Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3j7a; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ribosome-inhibitor
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.2 Å)
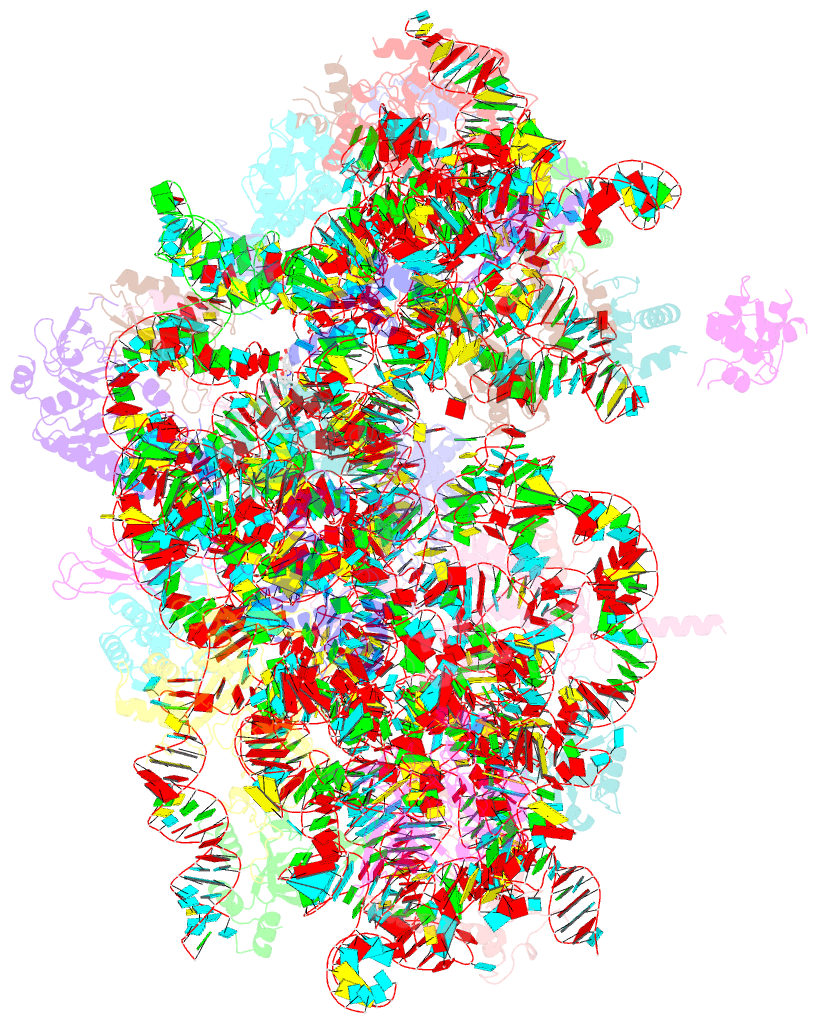
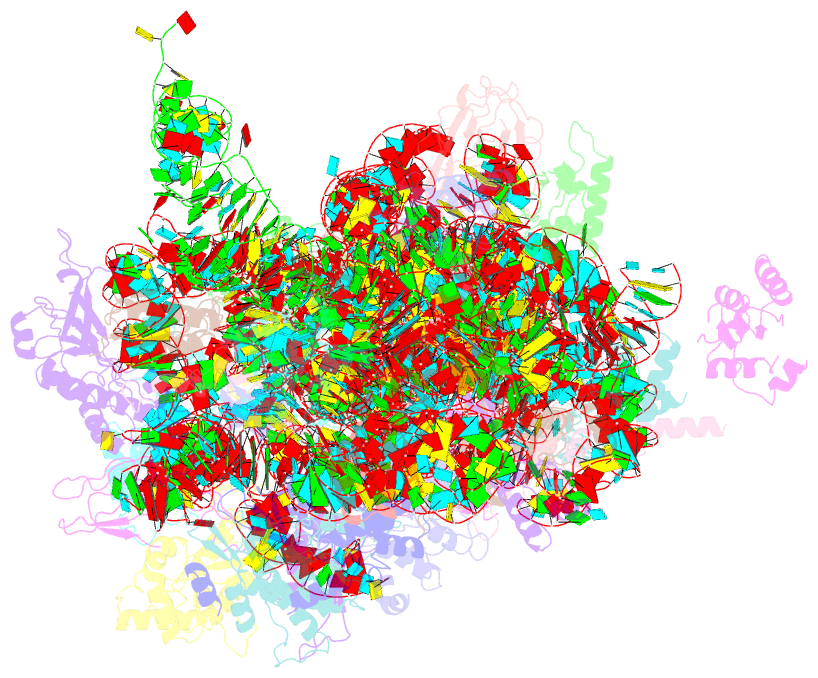
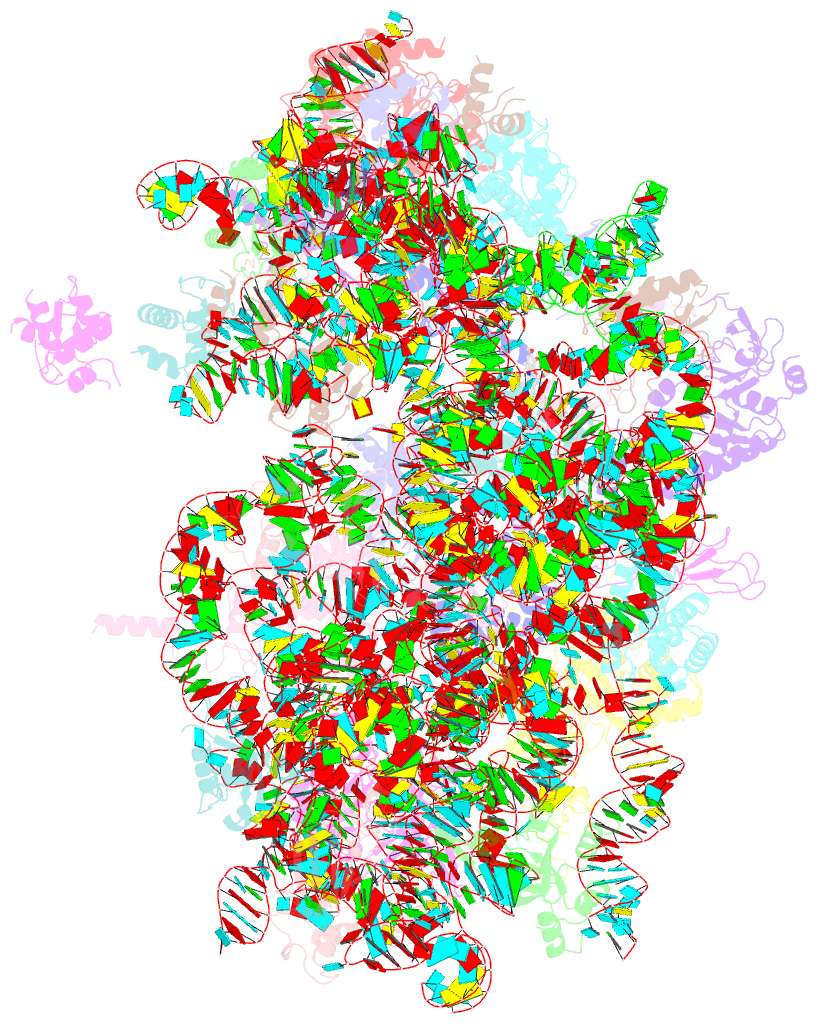
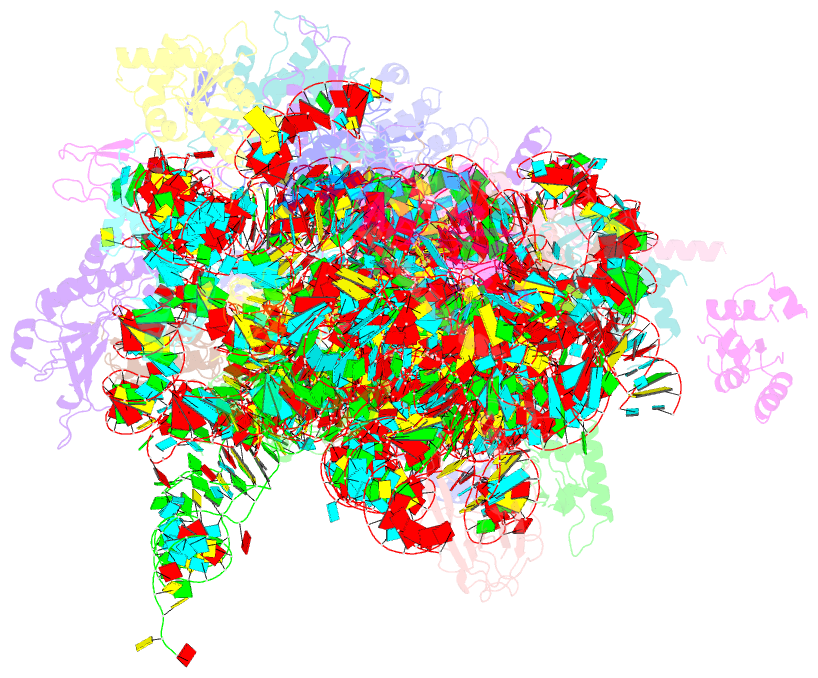
- Summary
- cryo-EM structure of the plasmodium falciparum 80s ribosome bound to the anti-protozoan drug emetine, small subunit
- Reference
- Wong W, Bai XC, Brown A, Fernandez IS, Hanssen E, Condron M, Tan YH, Baum J, Scheres SH (2014): "Cryo-EM structure of the Plasmodium falciparum 80S ribosome bound to the anti-protozoan drug emetine." Elife, 3, e03080. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03080.
- Abstract
- Malaria inflicts an enormous burden on global human health. The emergence of parasite resistance to front-line drugs has prompted a renewed focus on the repositioning of clinically approved drugs as potential anti-malarial therapies. Antibiotics that inhibit protein translation are promising candidates for repositioning. We have solved the cryo-EM structure of the cytoplasmic ribosome from the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, in complex with emetine at 3.2 Å resolution. Emetine is an anti-protozoan drug used in the treatment of ameobiasis that also displays potent anti-malarial activity. Emetine interacts with the E-site of the ribosomal small subunit and shares a similar binding site with the antibiotic pactamycin, thereby delivering its therapeutic effect by blocking mRNA/tRNA translocation. As the first cryo-EM structure that visualizes an antibiotic bound to any ribosome at atomic resolution, this establishes cryo-EM as a powerful tool for screening and guiding the design of drugs that target parasite translation machinery.