Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3hvr; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- nucleic acid binding protein-DNA-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.211 Å)
- Summary
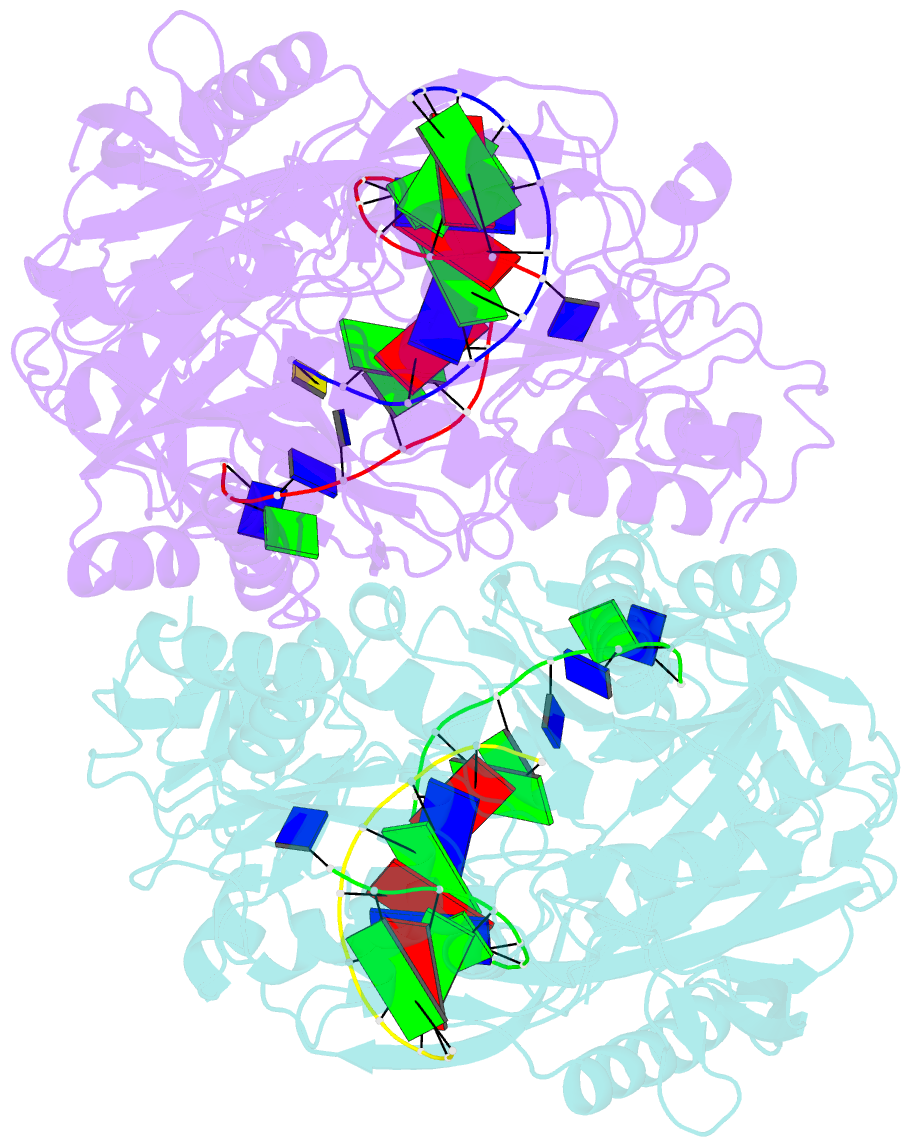
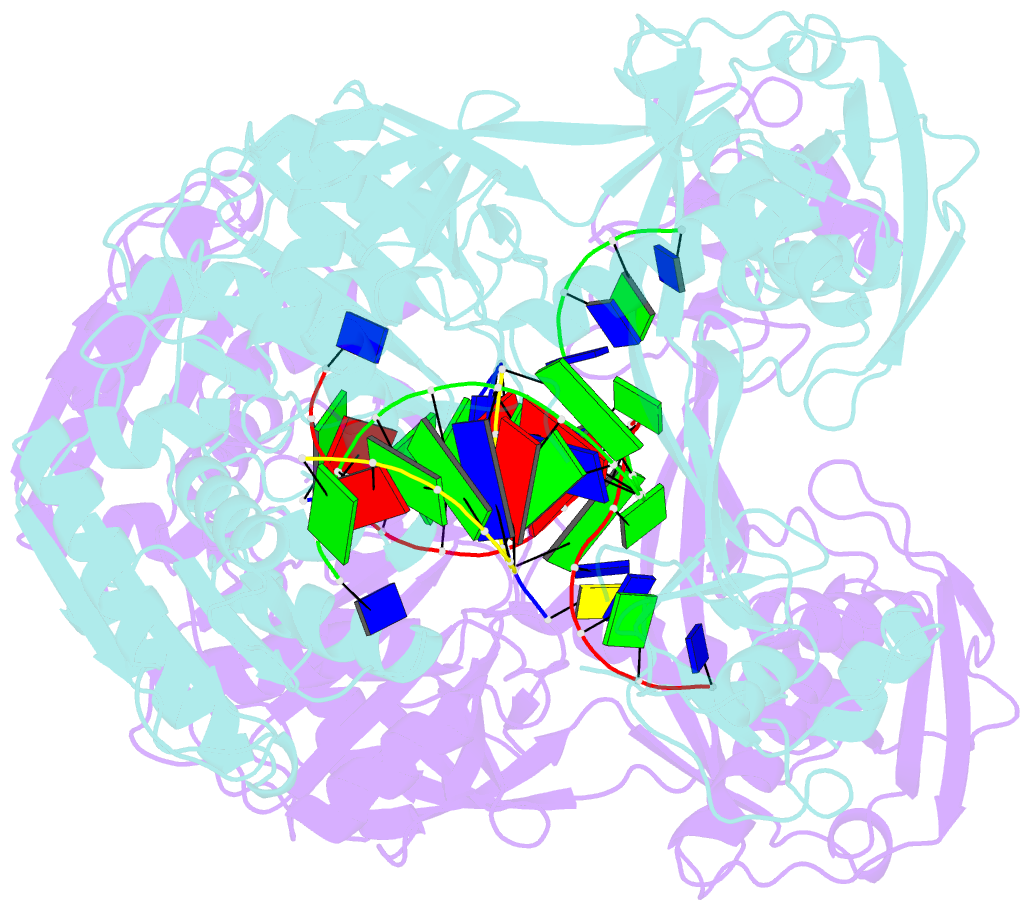
- Crystal structure of t. thermophilus argonaute complexed with DNA guide strand and 19-nt RNA target strand with two mg2+ at the cleavage site
- Reference
- Wang Y, Juranek S, Li H, Sheng G, Wardle GS, Tuschl T, Patel DJ (2009): "Nucleation, propagation and cleavage of target RNAs in Ago silencing complexes." Nature, 461, 754-761. doi: 10.1038/nature08434.
- Abstract
- The slicer activity of the RNA-induced silencing complex resides within its Argonaute (Ago) component, in which the PIWI domain provides the catalytic residues governing guide-strand mediated site-specific cleavage of target RNA. Here we report on structures of ternary complexes of Thermus thermophilus Ago catalytic mutants with 5'-phosphorylated 21-nucleotide guide DNA and complementary target RNAs of 12, 15 and 19 nucleotides in length, which define the molecular basis for Mg(2+)-facilitated site-specific cleavage of the target. We observe pivot-like domain movements within the Ago scaffold on proceeding from nucleation to propagation steps of guide-target duplex formation, with duplex zippering beyond one turn of the helix requiring the release of the 3'-end of the guide from the PAZ pocket. Cleavage assays on targets of various lengths supported this model, and sugar-phosphate-backbone-modified target strands showed the importance of structural and catalytic divalent metal ions observed in the crystal structures.