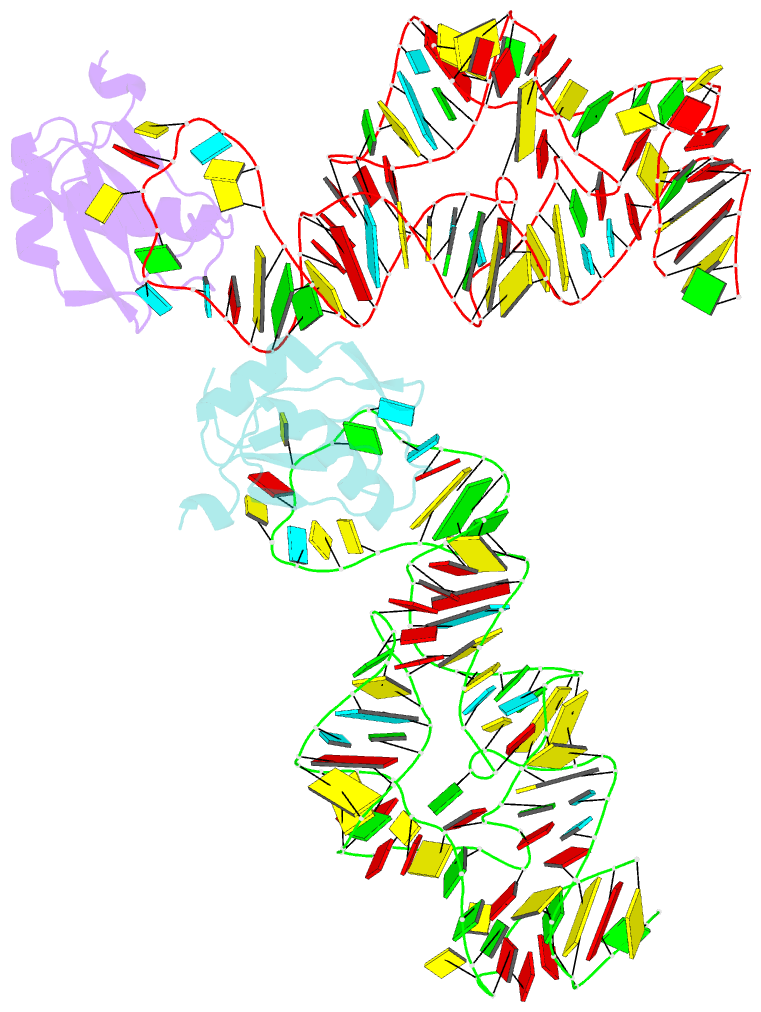
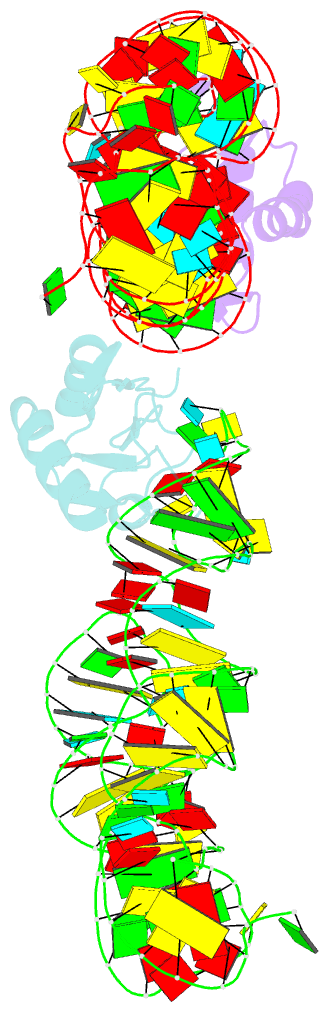
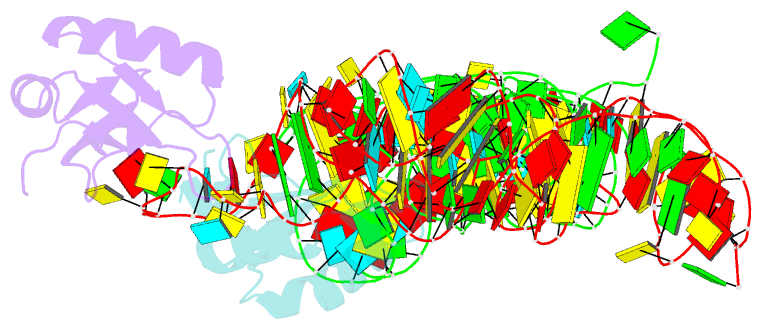
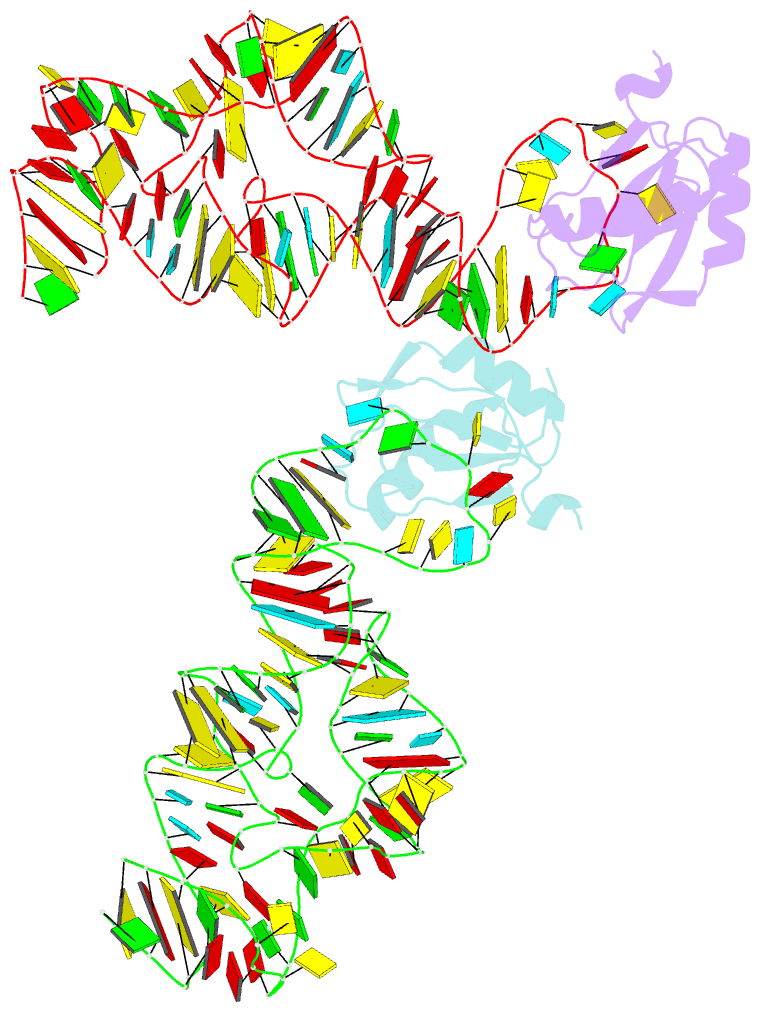
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3iwn; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA-RNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (3.2 Å)
- Summary
- Co-crystal structure of a bacterial c-di-gmp riboswitch
- Reference
- Kulshina N, Baird NJ, Ferre-D'Amare AR (2009): "Recognition of the bacterial second messenger cyclic diguanylate by its cognate riboswitch." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 16, 1212-1217. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1701.
- Abstract
- The cyclic diguanylate (bis-(3'-5')-cyclic dimeric guanosine monophosphate, c-di-GMP) riboswitch is the first known example of a gene-regulatory RNA that binds a second messenger. c-di-GMP is widely used by bacteria to regulate processes ranging from biofilm formation to the expression of virulence genes. The cocrystal structure of the c-di-GMP responsive GEMM riboswitch upstream of the tfoX gene of Vibrio cholerae reveals the second messenger binding the RNA at a three-helix junction. The two-fold symmetric second messenger is recognized asymmetrically by the monomeric riboswitch using canonical and noncanonical base-pairing as well as intercalation. These interactions explain how the RNA discriminates against cyclic diadenylate (c-di-AMP), a putative bacterial second messenger. Small-angle X-ray scattering and biochemical analyses indicate that the RNA undergoes compaction and large-scale structural rearrangement in response to ligand binding, consistent with organization of the core three-helix junction of the riboswitch concomitant with binding of c-di-GMP.