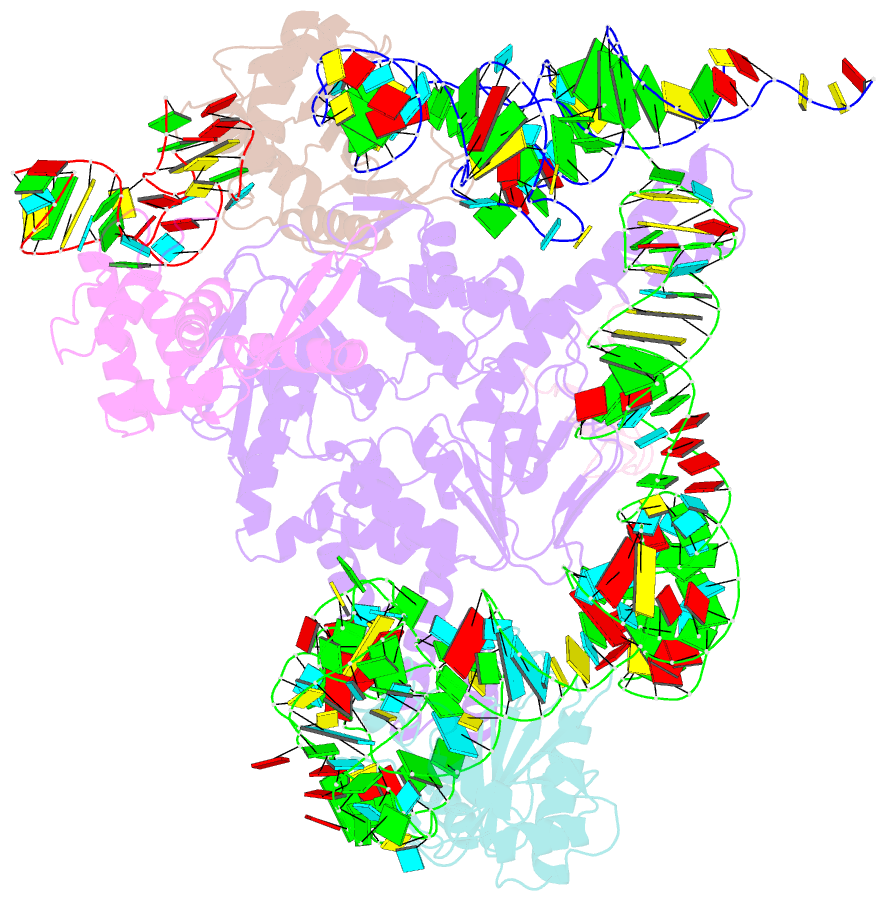
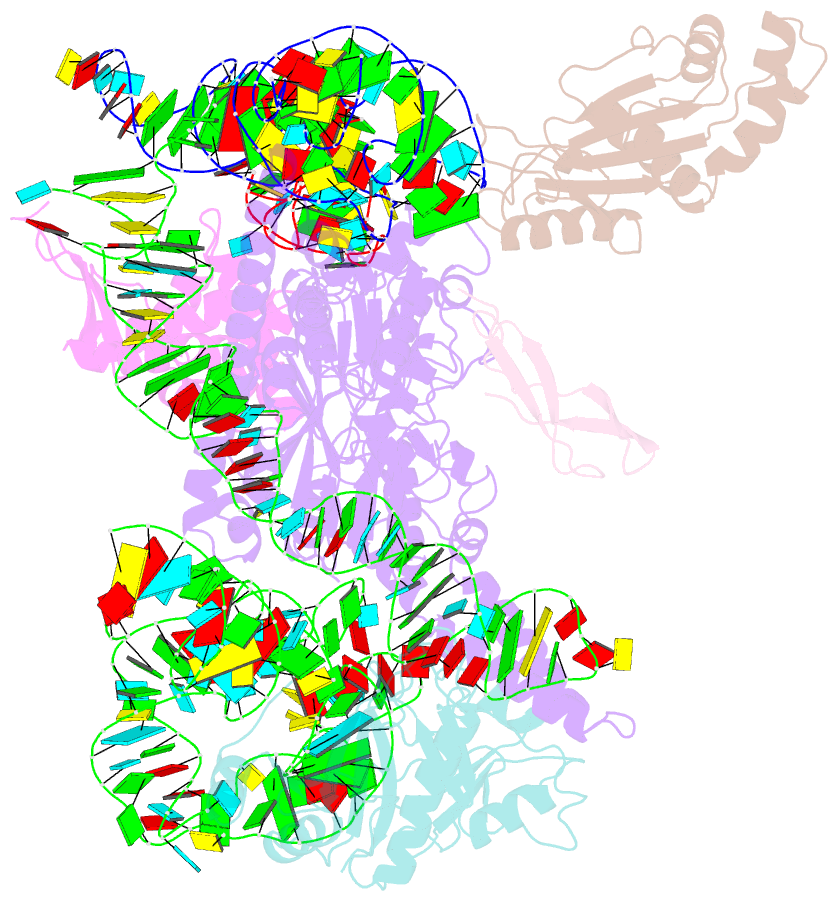
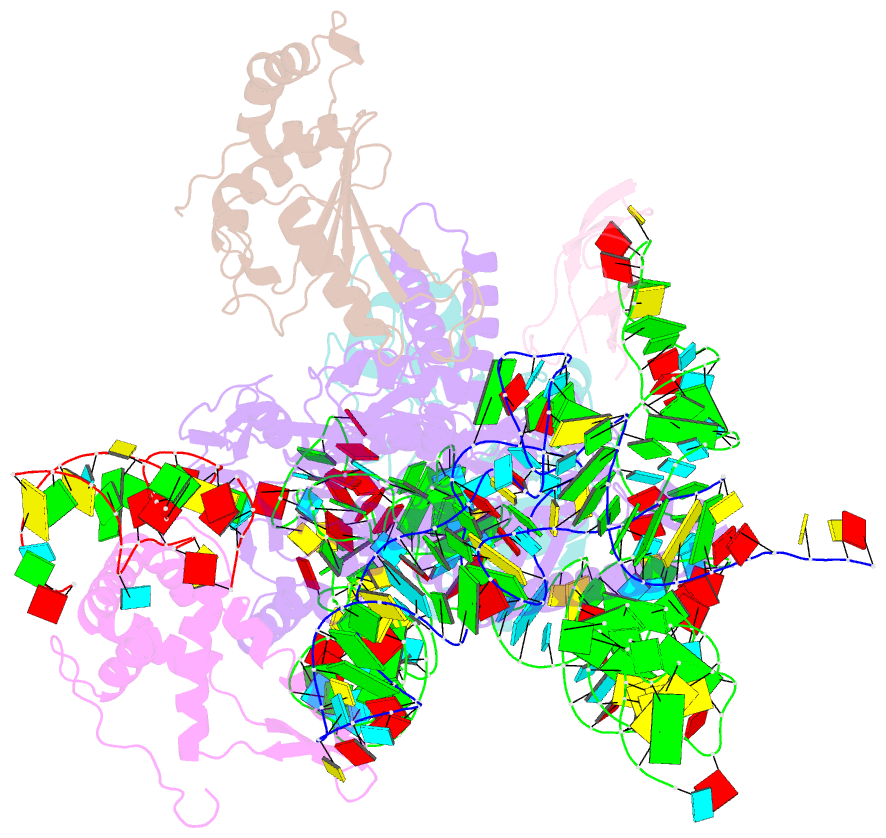
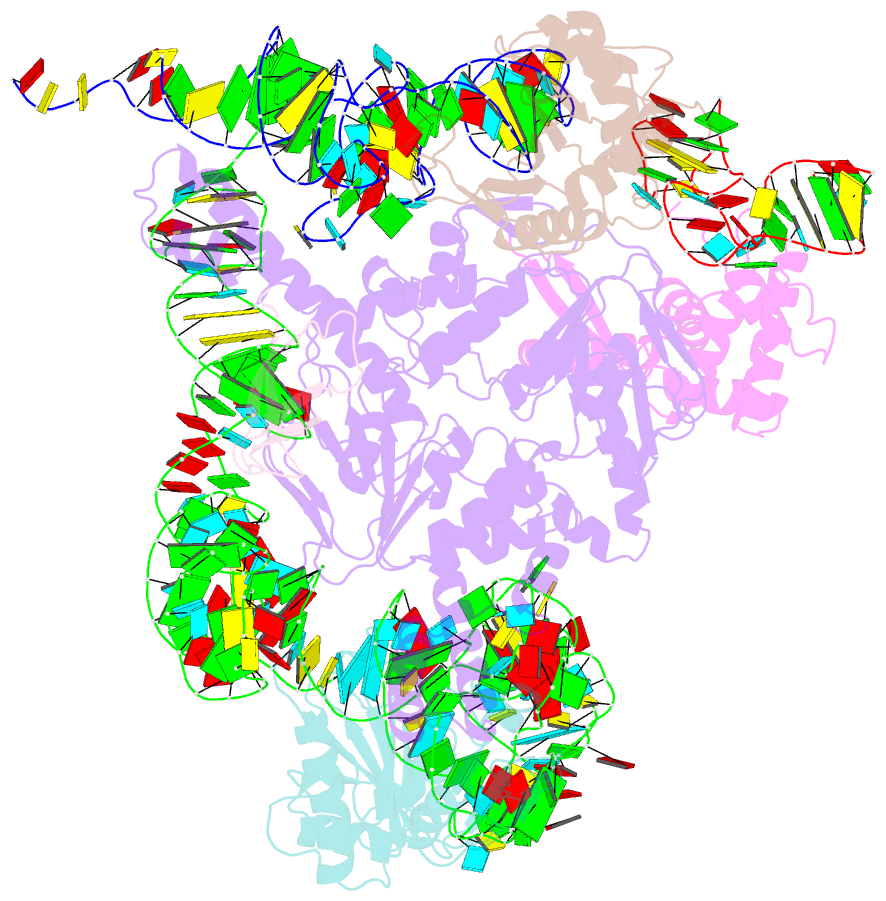
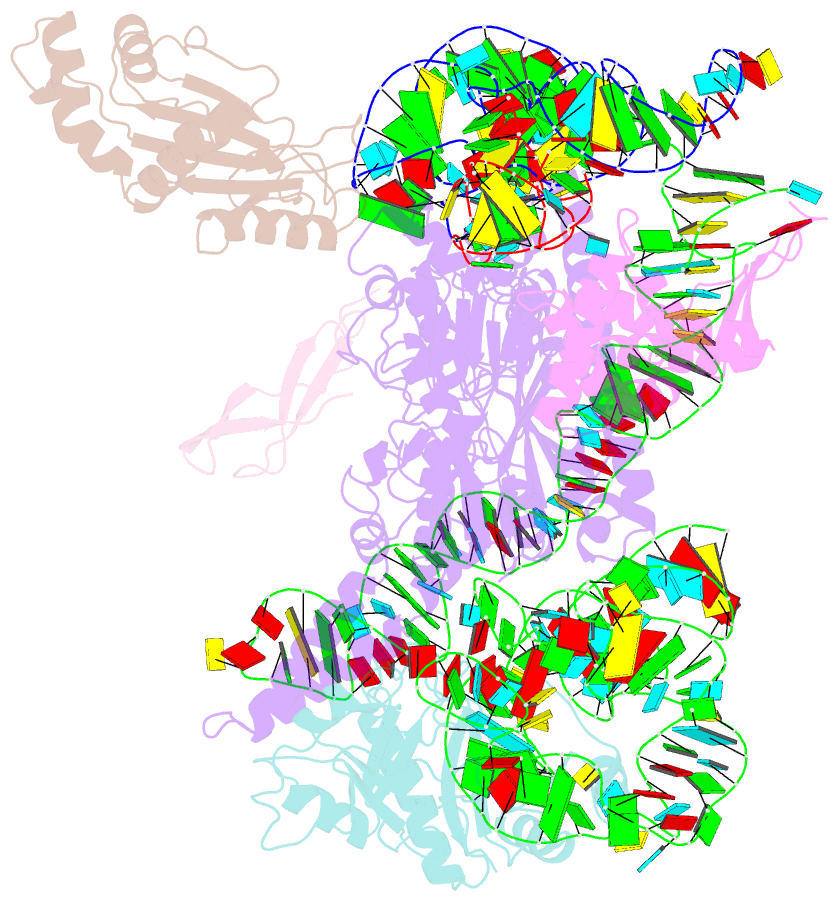
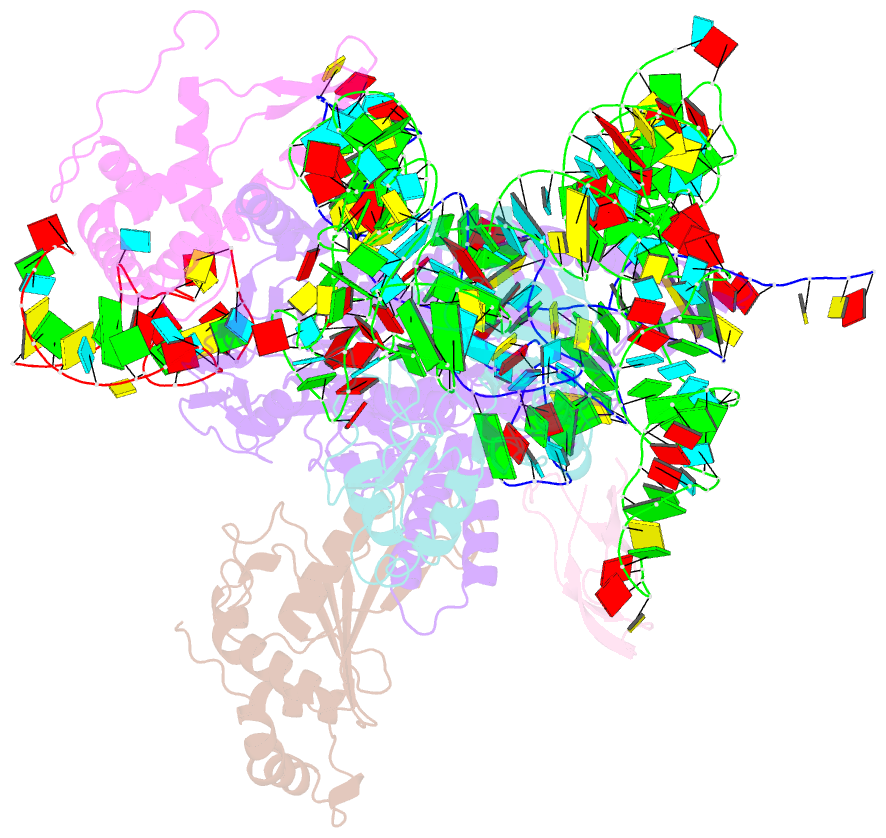
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
3j5s;
DSSR-derived features in text and
JSON formats; DNAproDB
- Class
- ribosome-translation
- Method
- cryo-EM (7.5 Å)
- Summary
- Etta binds to ribosome exit site and regulates
translation by restricting ribosome and trna dynamics
- Reference
-
Chen B, Boel G, Hashem Y, Ning W, Fei J, Wang C, Gonzalez
RL, Hunt JF, Frank J (2014): "EttA
regulates translation by binding the ribosomal E site and
restricting ribosome-tRNA dynamics."
Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 21,
152-159. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2741.
- Abstract
- Cells express many ribosome-interacting factors whose
functions and molecular mechanisms remain unknown. Here, we
elucidate the mechanism of a newly characterized regulatory
translation factor, energy-dependent translational throttle
A (EttA), which is an Escherichia coli representative of
the ATP-binding cassette F (ABC-F) protein family. Using
cryo-EM, we demonstrate that the ATP-bound form of EttA
binds to the ribosomal tRNA-exit site, where it forms
bridging interactions between the ribosomal L1 stalk and
the tRNA bound in the peptidyl-tRNA-binding site. Using
single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer, we
show that the ATP-bound form of EttA restricts ribosome and
tRNA dynamics required for protein synthesis. This work
represents the first example, to our knowledge, in which
the detailed molecular mechanism of any ABC-F family
protein has been determined and establishes a framework for
elucidating the mechanisms of other regulatory translation
factors.