Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3gfi; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.1 Å)
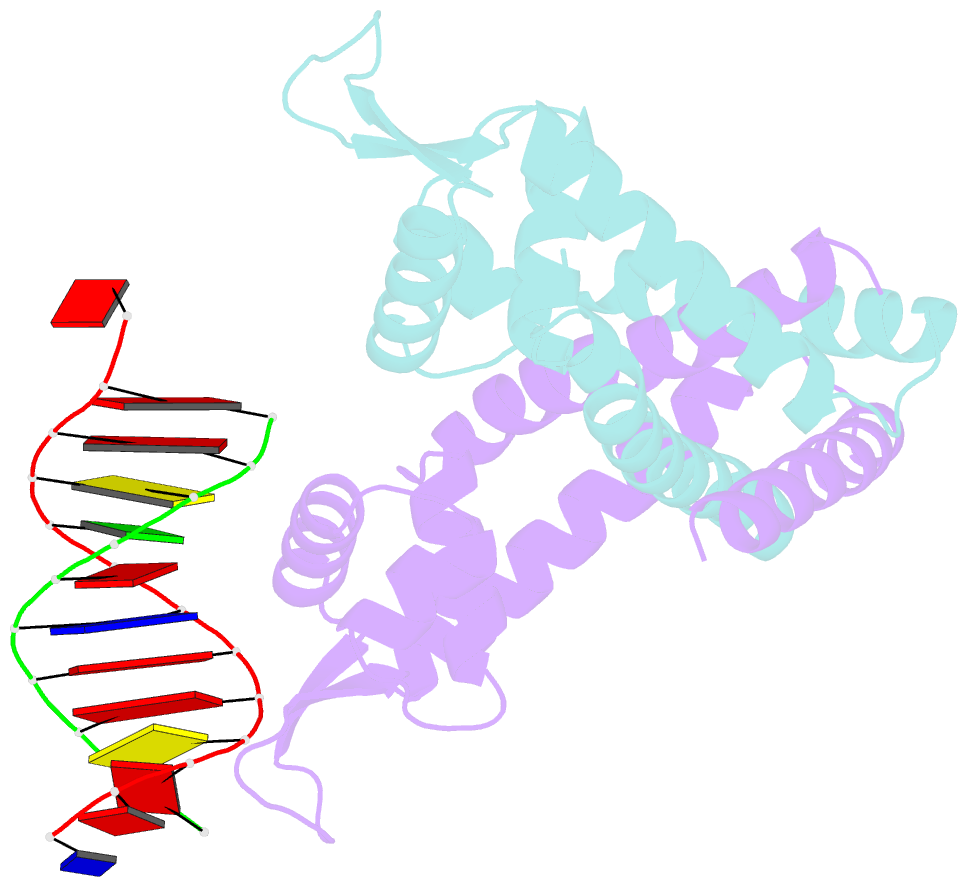
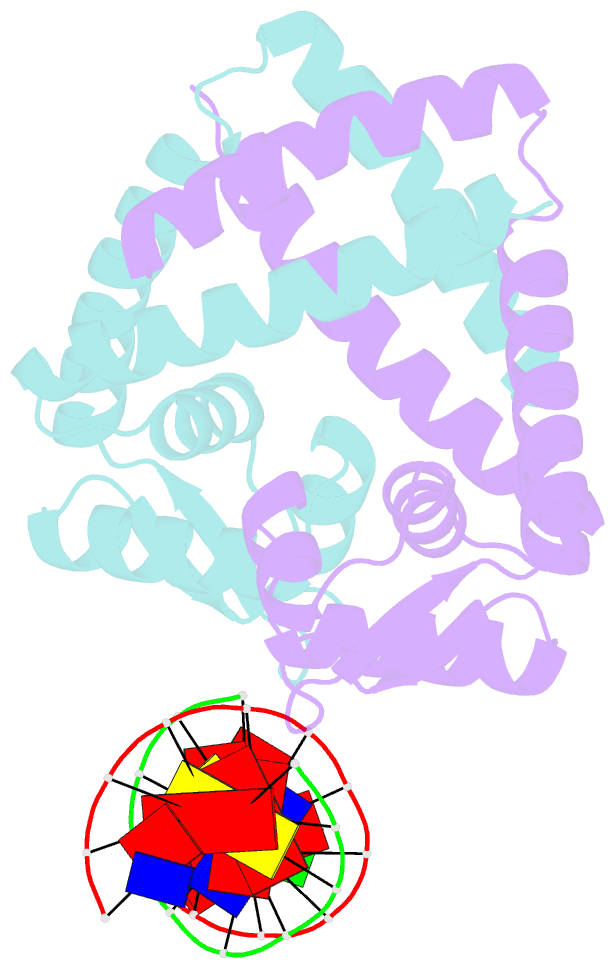
- Summary
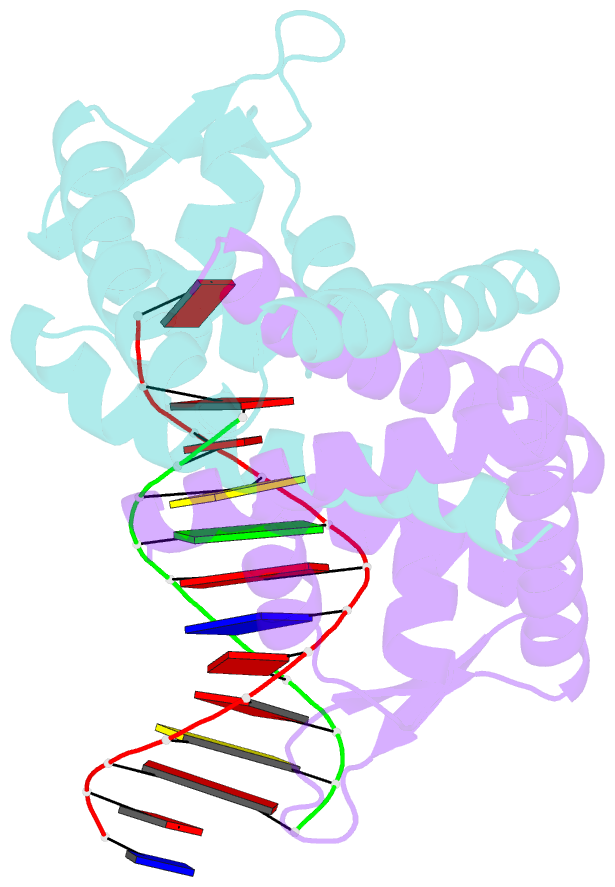
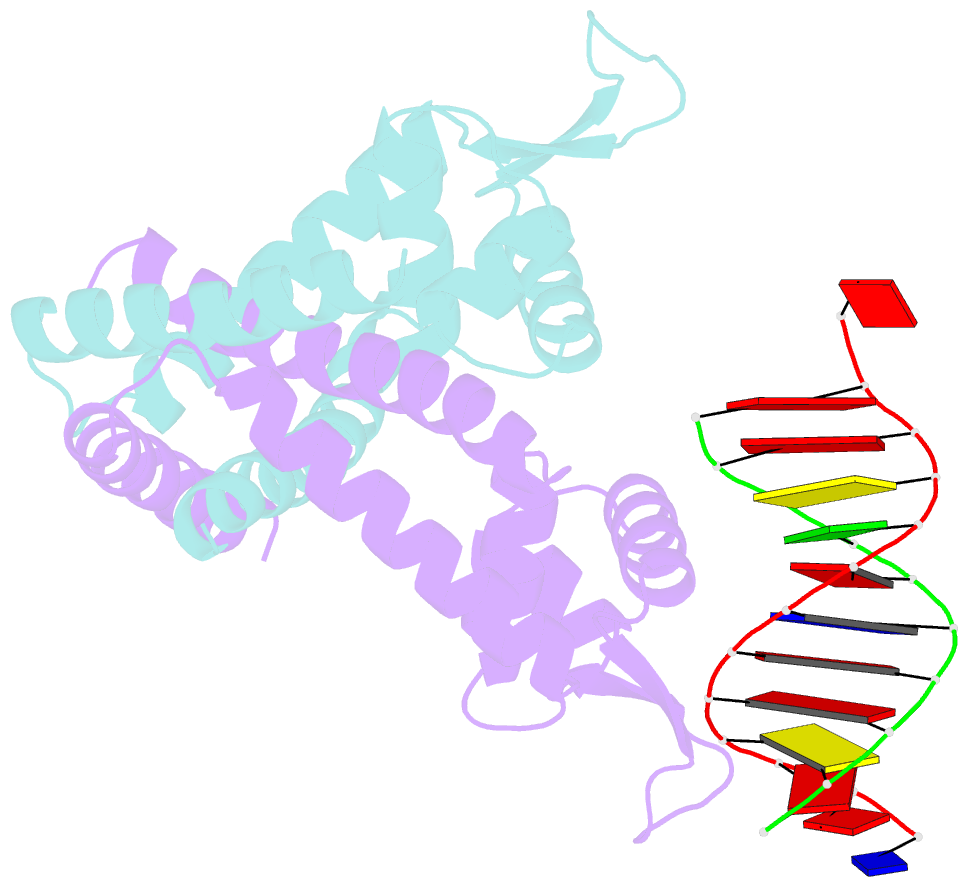
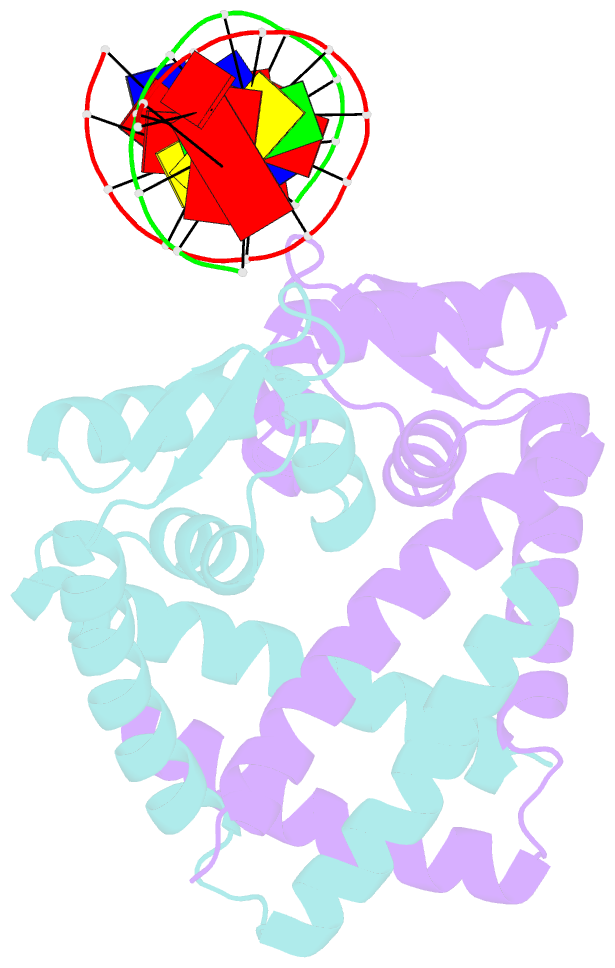
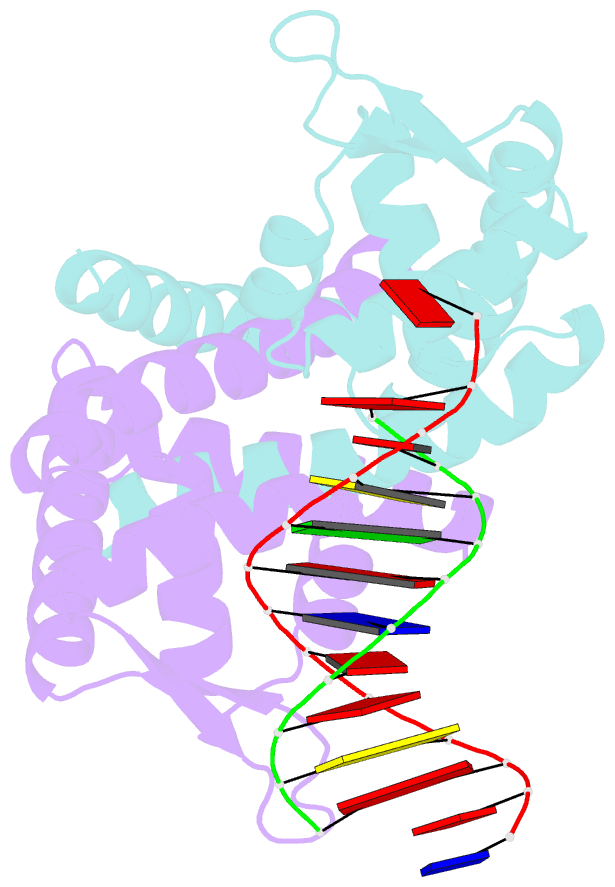
- Crystal structure of st1710 complexed with its promoter DNA
- Reference
- Kumarevel T, Tanaka T, Umehara T, Yokoyama S (2009): "ST1710-DNA complex crystal structure reveals the DNA binding mechanism of the MarR family of regulators." Nucleic Acids Res., 37, 4723-4735. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp496.
- Abstract
- ST1710, a member of the multiple antibiotic resistance regulator (MarR) family of regulatory proteins in bacteria and archaea, plays important roles in development of antibiotic resistance, a global health problem. Here, we present the crystal structure of ST1710 from Sulfolobus tokodaii strain 7 complexed with salicylate, a well-known inhibitor of MarR proteins and the ST1710 complex with its promoter DNA, refined to 1.8 and 2.10 A resolutions, respectively. The ST1710-DNA complex shares the topology of apo-ST1710 and MarR proteins, with each subunit containing a winged helix-turn-helix (wHtH) DNA binding motif. Significantly large conformational changes occurred upon DNA binding and in each of the dimeric monomers in the asymmetric unit of the ST1710-DNA complex. Conserved wHtH loop residues interacting with the bound DNA and mutagenic analysis indicated that R89, R90 and K91 were important for DNA recognition. Significantly, the bound DNA exhibited a new binding mechanism.