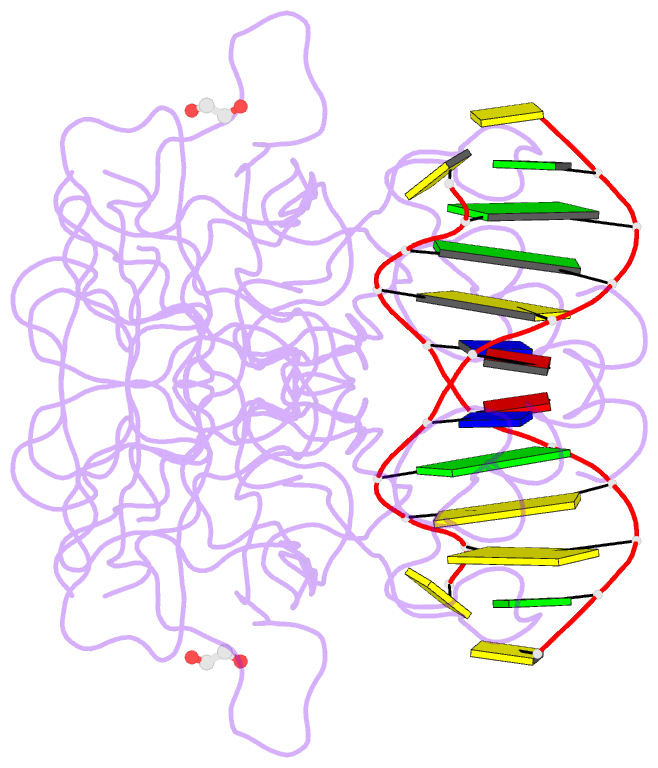
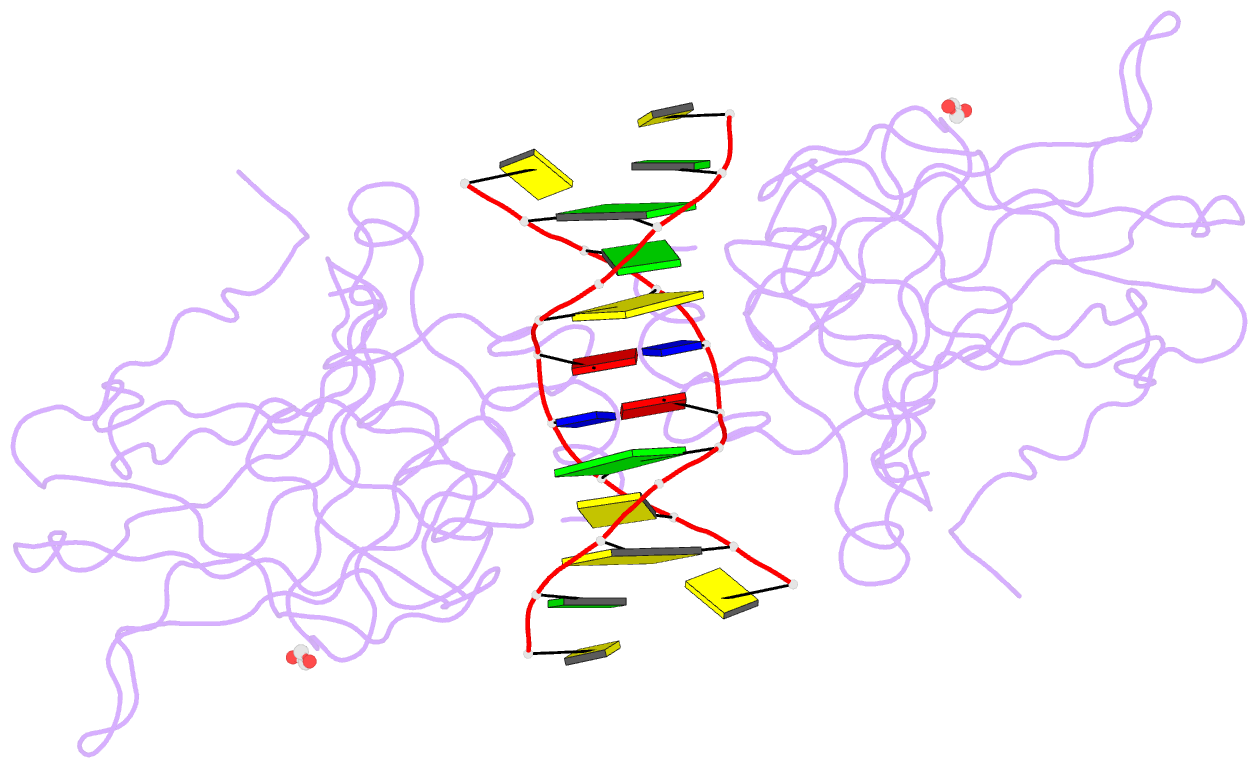
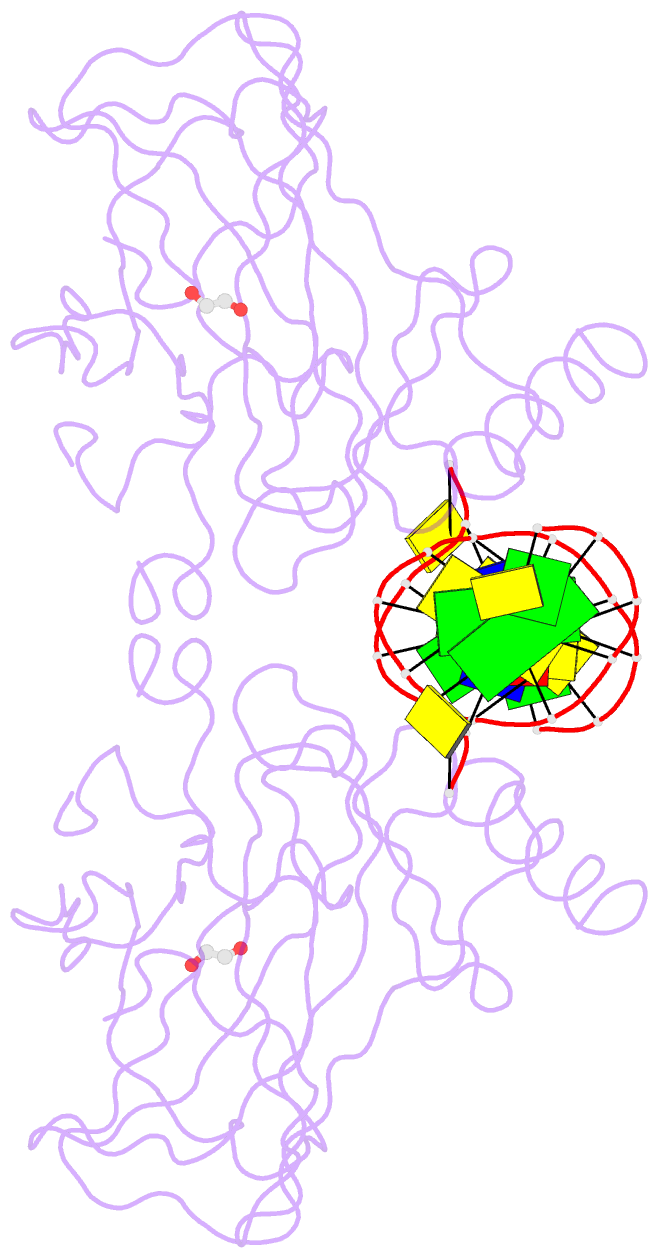
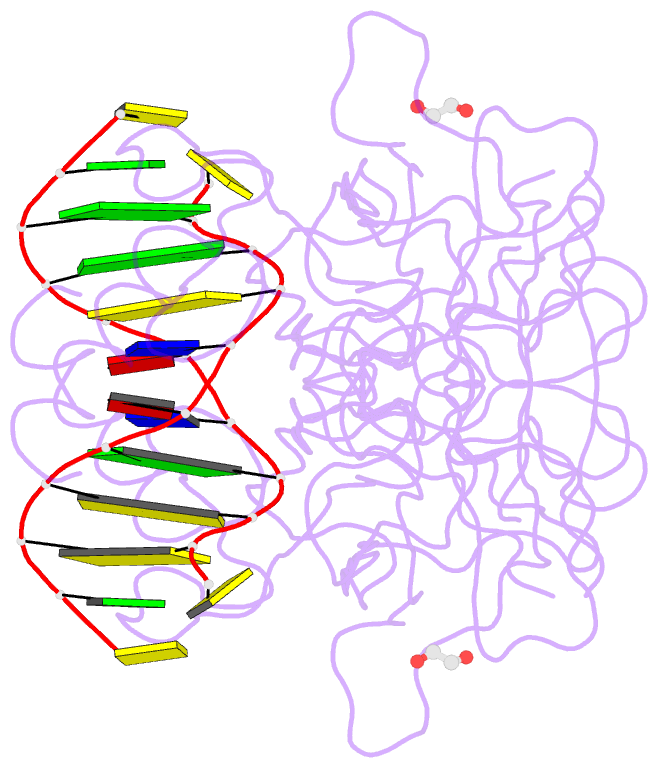
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3igl; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.8 Å)
- Summary
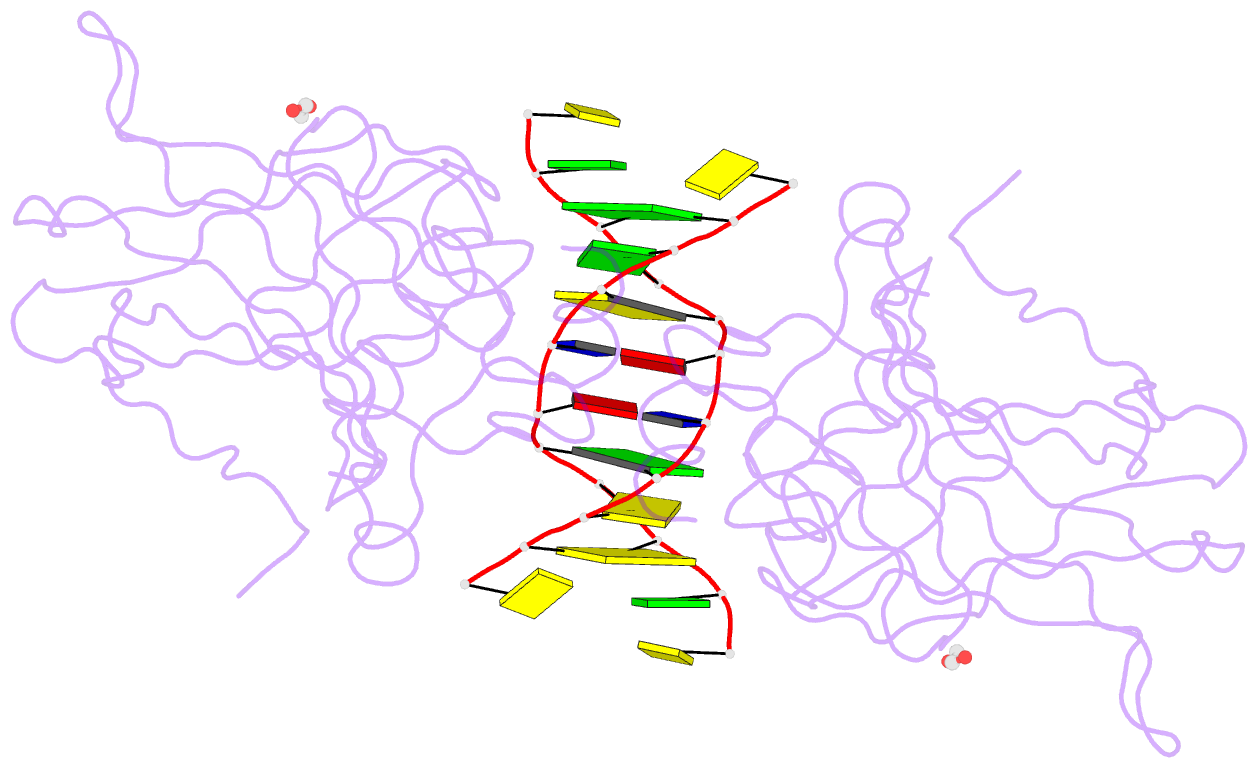
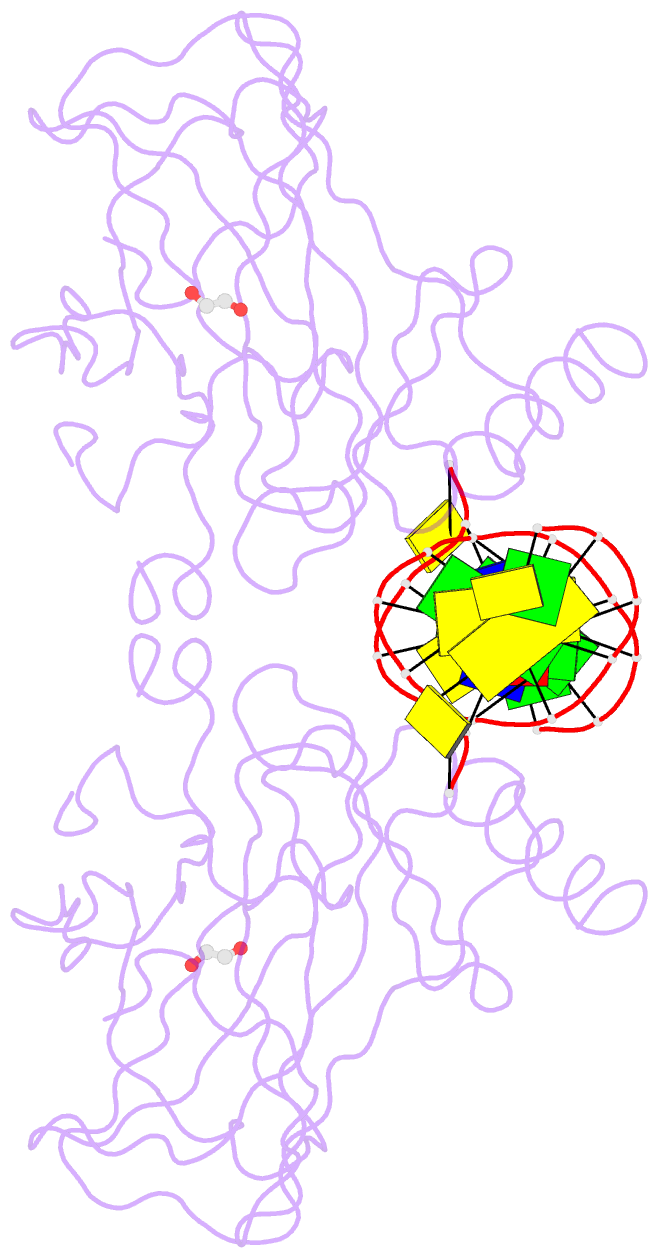
- Diversity in DNA recognition by p53 revealed by crystal structures with hoogsteen base pairs (p53-DNA complex 1)
- Reference
- Kitayner M, Rozenberg H, Rohs R, Suad O, Rabinovich D, Honig B, Shakked Z (2010): "Diversity in DNA recognition by p53 revealed by crystal structures with Hoogsteen base pairs." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 17, 423-429. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1800.
- Abstract
- p53 binds as a tetramer to DNA targets consisting of two decameric half-sites separated by a variable spacer. Here we present high-resolution crystal structures of complexes between p53 core-domain tetramers and DNA targets consisting of contiguous half-sites. In contrast to previously reported p53-DNA complexes that show standard Watson-Crick base pairs, the newly reported structures show noncanonical Hoogsteen base-pairing geometry at the central A-T doublet of each half-site. Structural and computational analyses show that the Hoogsteen geometry distinctly modulates the B-DNA helix in terms of local shape and electrostatic potential, which, together with the contiguous DNA configuration, results in enhanced protein-DNA and protein-protein interactions compared to noncontiguous half-sites. Our results suggest a mechanism relating spacer length to protein-DNA binding affinity. Our findings also expand the current understanding of protein-DNA recognition and establish the structural and chemical properties of Hoogsteen base pairs as the basis for a novel mode of sequence readout.