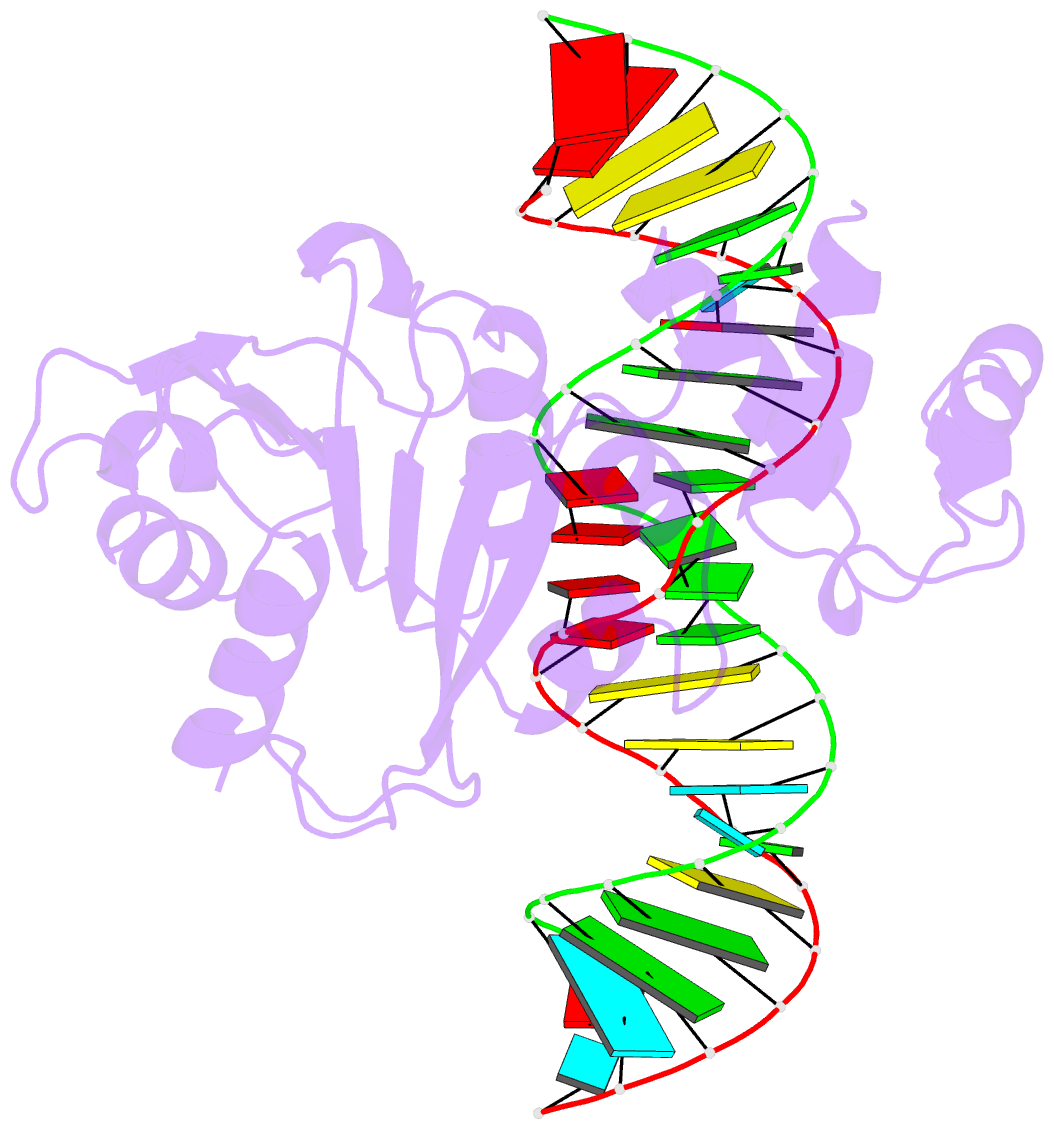
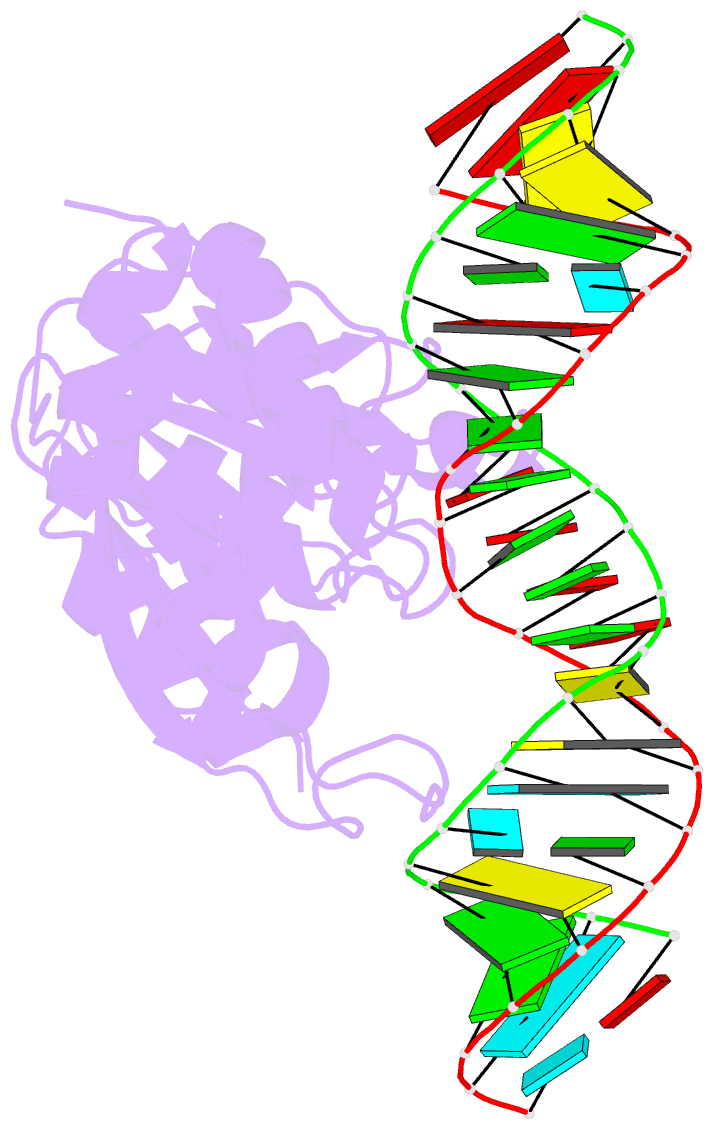
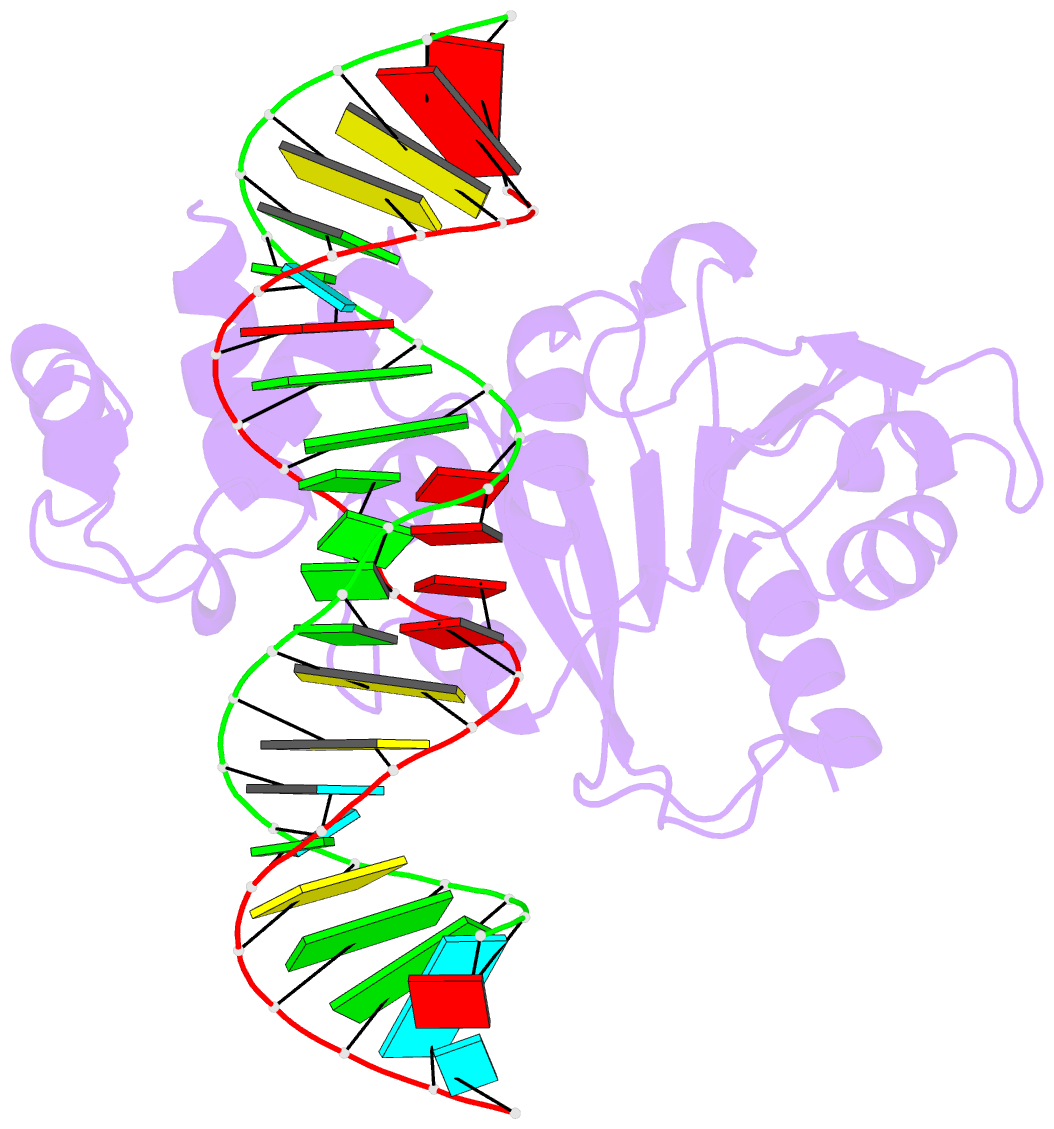
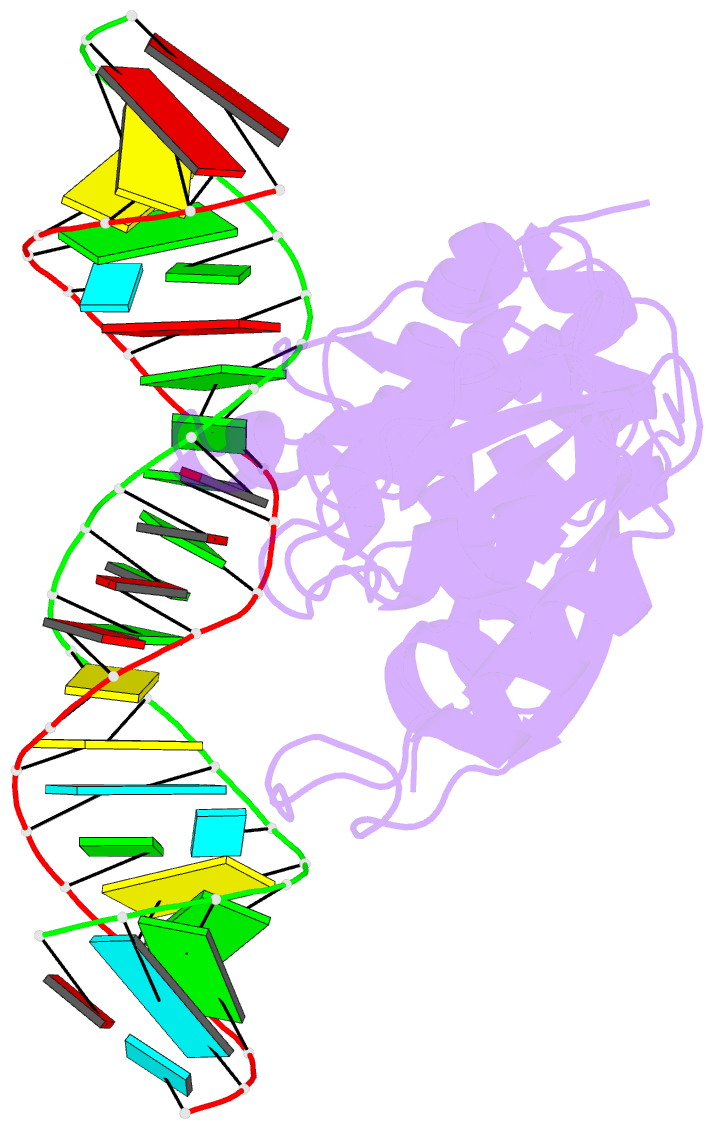
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3fte; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.0 Å)
- Summary
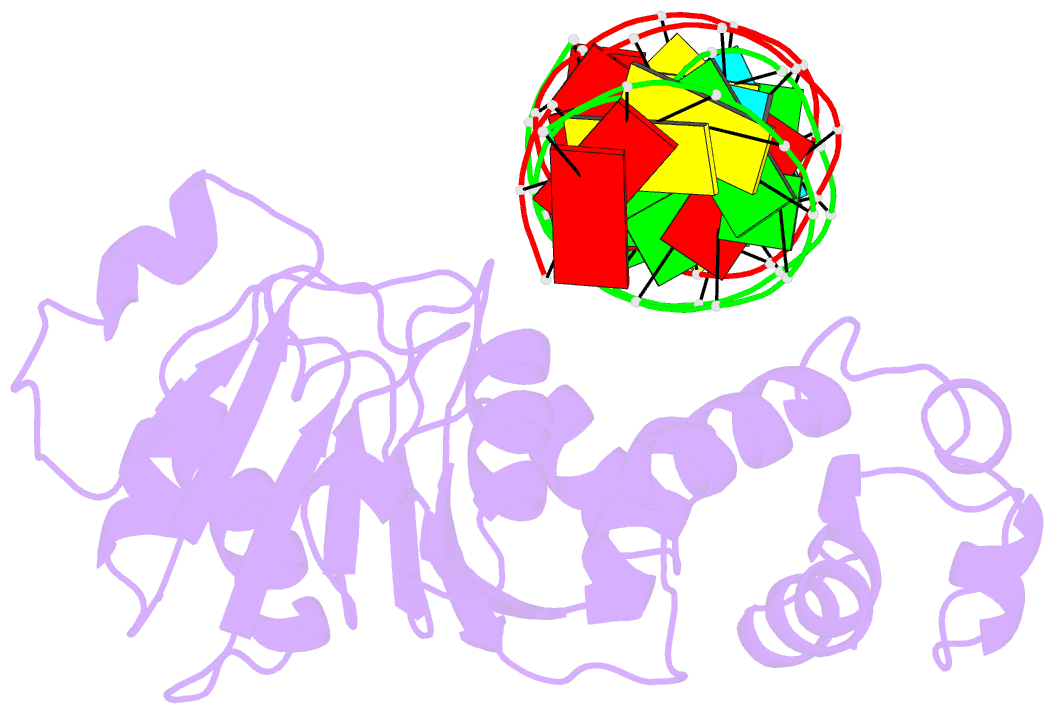
- Crystal structure of a. aeolicus ksga in complex with RNA
- Reference
- Tu C, Tropea JE, Austin BP, Court DL, Waugh DS, Ji X (2009): "Structural Basis for Binding of RNA and Cofactor by a KsgA Methyltransferase." Structure, 17, 374-385. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2009.01.010.
- Abstract
- Among methyltransferases, KsgA and the reaction it catalyzes are conserved throughout evolution. However, the specifics of substrate recognition by the enzyme remain unknown. Here we report structures of Aquifex aeolicus KsgA, in its ligand-free form, in complex with RNA, and in complex with both RNA and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH, reaction product of cofactor S-adenosylmethionine), revealing critical structural information on KsgA-RNA and KsgA-SAH interactions. Moreover, the structures show how conformational changes that occur upon RNA binding create the cofactor-binding site. There are nine conserved functional motifs (motifs I-VIII and X) in KsgA. Prior to RNA binding, motifs I and VIII are flexible, each exhibiting two distinct conformations. Upon RNA binding, the two motifs become stabilized in one of these conformations, which is compatible with the binding of SAH. Motif X, which is also stabilized upon RNA binding, is directly involved in the binding of SAH.