Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3khc; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- oxidoreductase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.2 Å)
- Summary
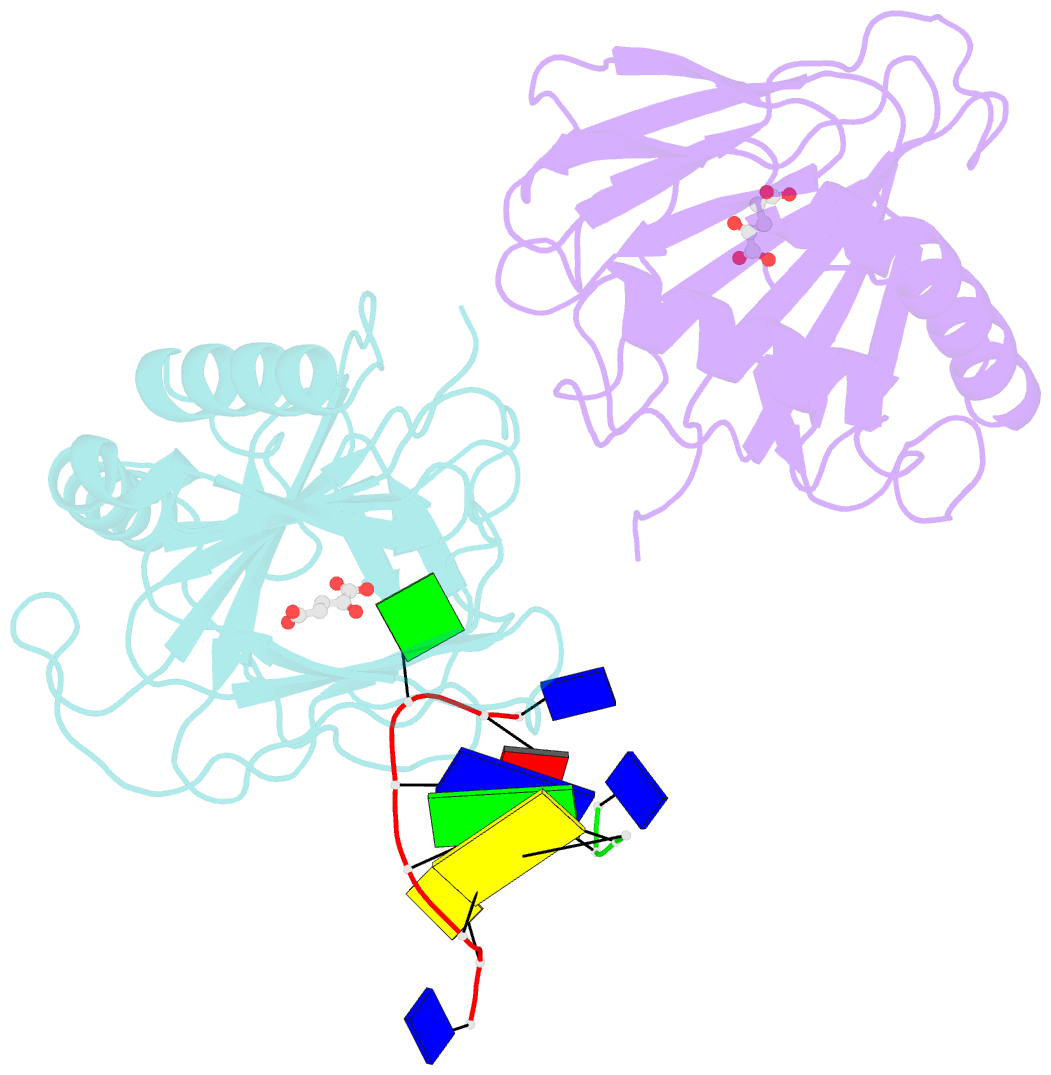
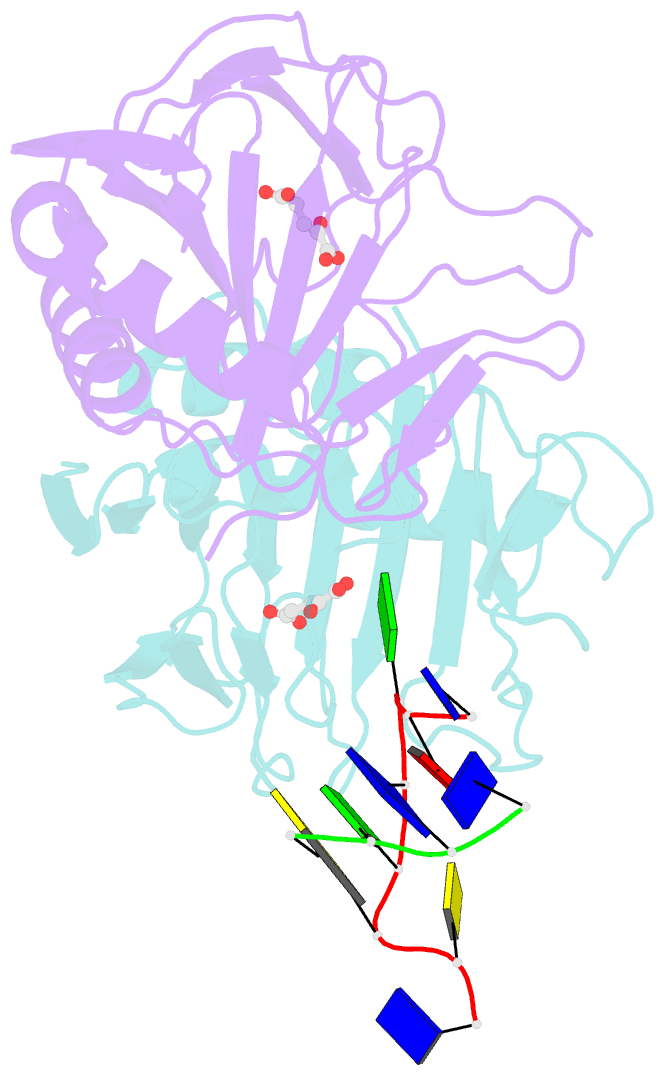
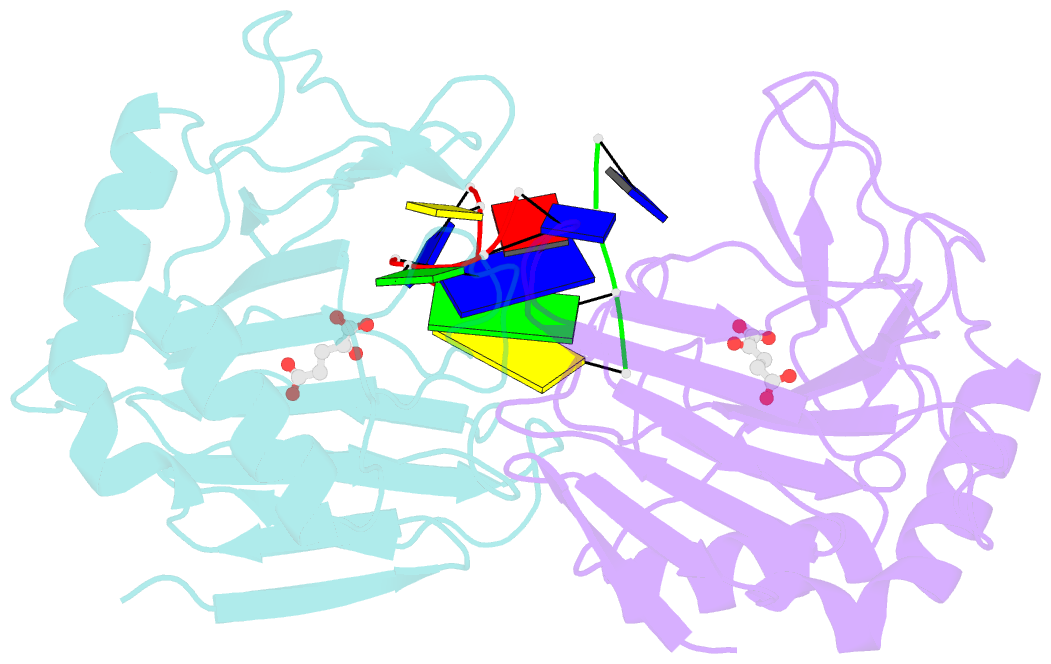
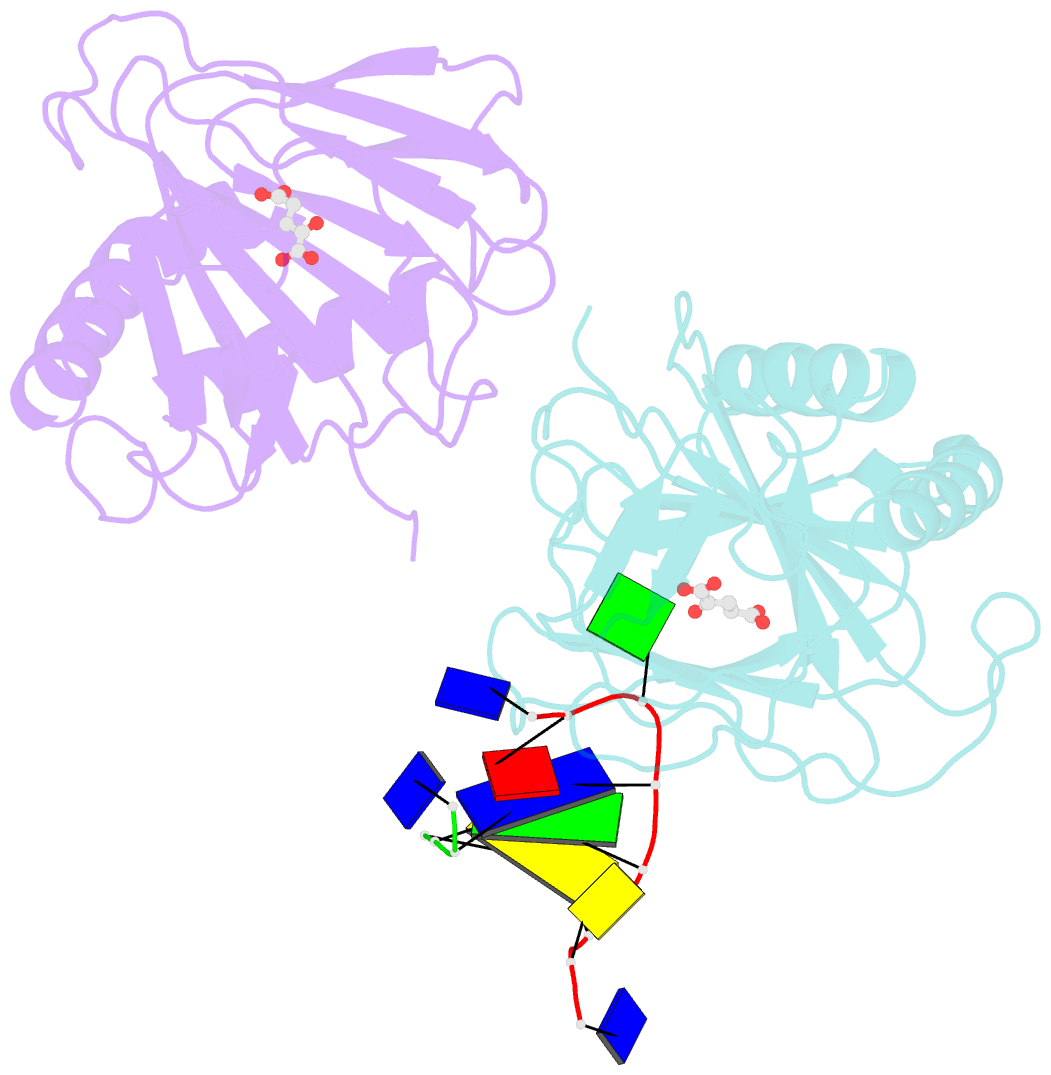
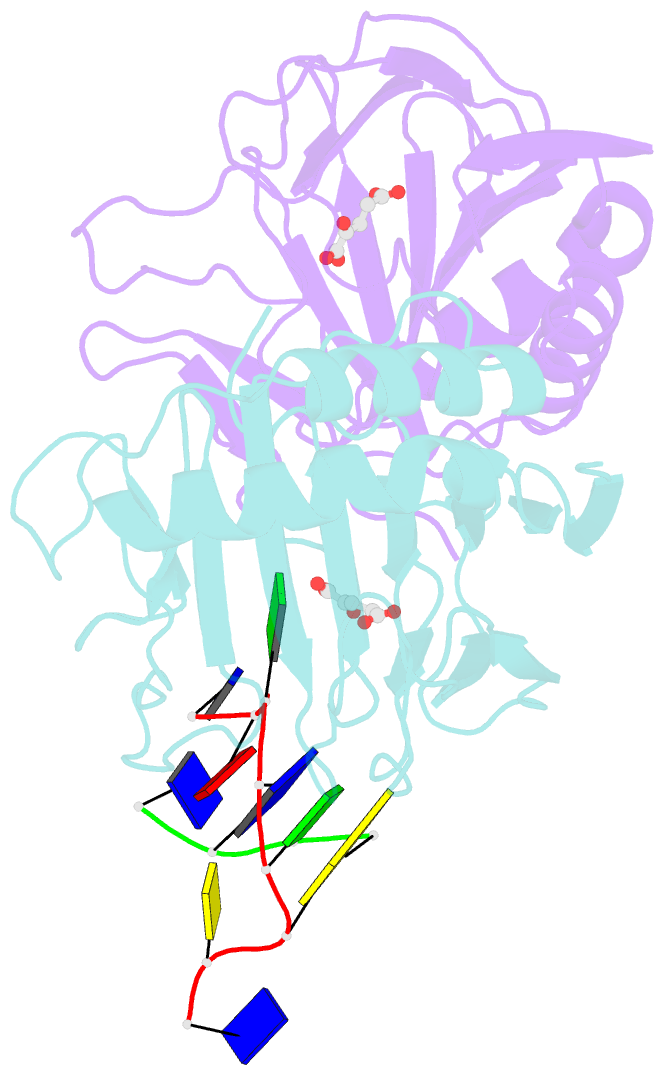
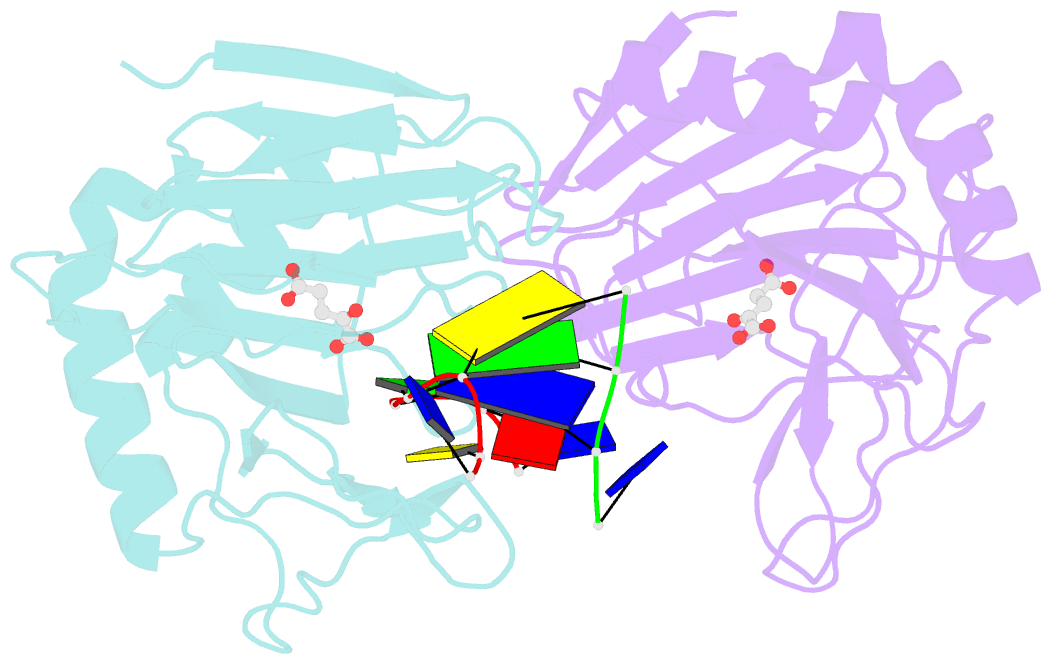
- Crystal structure of escherichia coli alkb in complex with ssDNA containing a 1-methylguanine lesion
- Reference
- Holland PJ, Hollis T (2010): "Structural and mutational analysis of Escherichia coli AlkB provides insight into substrate specificity and DNA damage searching." Plos One, 5, e8680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008680.
- Abstract
- Background: In Escherichia coli, cytotoxic DNA methyl lesions on the N1 position of purines and N3 position of pyrimidines are primarily repaired by the 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG) iron(II) dependent dioxygenase, AlkB. AlkB repairs 1-methyladenine (1-meA) and 3-methylcytosine (3-meC) lesions, but it also repairs 1-methylguanine (1-meG) and 3-methylthymine (3-meT) at a much less efficient rate. How the AlkB enzyme is able to locate and identify methylated bases in ssDNA has remained an open question.