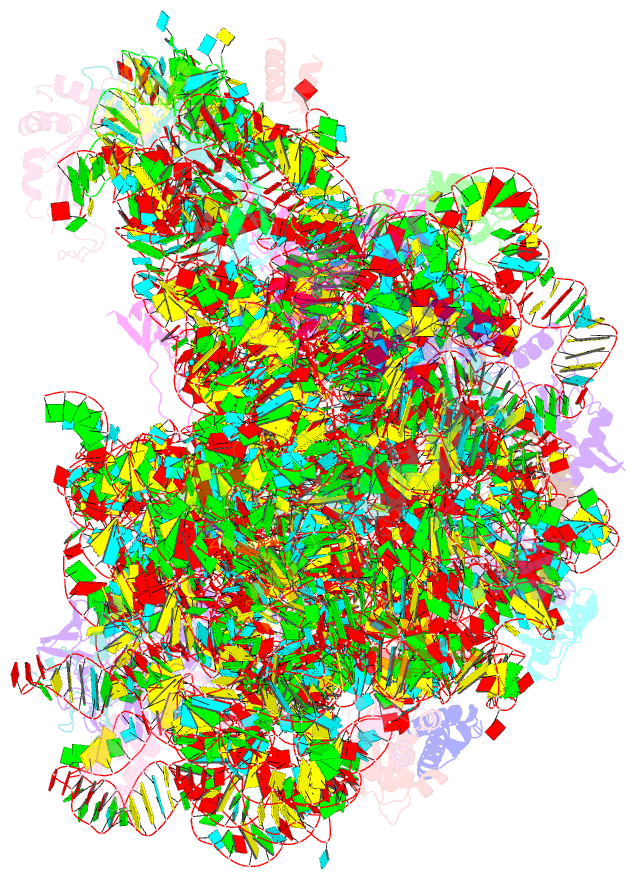
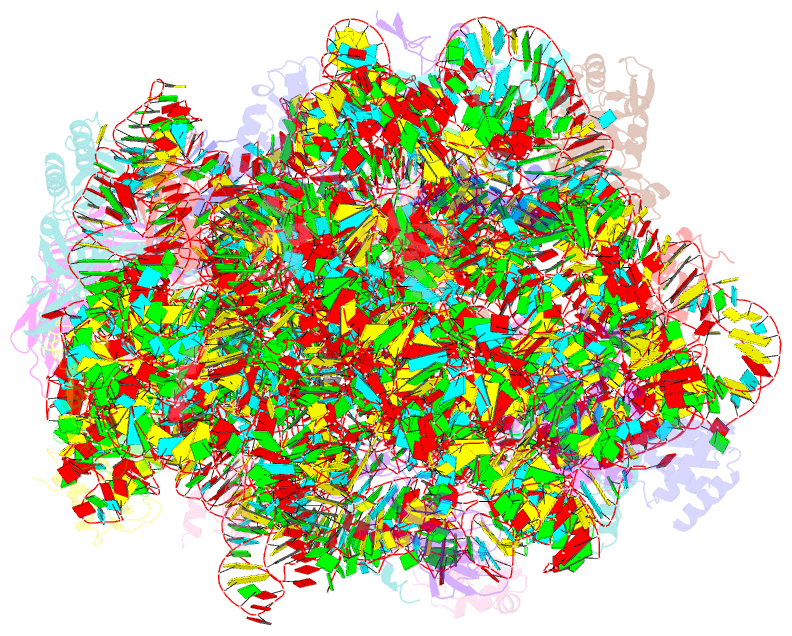
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
3g71;
DSSR-derived features in text and
JSON formats; DNAproDB
- Class
- ribosome
- Method
- X-ray (2.85 Å)
- Summary
- Co-crystal structure of bruceantin bound to the large
ribosomal subunit
- Reference
-
Gurel G, Blaha G, Moore PB, Steitz TA (2009): "U2504
determines the species specificity of the A-site cleft
antibiotics: the structures of tiamulin,
homoharringtonine, and bruceantin bound to the
ribosome." J.Mol.Biol.,
389, 146-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.005.
- Abstract
- Structures have been obtained for the complexes that
tiamulin, homoharringtonine, and bruceantin form with the
large ribosomal subunit of Haloarcula marismortui at
resolutions ranging from 2.65 to 3.2 A. They show that all
these inhibitors block protein synthesis by competing with
the amino acid side chains of incoming aminoacyl-tRNAs for
binding in the A-site cleft in the peptidyl-transferase
center, which is universally conserved. In addition, these
structures support the hypothesis that the species
specificity exhibited by the A-site cleft inhibitors is
determined by the interactions they make, or fail to make,
with a single nucleotide, U2504 (Escherichia coli). In the
ribosome, the position of U2504 is controlled by its
interactions with neighboring nucleotides, whose identities
vary among kingdoms.