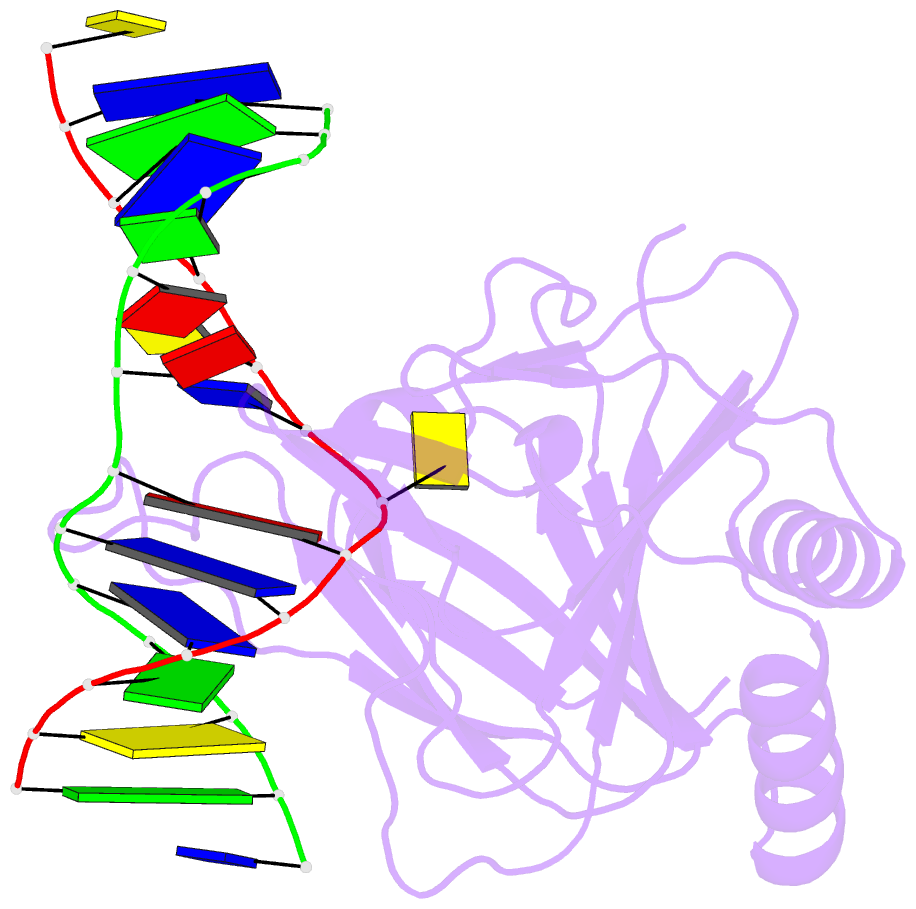
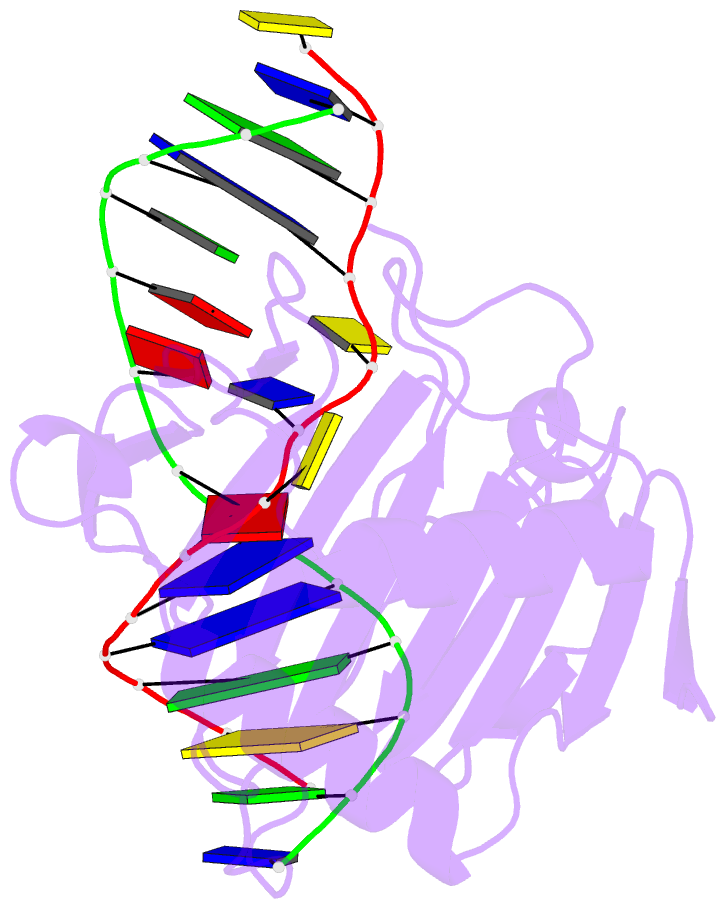
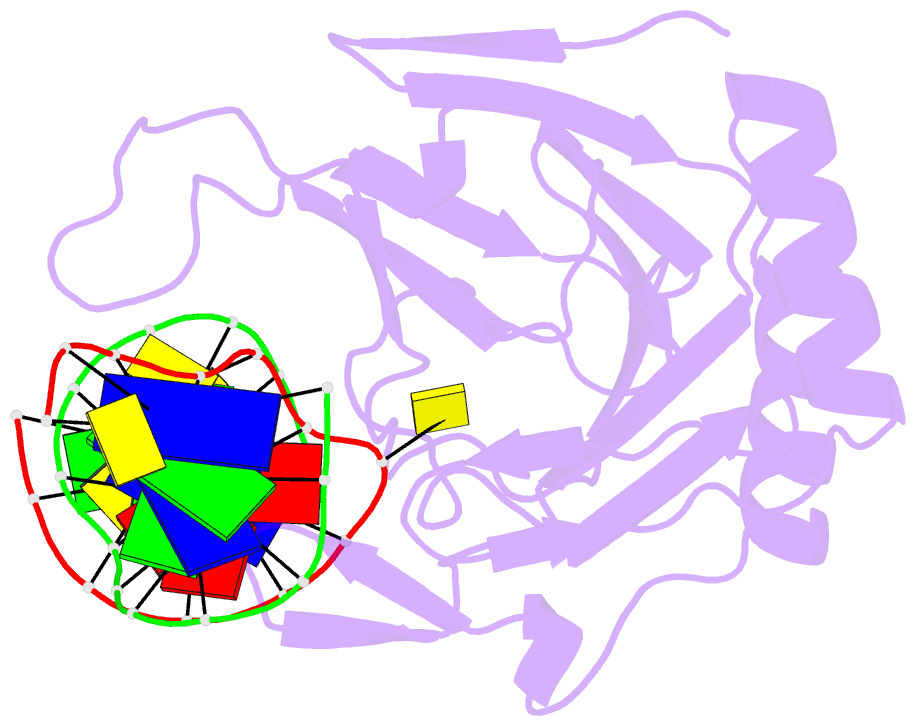
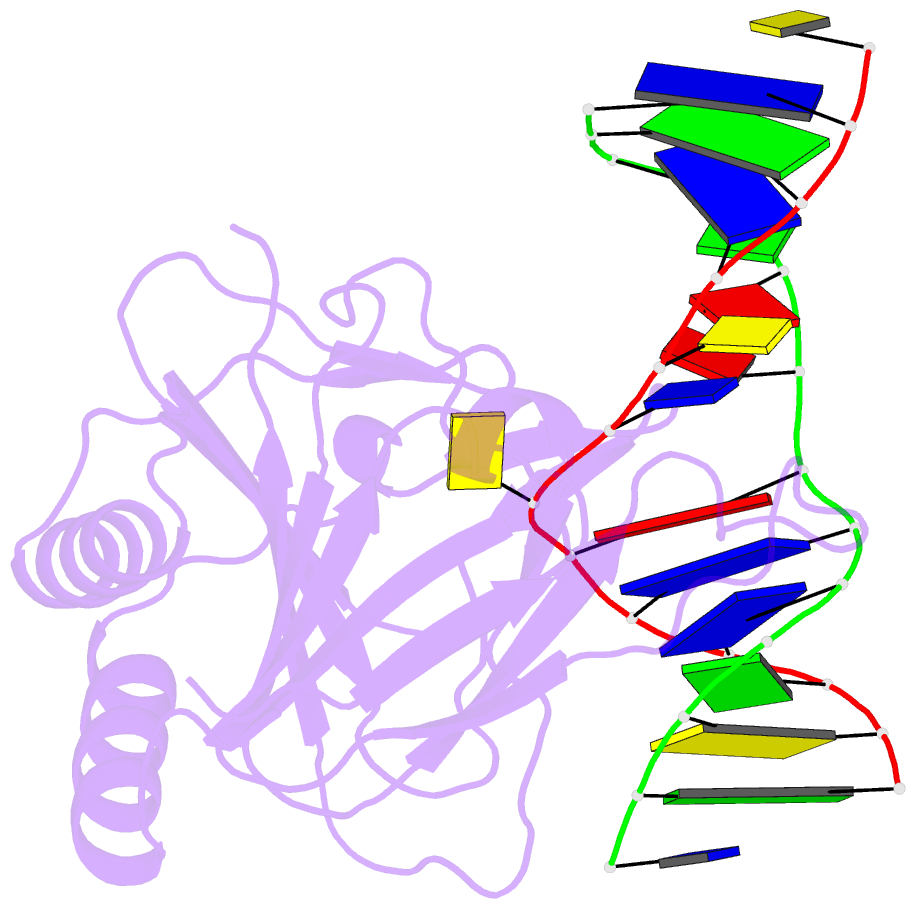
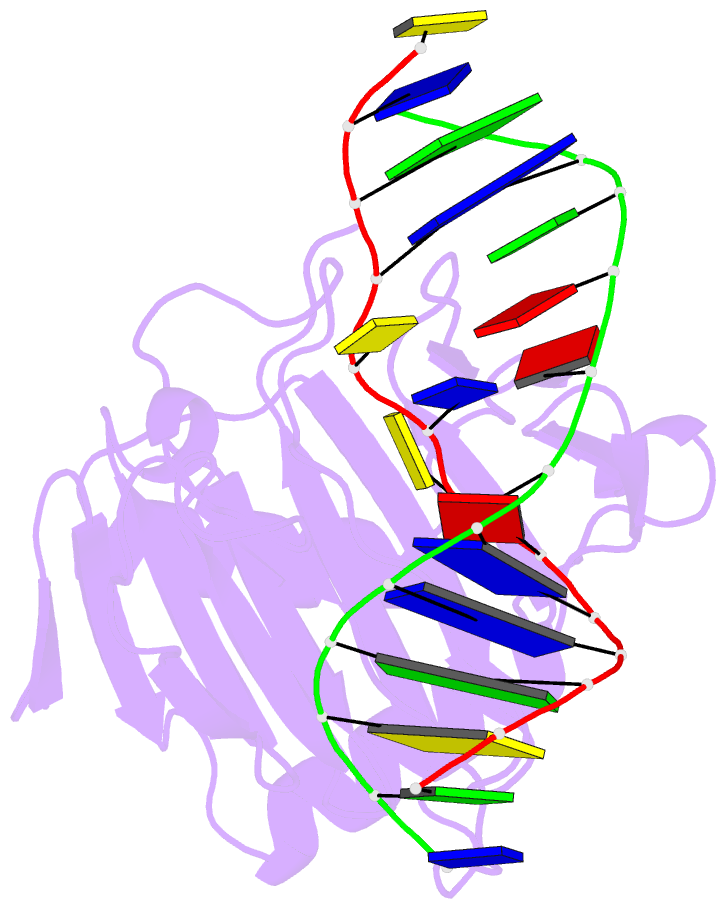
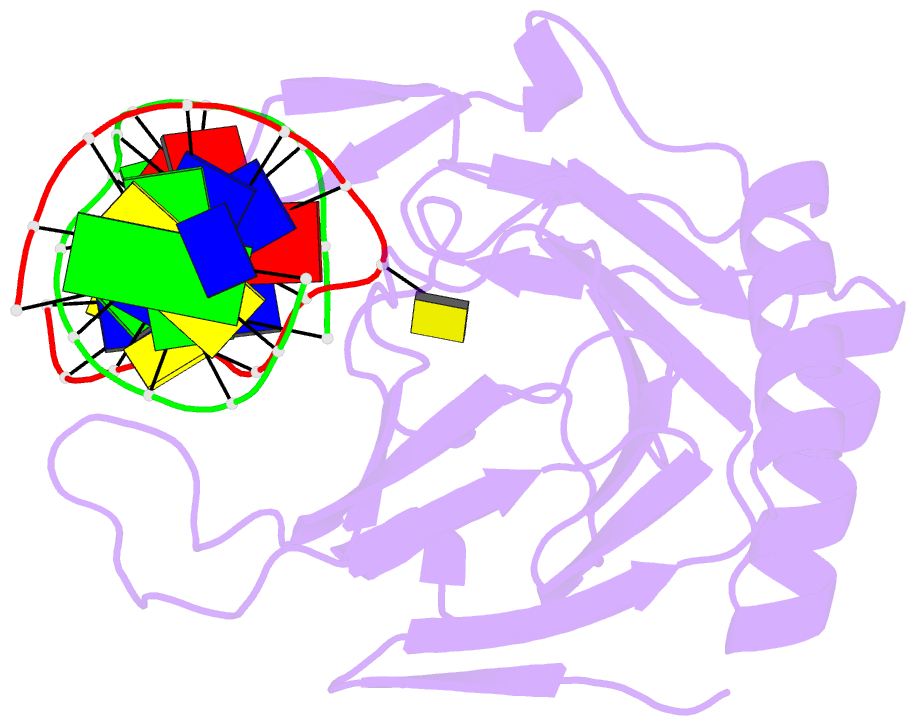
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3h8x; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- oxidoreductase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.95 Å)
- Summary
- Structure determination of DNA methylation lesions n1-mea and n3-mec in duplex DNA using a cross-linked host-guest system
- Reference
- Lu L, Yi C, Jian X, Zheng G, He C (2010): "Structure determination of DNA methylation lesions N1-meA and N3-meC in duplex DNA using a cross-linked protein-DNA system." Nucleic Acids Res., 38, 4415-4425. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq129.
- Abstract
- N(1)-meA and N(3)-meC are cytotoxic DNA base methylation lesions that can accumulate in the genomes of various organisms in the presence of S(N)2 type methylating agents. We report here the structural characterization of these base lesions in duplex DNA using a cross-linked protein-DNA crystallization system. The crystal structure of N(1)-meA:T pair shows an unambiguous Hoogsteen base pair with a syn conformation adopted by N(1)-meA, which exhibits significant changes in the opening, roll and twist angles as compared to the normal A:T base pair. Unlike N(1)-meA, N(3)-meC does not establish any interaction with the opposite G, but remains partially intrahelical. Also, structurally characterized is the N(6)-meA base modification that forms a normal base pair with the opposite T in duplex DNA. Structural characterization of these base methylation modifications provides molecular level information on how they affect the overall structure of duplex DNA. In addition, the base pairs containing N(1)-meA or N(3)-meC do not share any specific characteristic properties except that both lesions create thermodynamically unstable regions in a duplex DNA, a property that may be explored by the repair proteins to locate these lesions.