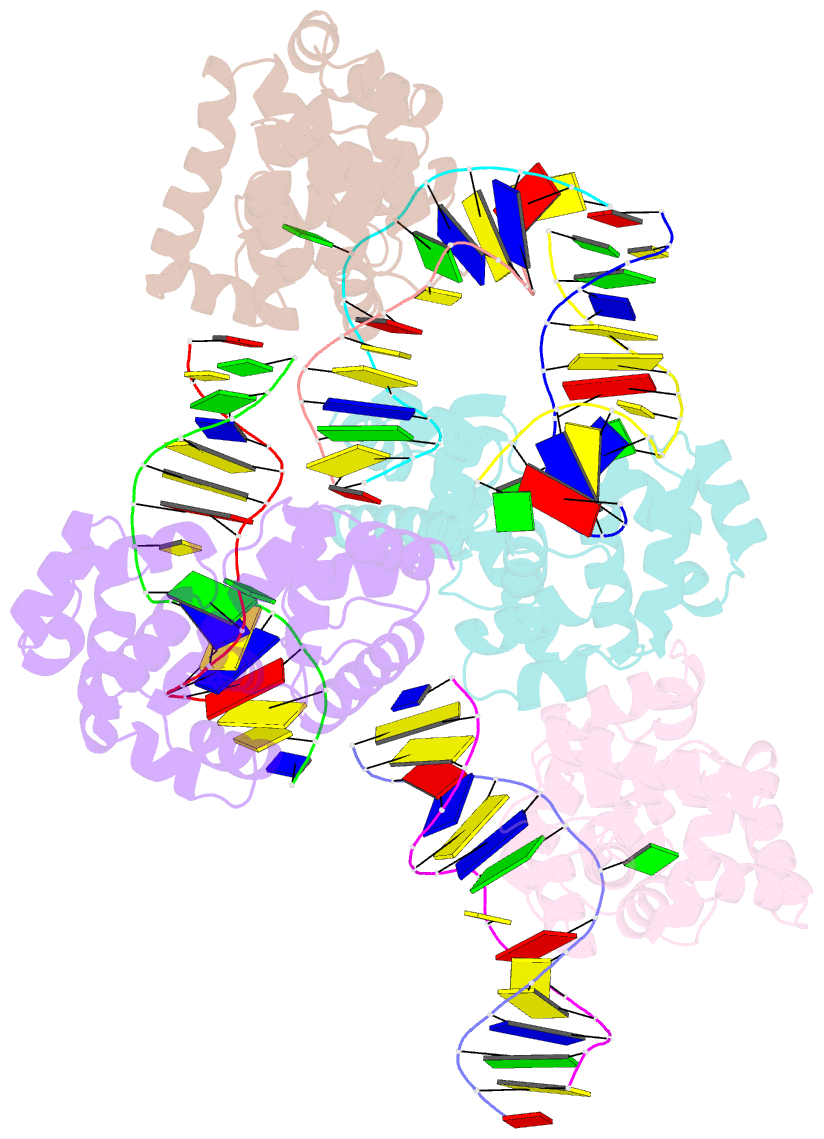
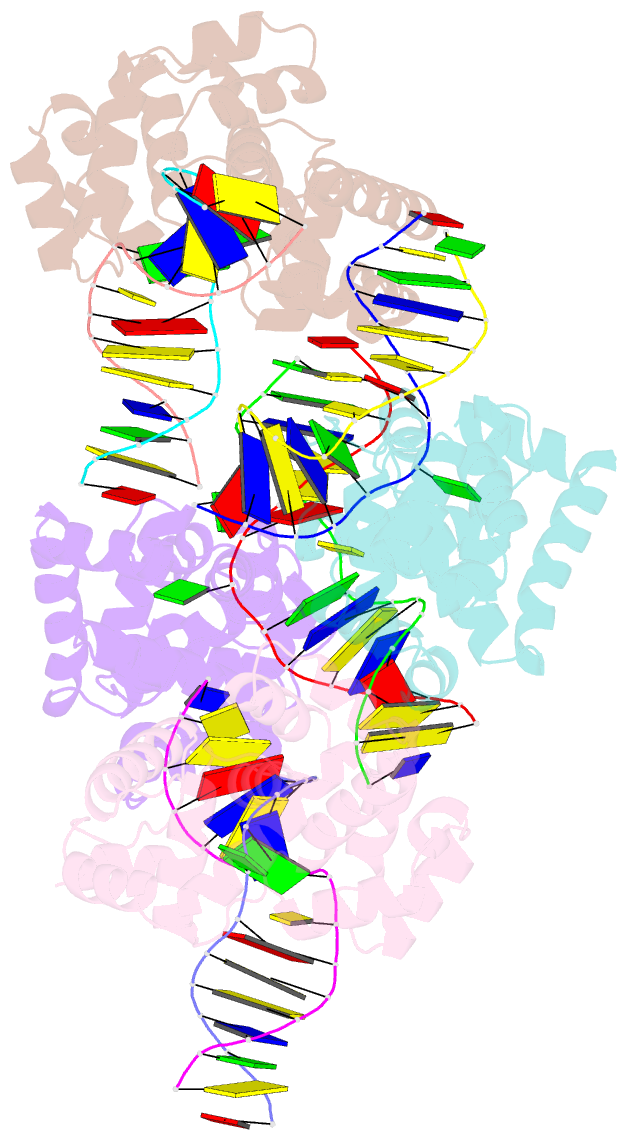
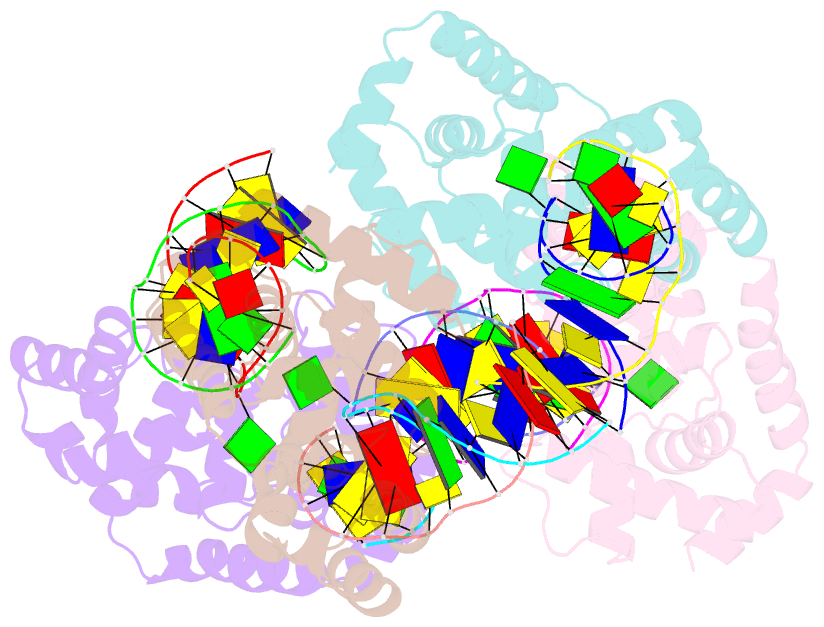
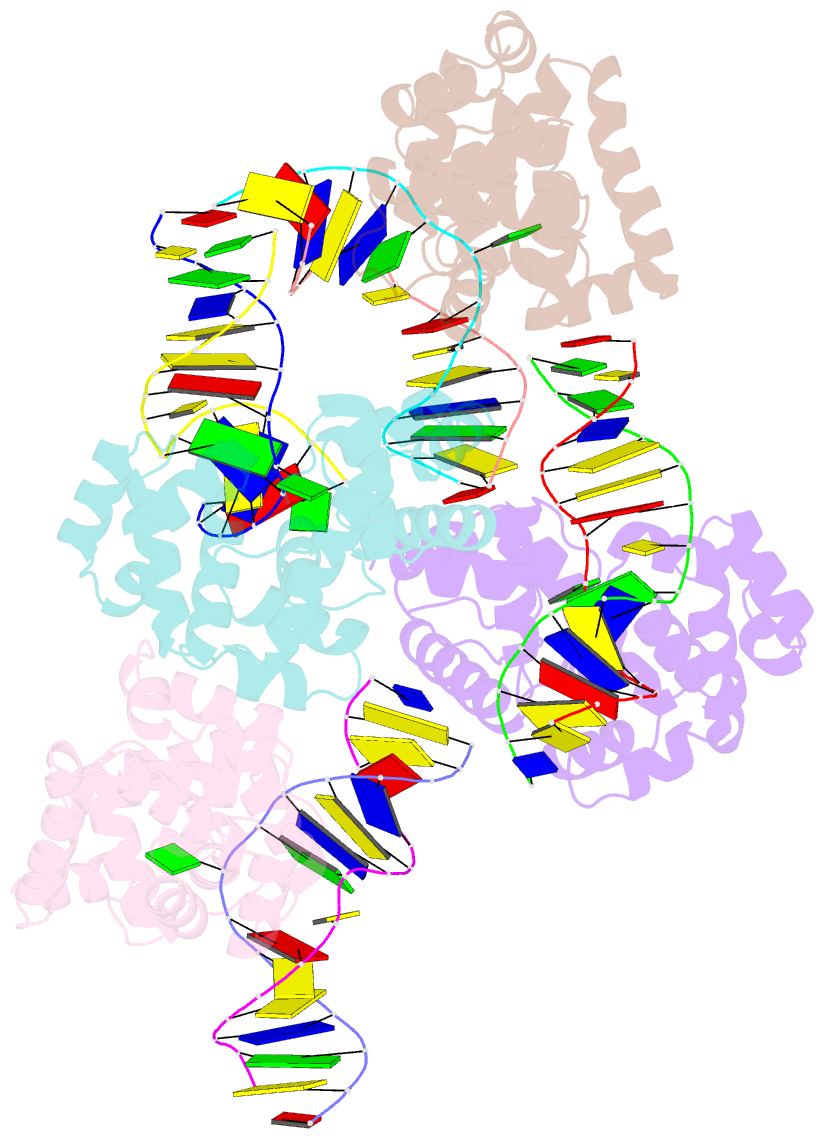
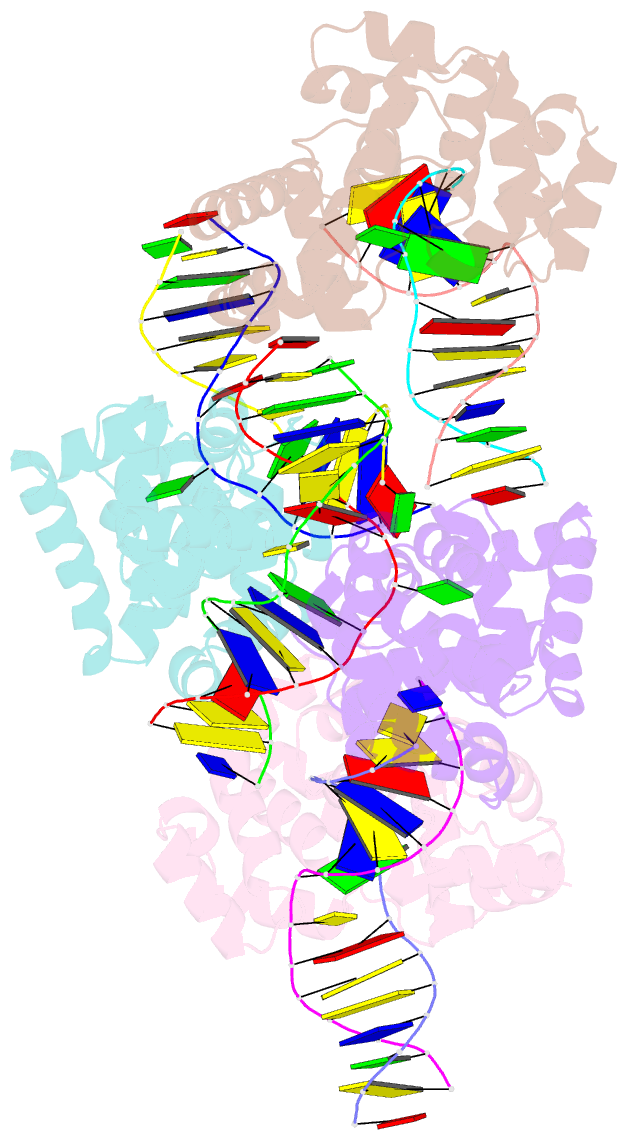
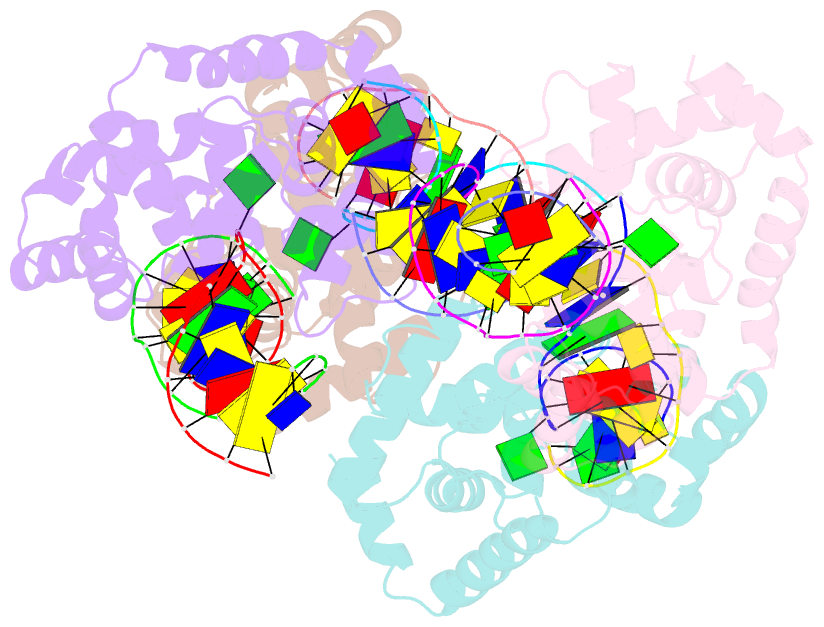
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3knt; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase, lyase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.7 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of methanocaldococcus jannaschii 8-oxoguanine glycosylase-lyase in complex with 15mer DNA containing 8-oxoguanine
- Reference
- Faucher F, Wallace SS, Doublie S (2010): "The C-terminal Lysine of Ogg2 DNA Glycosylases is a Major Molecular Determinant for Guanine/8-Oxoguanine Distinction." J.Mol.Biol., 397, 46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.024.
- Abstract
- 7,8-Dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG) is a major oxidative lesion found in DNA. The 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylases (Ogg) responsible for the removal of 8-oxoG are divided into three families Ogg1, Ogg2 and AGOG. The Ogg2 members are devoid of the recognition loop used by Ogg1 to discriminate between 8-oxoG and guanine and it was unclear until recently how Ogg2 enzymes recognize the oxidized base. We present here the first crystallographic structure of an Ogg2 member, Methanocaldococcus janischii Ogg, in complex with a DNA duplex containing the 8-oxoG lesion. This structure highlights the crucial role of the C-terminal lysine, strictly conserved in Ogg2, in the recognition of 8-oxoG. The structure also reveals that Ogg2 undergoes a conformational change upon DNA binding similar to that observed in Ogg1 glycosylases. Furthermore, this work provides a structural rationale for the lack of opposite base specificity in this family of enzymes.