Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3in5; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.2 Å)
- Summary
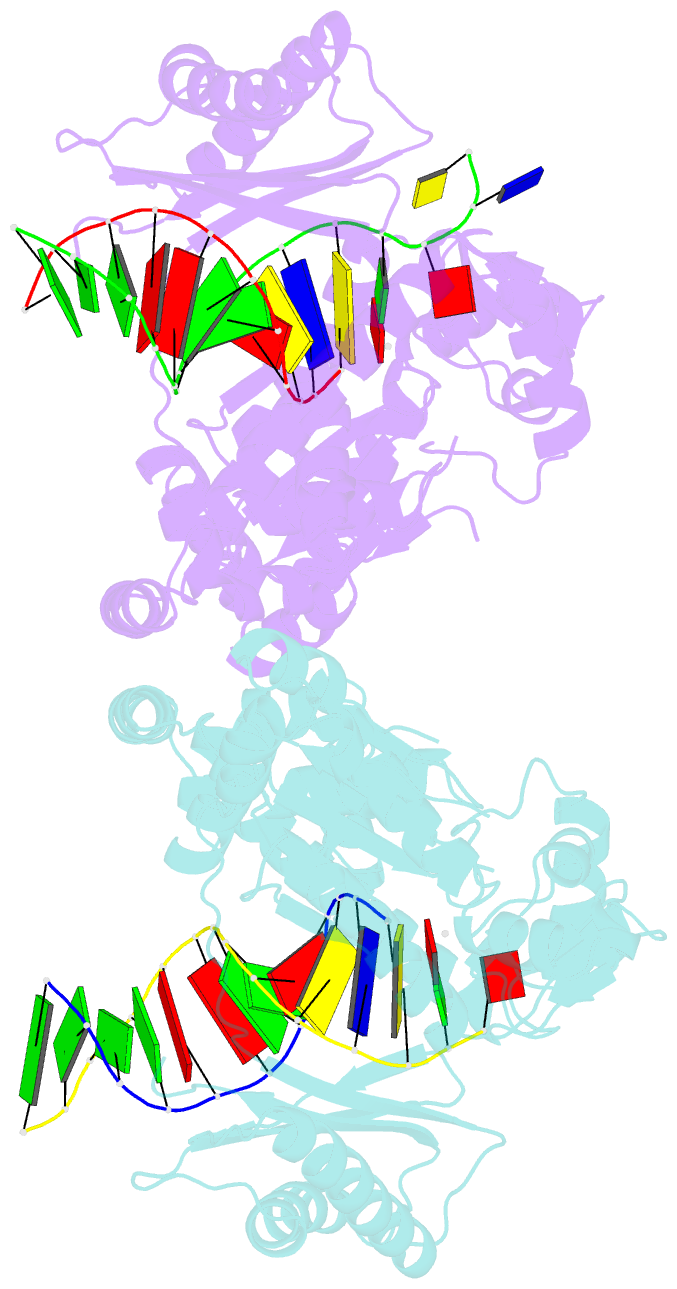
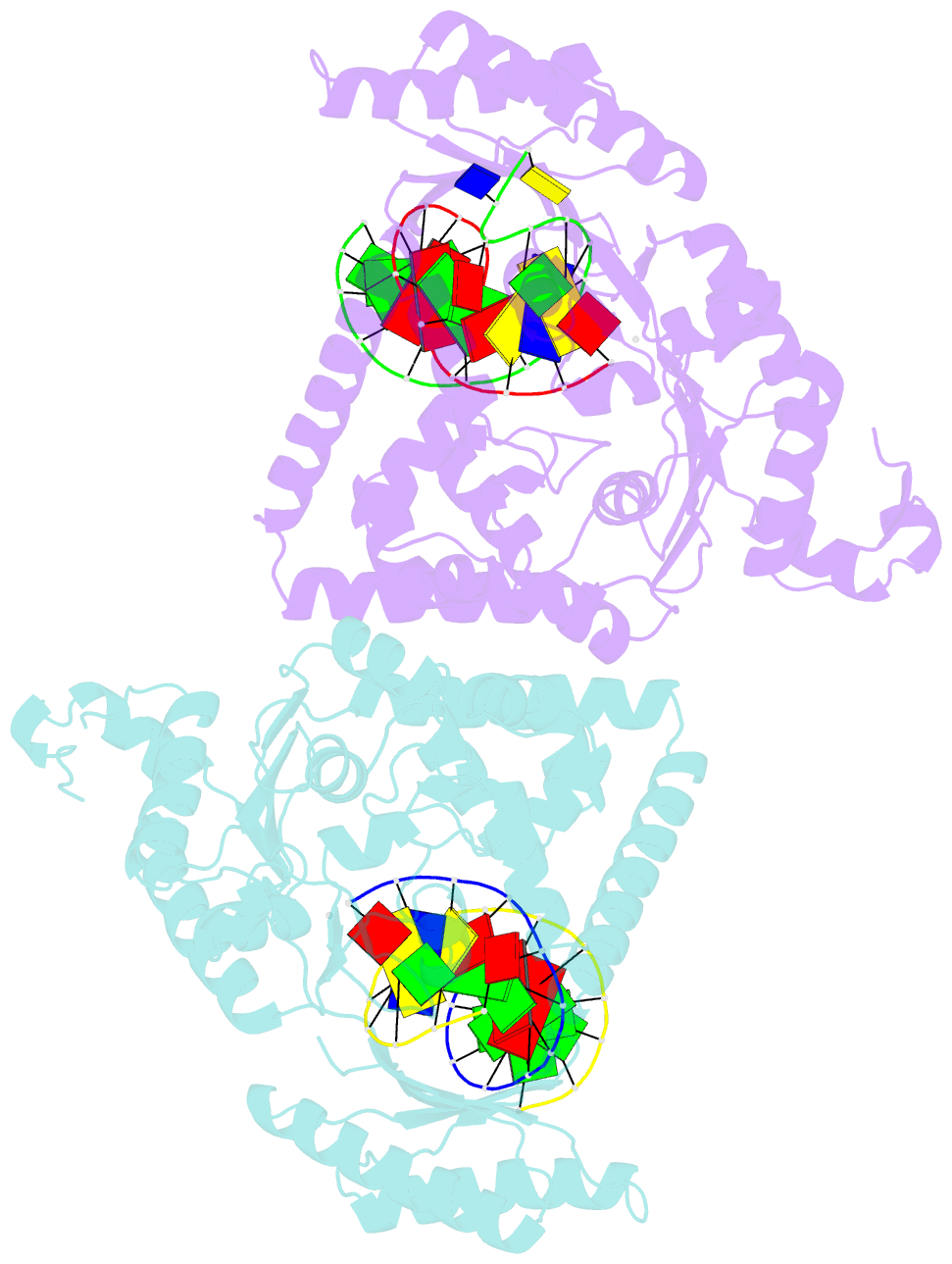
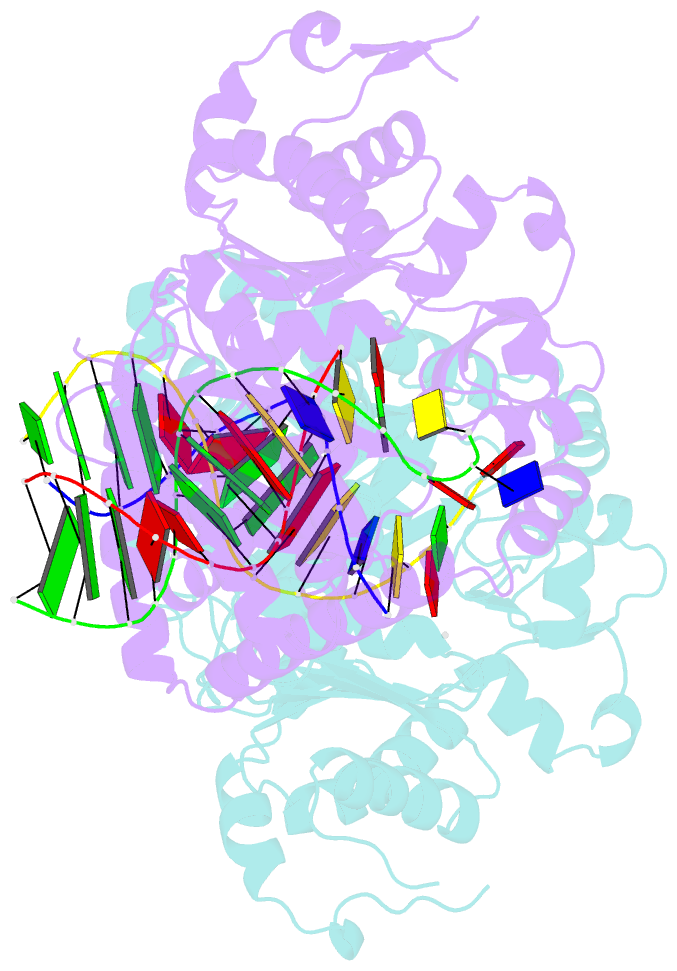
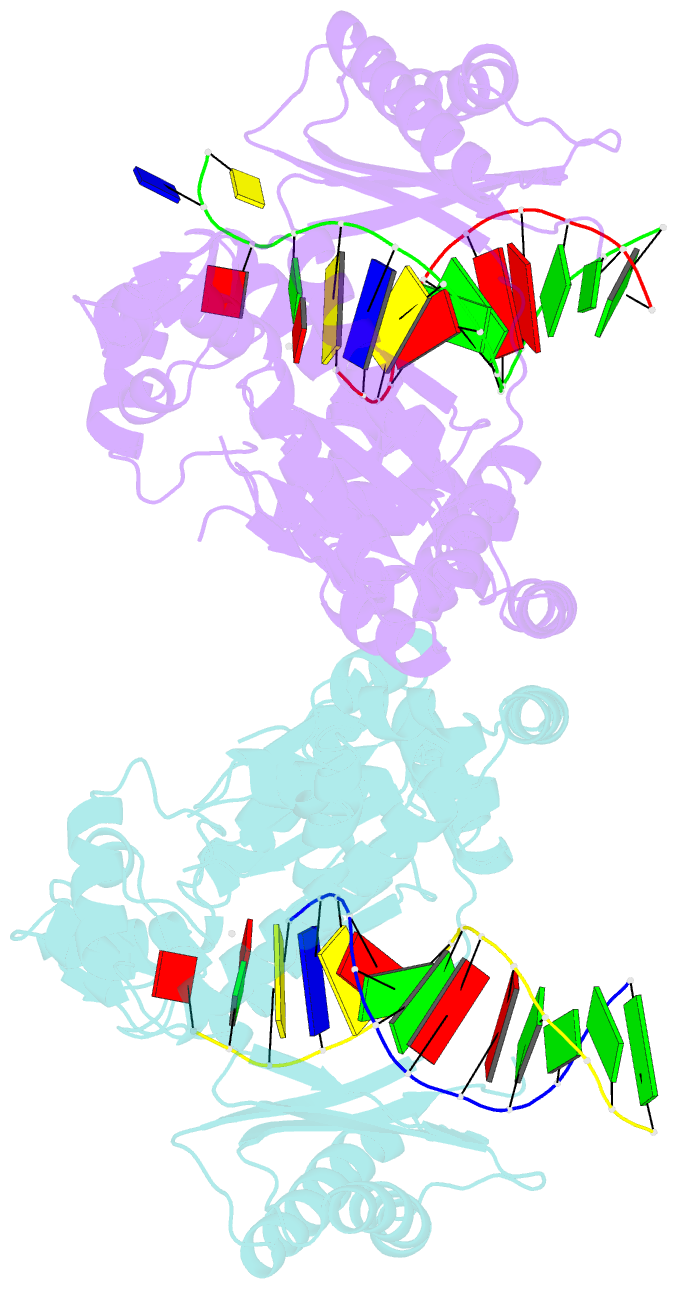
- Structure of human DNA polymerase kappa inserting datp opposite an 8-oxog DNA lesion
- Reference
- Vasquez-Del Carpio R, Silverstein TD, Lone S, Swan MK, Choudhury JR, Johnson RE, Prakash S, Prakash L, Aggarwal AK (2009): "Structure of human DNA polymerase kappa inserting dATP opposite an 8-oxoG DNA lesion." PLOS ONE, 4, e5766. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005766.
- Abstract
- Background: Oxygen-free radicals formed during normal aerobic cellular metabolism attack bases in DNA and 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG) is one of the major lesions formed. It is amongst the most mutagenic lesions in cells because of its dual coding potential, wherein 8-oxoG(syn) can pair with an A in addition to normal base pairing of 8-oxoG(anti) with a C. Human DNA polymerase kappa (Polkappa) is a member of the newly discovered Y-family of DNA polymerases that possess the ability to replicate through DNA lesions. To understand the basis of Polkappa's preference for insertion of an A opposite 8-oxoG lesion, we have solved the structure of Polkappa in ternary complex with a template-primer presenting 8-oxoG in the active site and with dATP as the incoming nucleotide.