Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3irw; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.7 Å)
- Summary
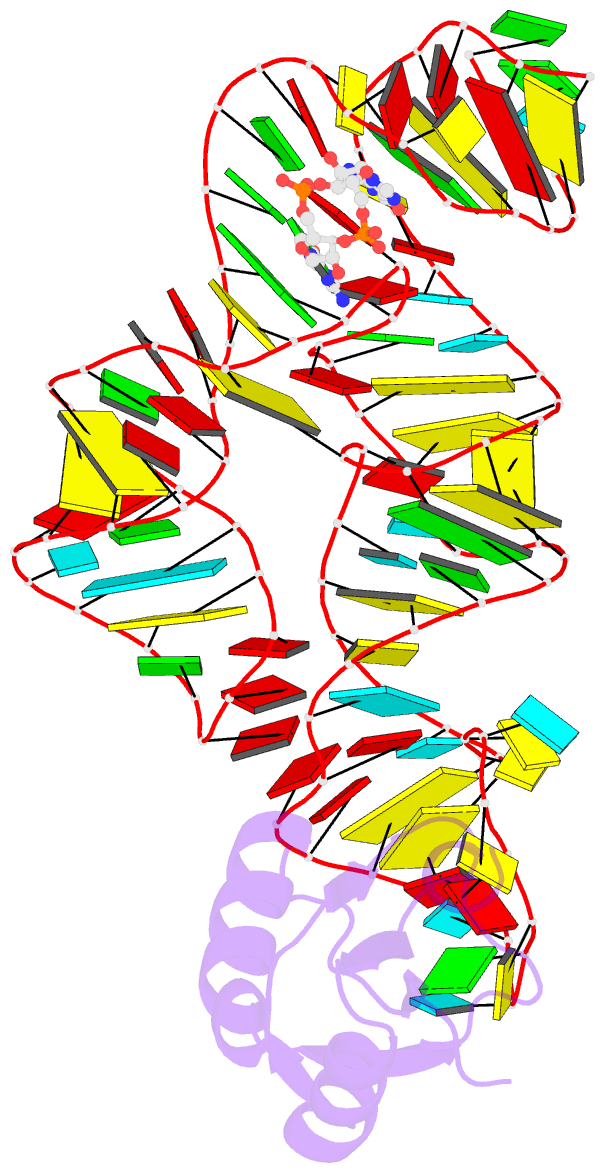
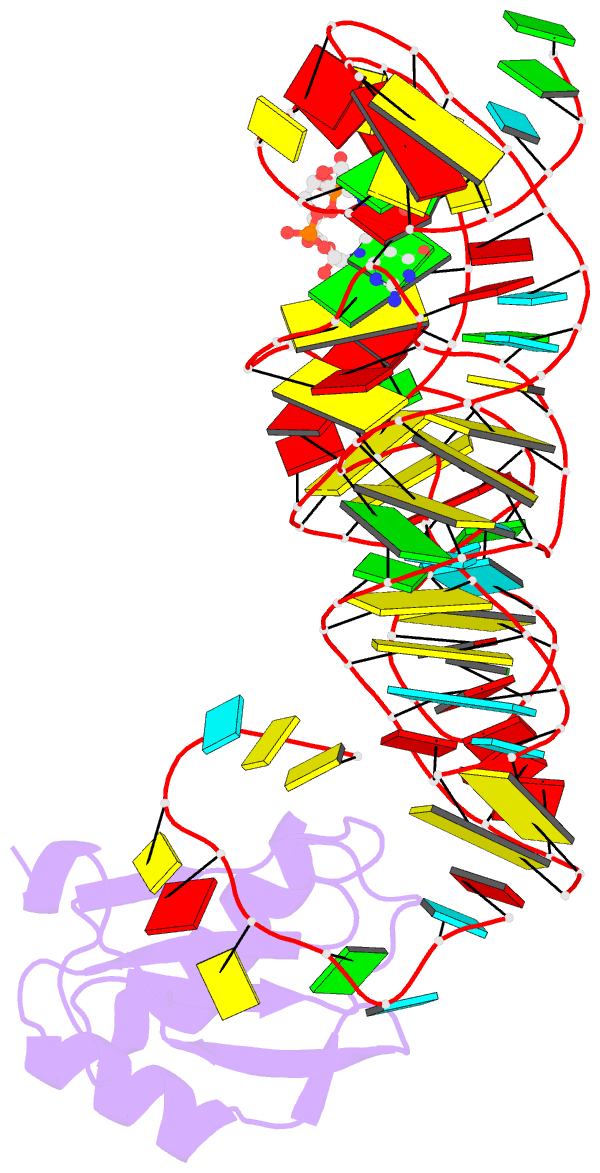
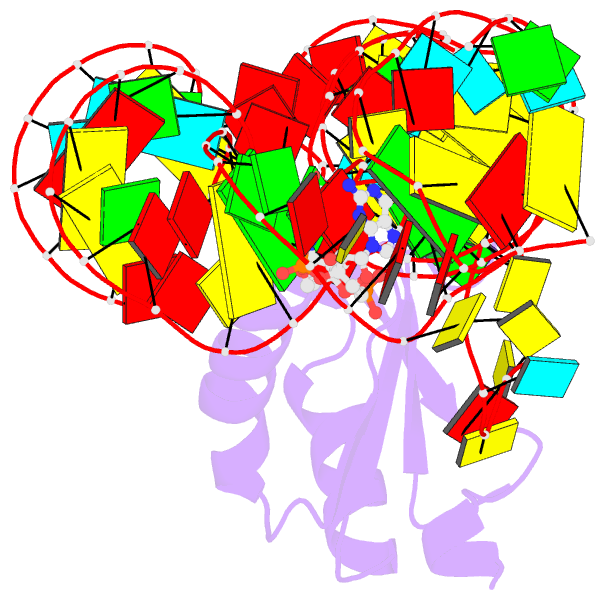
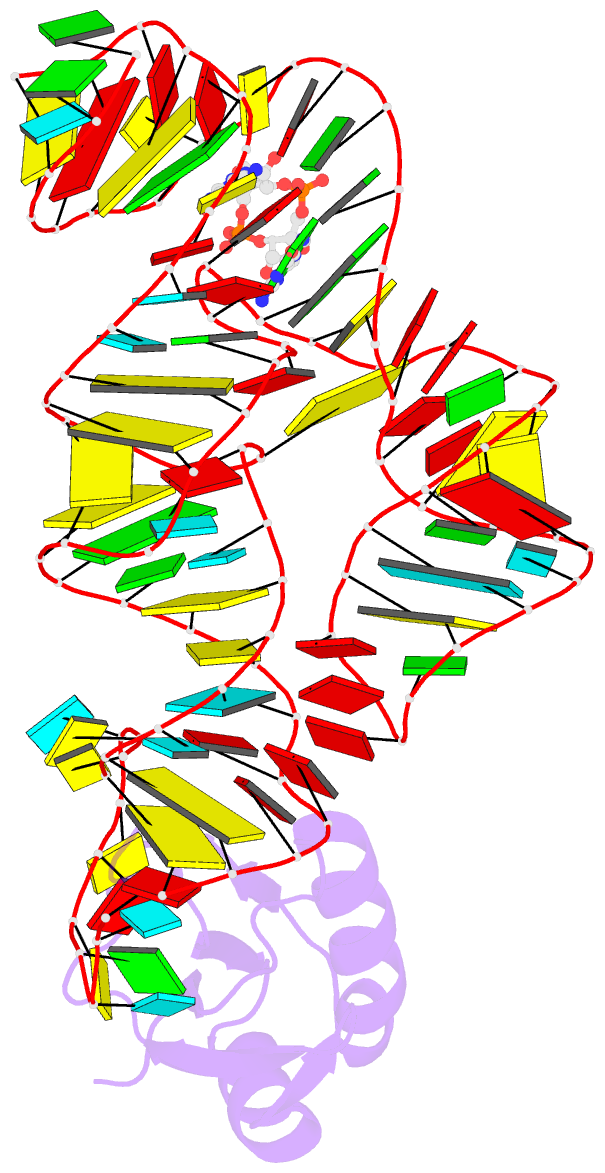
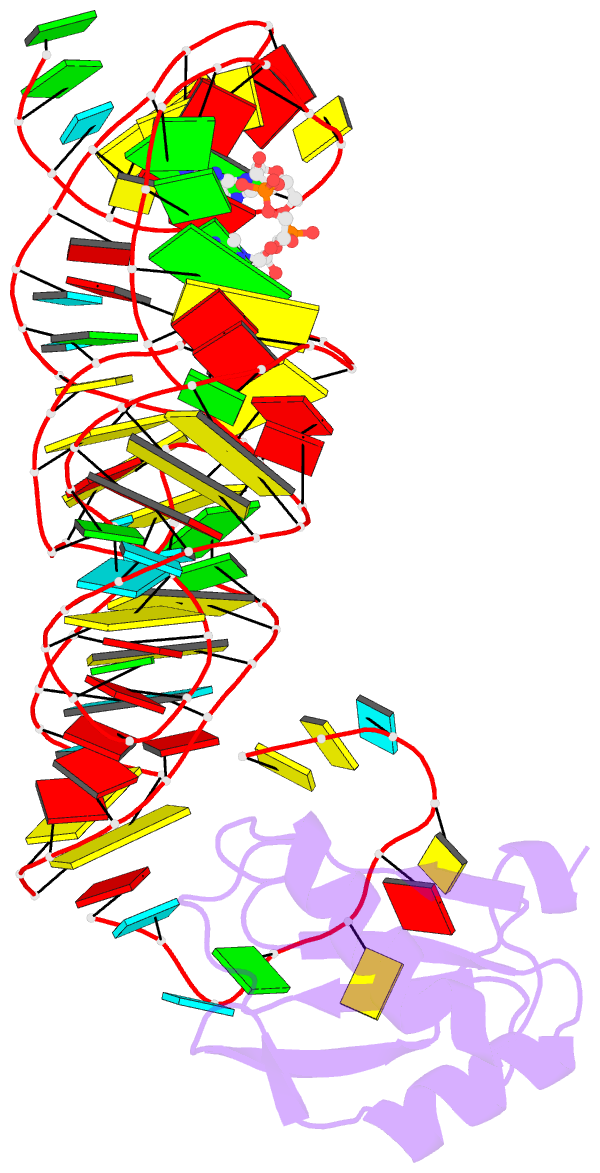
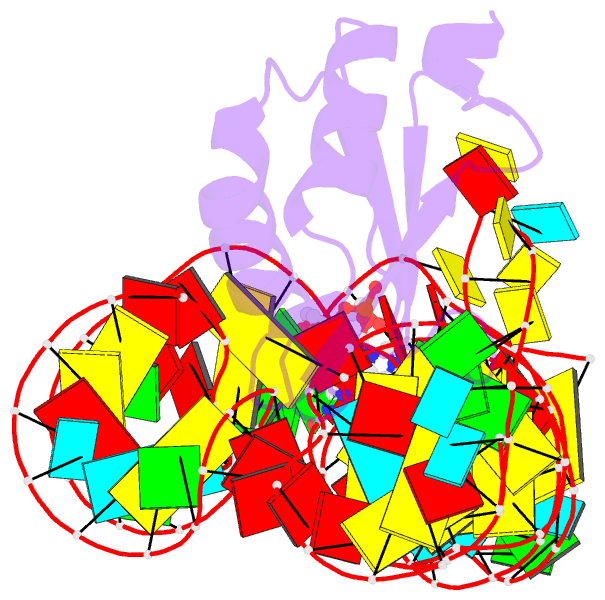
- Structure of a c-di-gmp riboswitch from v. cholerae
- Reference
- Smith KD, Lipchock SV, Ames TD, Wang J, Breaker RR, Strobel SA (2009): "Structural basis of ligand binding by a c-di-GMP riboswitch." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 16, 1218-1223. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1702.
- Abstract
- The second messenger signaling molecule bis-(3'-5')-cyclic dimeric guanosine monophosphate (c-di-GMP) regulates many processes in bacteria, including motility, pathogenesis and biofilm formation. c-di-GMP-binding riboswitches are important downstream targets in this signaling pathway. Here we report the crystal structure, at 2.7 A resolution, of a c-di-GMP riboswitch aptamer from Vibrio cholerae bound to c-di-GMP, showing that the ligand binds within a three-helix junction that involves base-pairing and extensive base-stacking. The symmetric c-di-GMP is recognized asymmetrically with respect to both the bases and the backbone. A mutant aptamer was engineered that preferentially binds the candidate signaling molecule c-di-AMP over c-di-GMP. Kinetic and structural data suggest that genetic regulation by the c-di-GMP riboswitch is kinetically controlled and that gene expression is modulated through the stabilization of a previously unidentified P1 helix, illustrating a direct mechanism for c-di-GMP signaling.