Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3h0d; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.4 Å)
- Summary
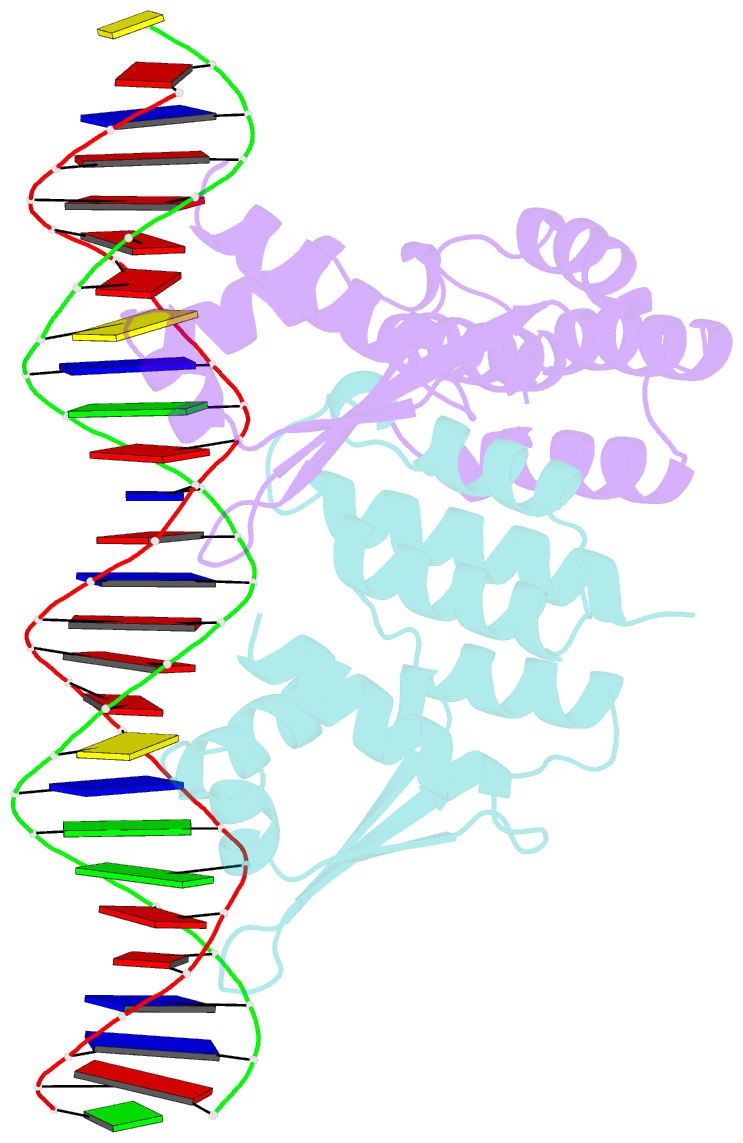
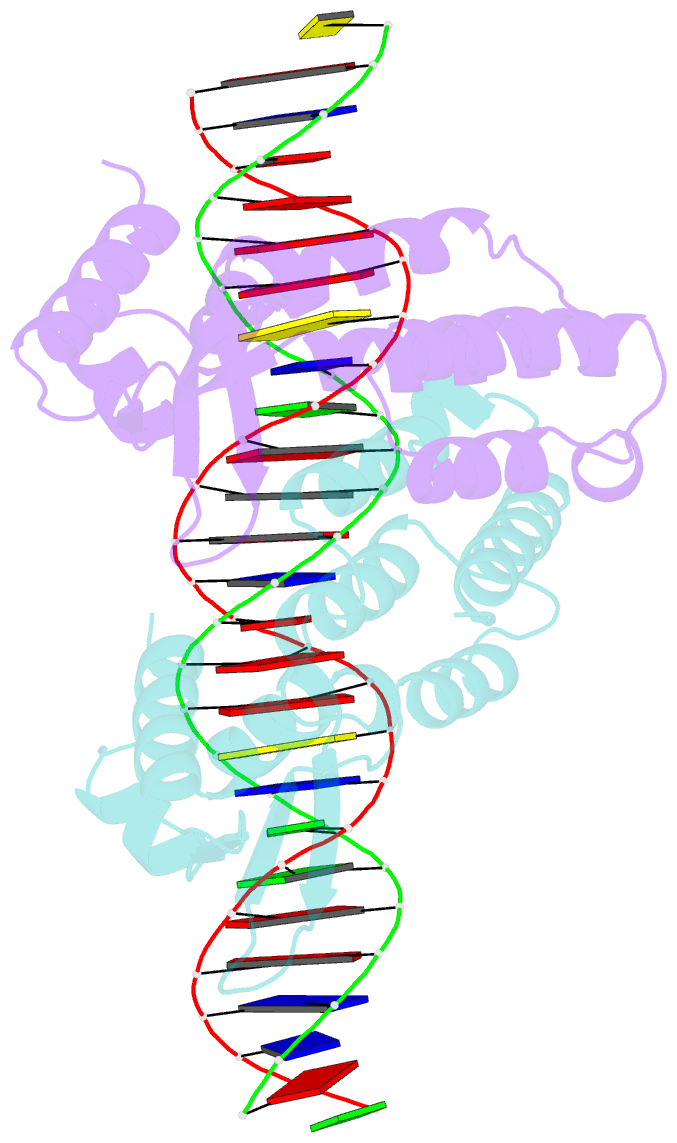
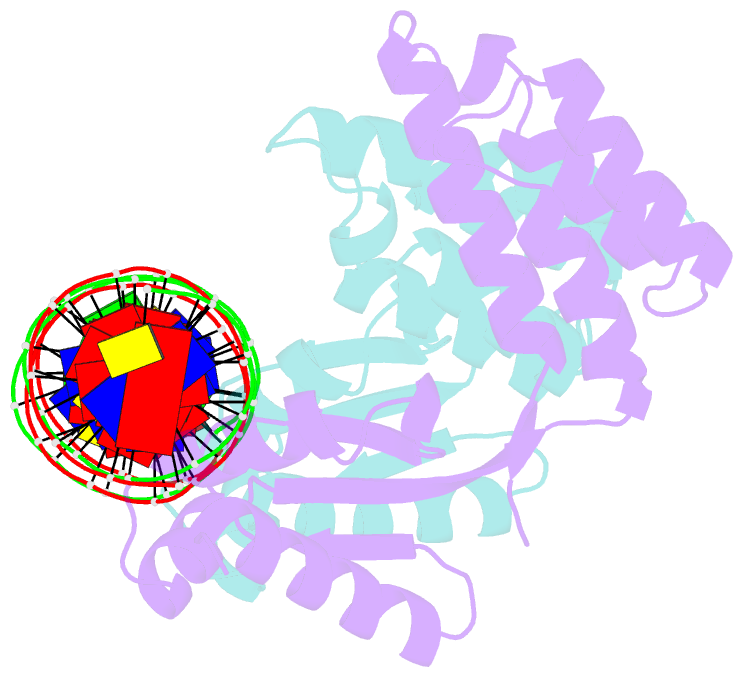
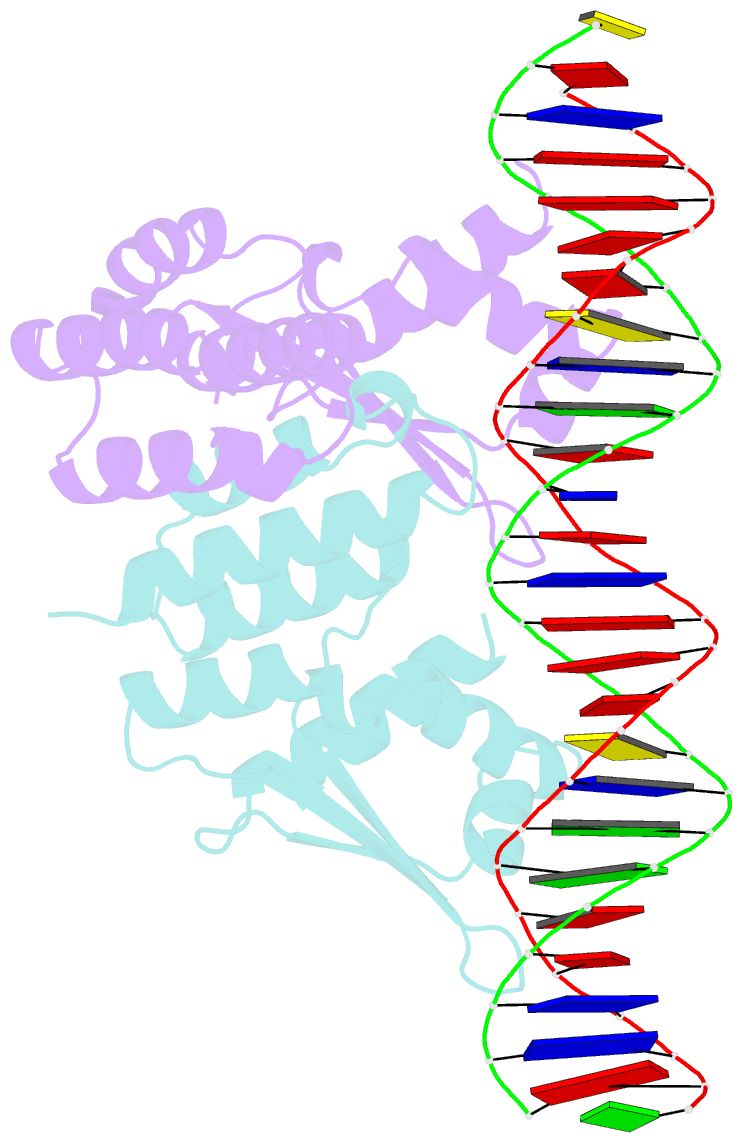
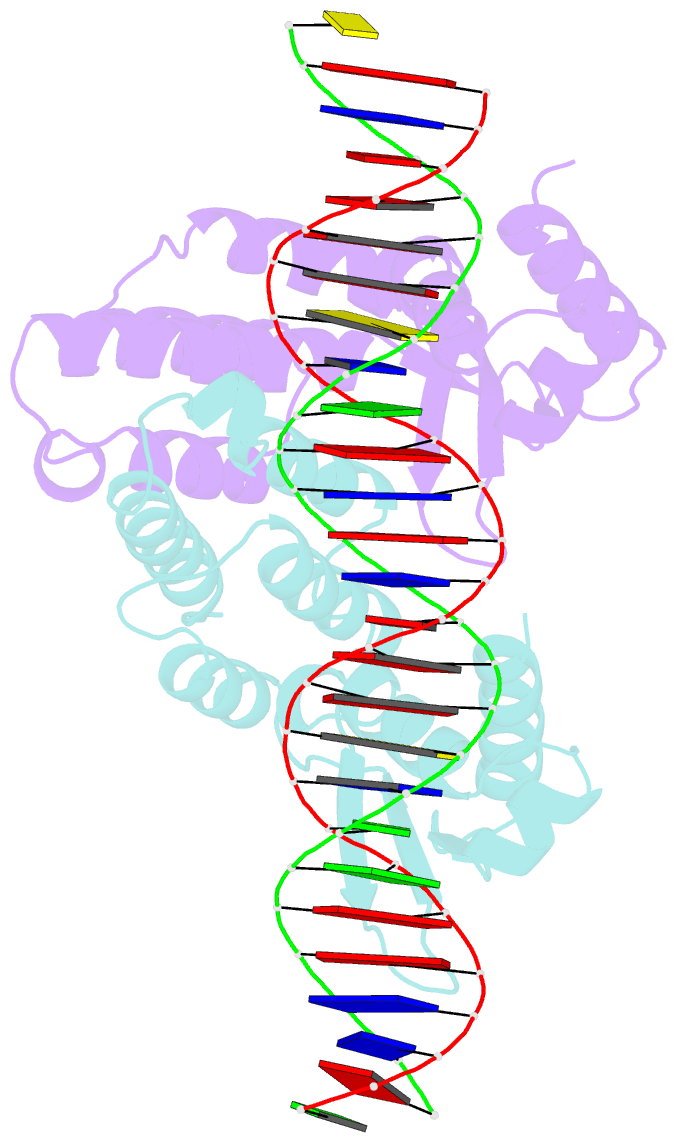
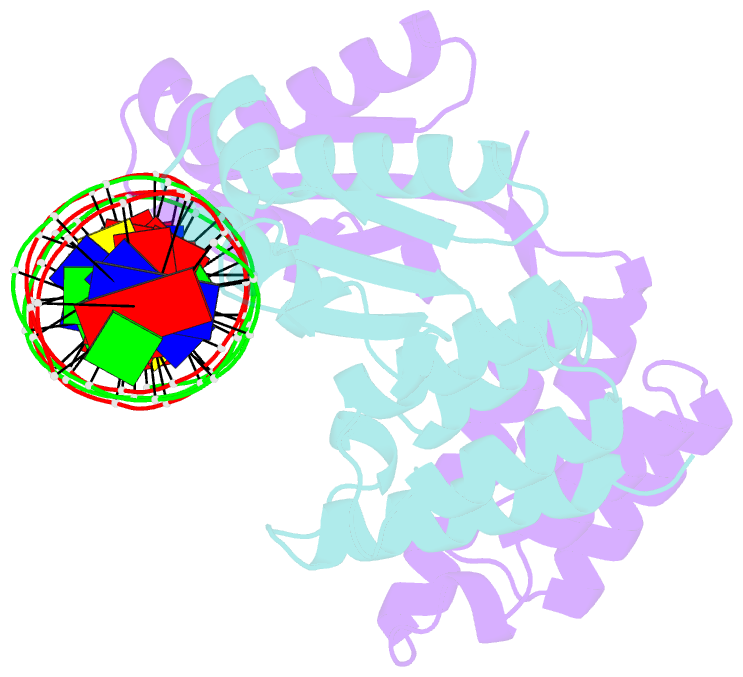
- Crystal structure of ctsr in complex with a 26bp DNA duplex
- Reference
- Fuhrmann J, Schmidt A, Spiess S, Lehner A, Turgay K, Mechtler K, Charpentier E, Clausen T (2009): "McsB is a protein arginine kinase that phosphorylates and inhibits the heat-shock regulator CtsR." Science, 324, 1323-1327. doi: 10.1126/science.1170088.
- Abstract
- All living organisms face a variety of environmental stresses that cause the misfolding and aggregation of proteins. To eliminate damaged proteins, cells developed highly efficient stress response and protein quality control systems. We performed a biochemical and structural analysis of the bacterial CtsR/McsB stress response. The crystal structure of the CtsR repressor, in complex with DNA, pinpointed key residues important for high-affinity binding to the promoter regions of heat-shock genes. Moreover, biochemical characterization of McsB revealed that McsB specifically phosphorylates arginine residues in the DNA binding domain of CtsR, thereby impairing its function as a repressor of stress response genes. Identification of the CtsR/McsB arginine phospho-switch expands the repertoire of possible protein modifications involved in prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcriptional regulation.