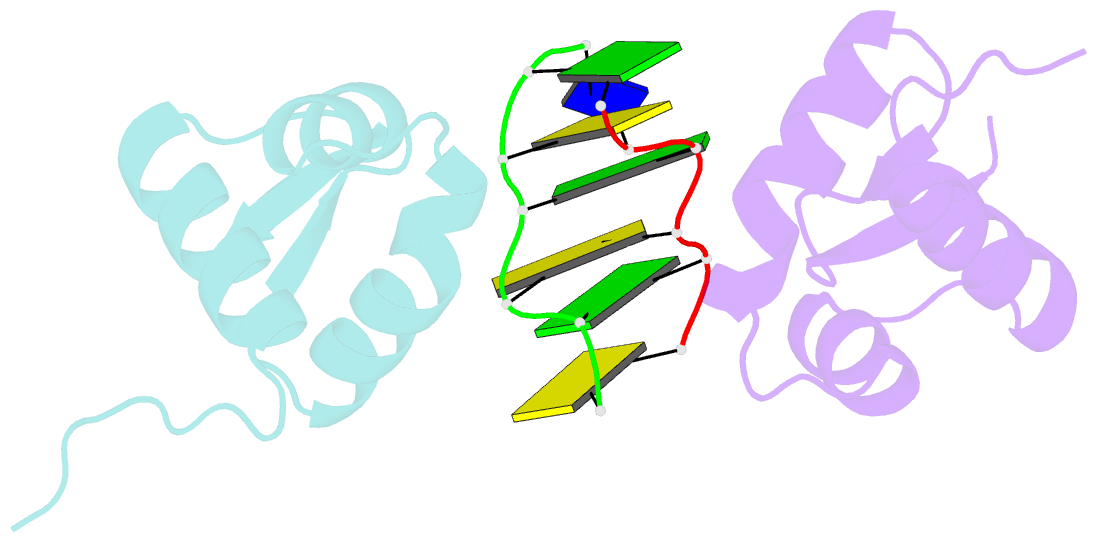
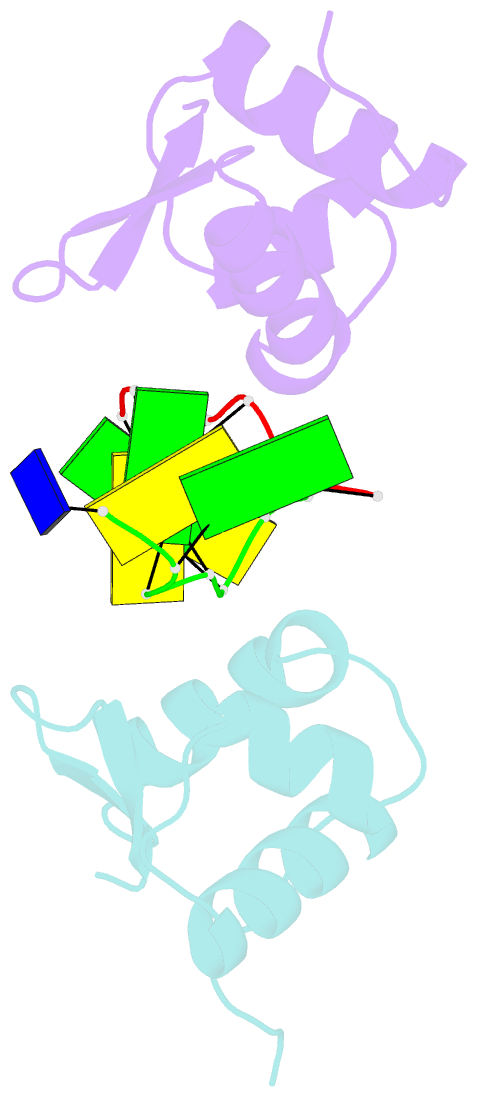
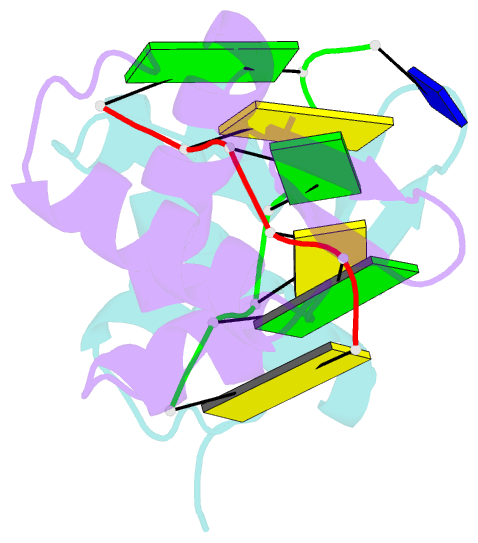
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3eyi; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.45 Å)
- Summary
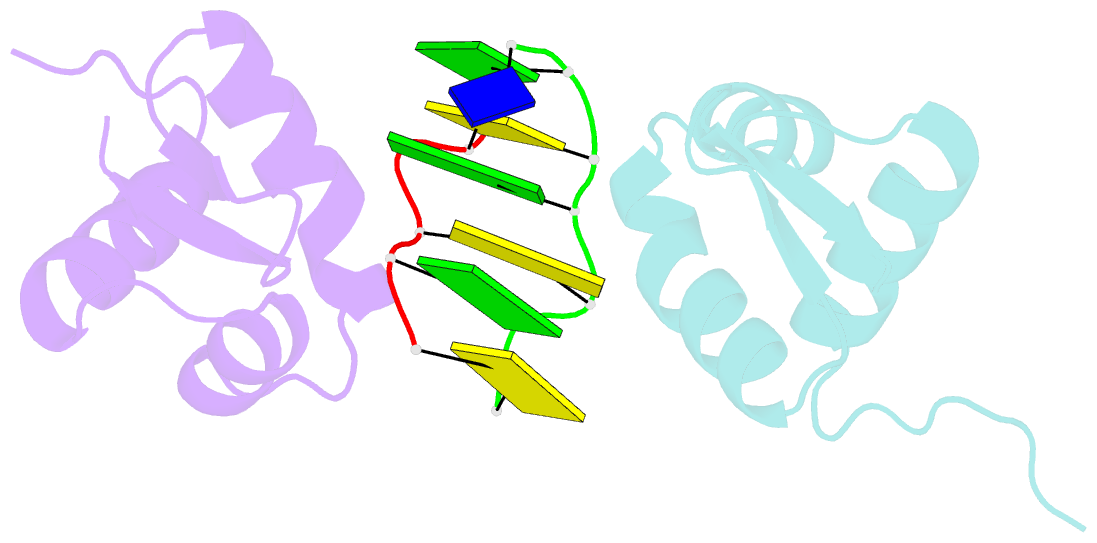
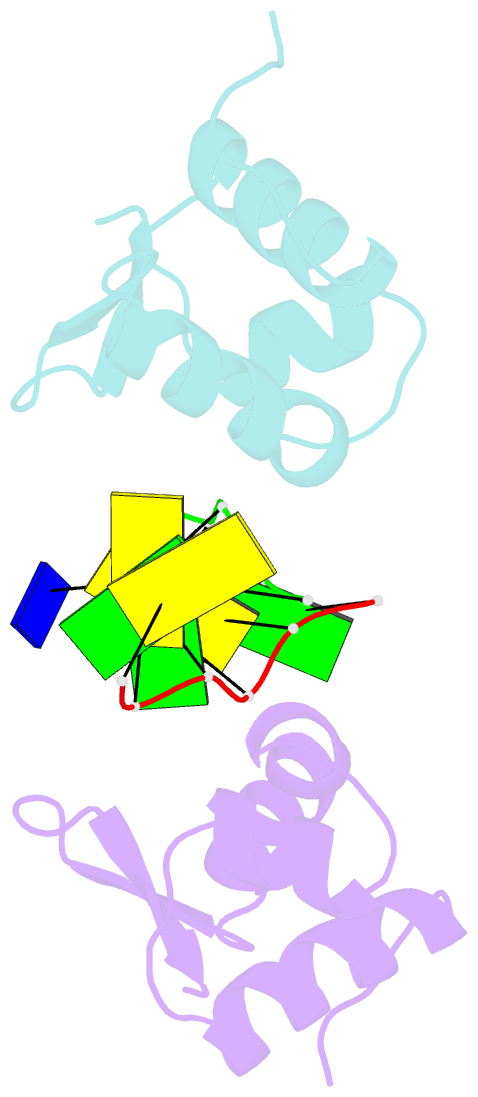
- The crystal structure of the second z-DNA binding domain of human dai (zbp1) in complex with z-DNA
- Reference
- Ha SC, Kim D, Hwang HY, Rich A, Kim YG, Kim KK (2008): "The crystal structure of the second Z-DNA binding domain of human DAI (ZBP1) in complex with Z-DNA reveals an unusual binding mode to Z-DNA." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 105, 20671-20676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810463106.
- Abstract
- Mammalian DAI (DNA-dependent activator of IFN-regulatory factors), an activator of the innate immune response, senses cytosolic DNA by using 2 N-terminal Z-DNA binding domains (ZBDs) and a third putative DNA binding domain located next to the second ZBD. Compared with other previously known ZBDs, the second ZBD of human DAI (hZbeta(DAI)) shows significant variation in the sequence of the residues that are essential for DNA binding. In this article, the crystal structure of the hZbeta(DAI)/Z-DNA complex reveals that hZbeta(DAI) has a similar fold to that of other ZBDs, but adopts an unusual binding mode for recognition of Z-DNA. A residue in the first beta-strand rather than residues in the beta-loop contributes to DNA binding, and part of the (alpha3) recognition helix adopts a 3(10) helix conformation. The role of each residue that makes contact with DNA was confirmed by mutational analysis. The 2 ZBDs of DAI can together bind to DNA and both are necessary for full B-to-Z conversion. It is possible that binding 2 DAIs to 1 dsDNA brings about dimerization of DAI that might facilitate DNA-mediated innate immune activation.