Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3kuy; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- structural protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.9 Å)
- Summary
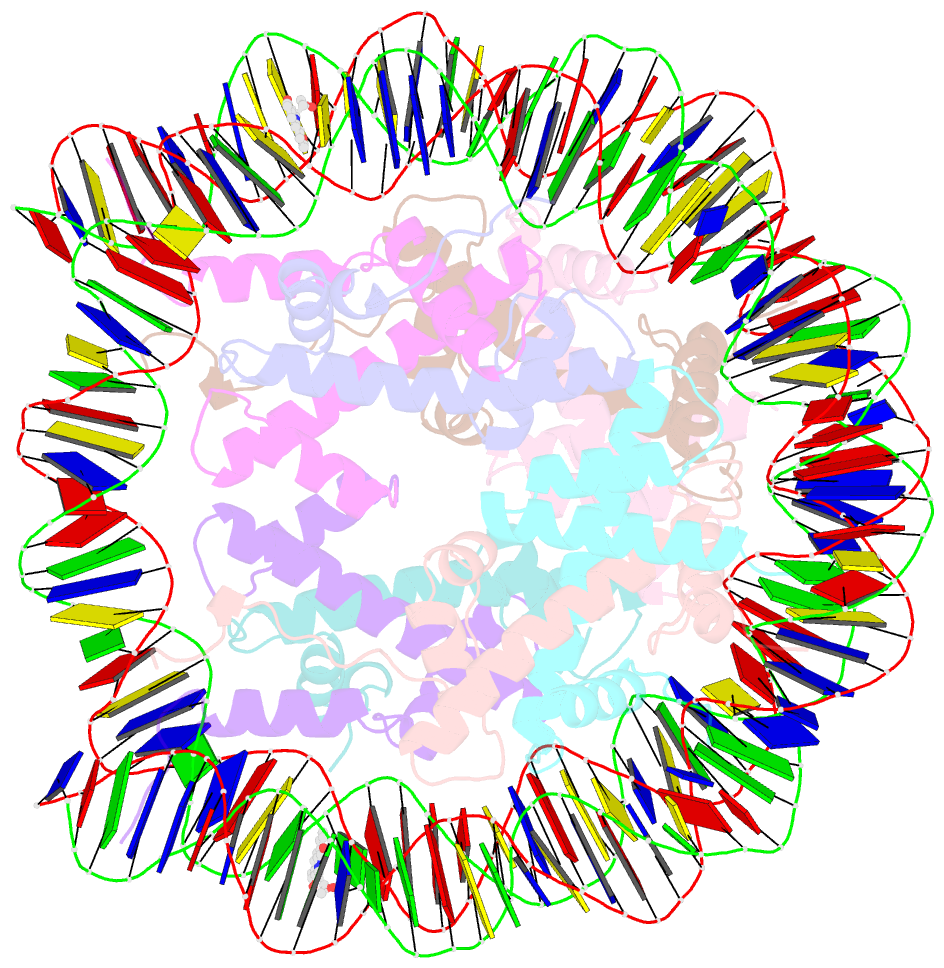
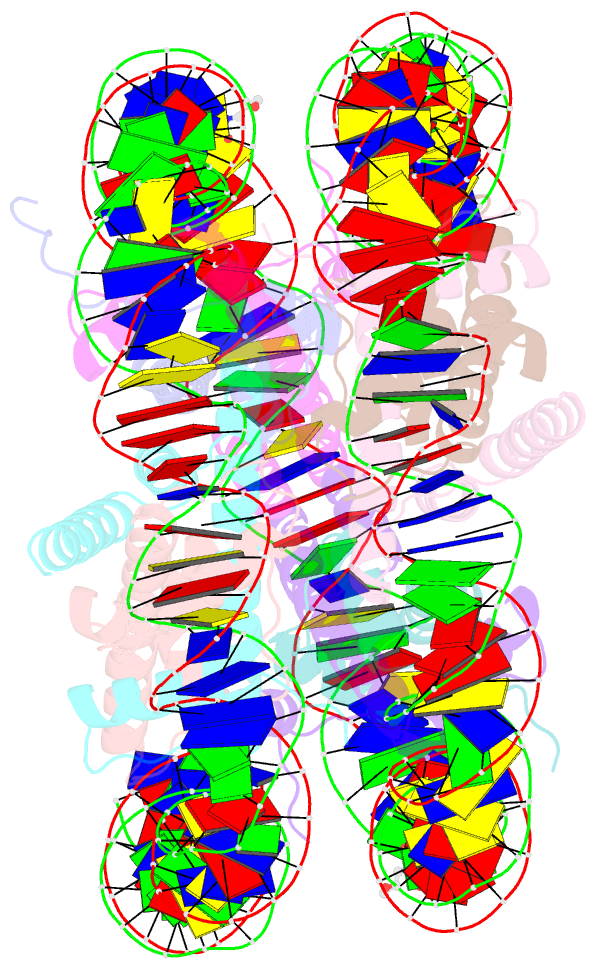
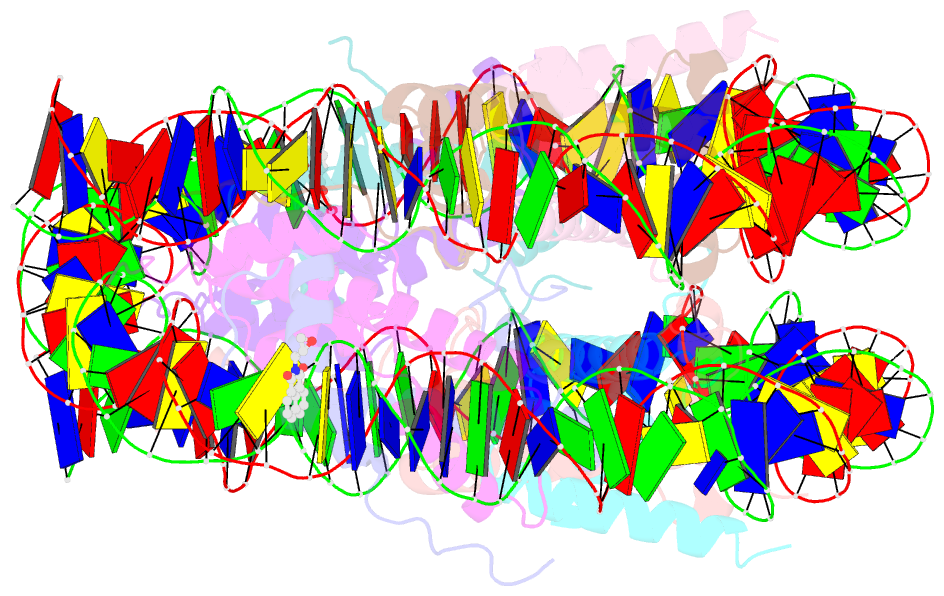
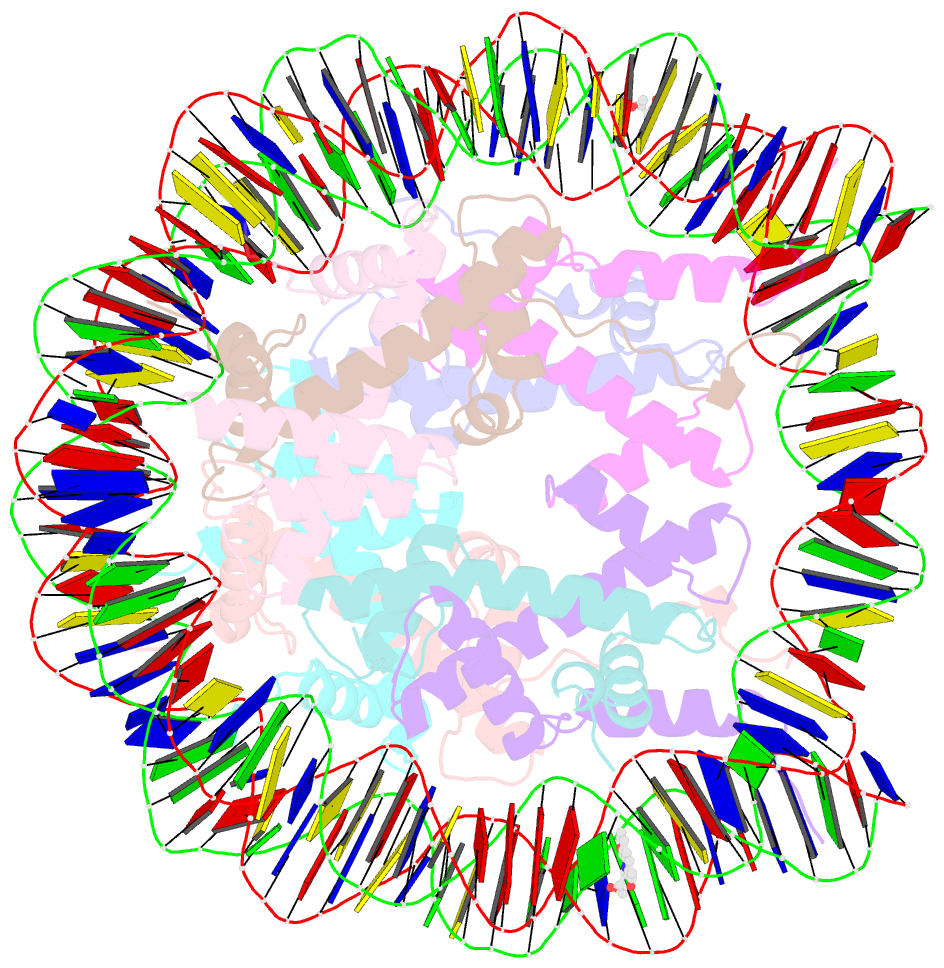
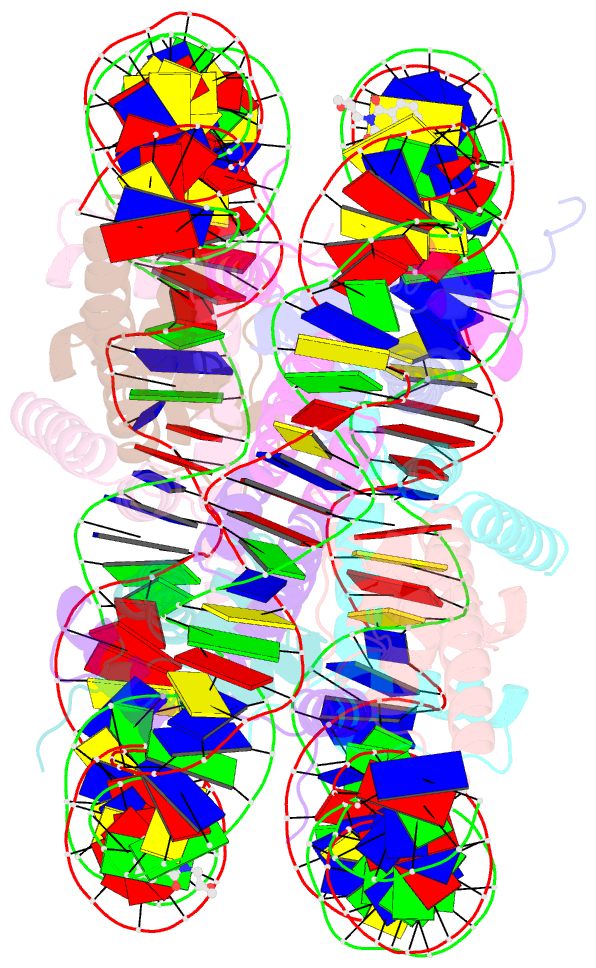
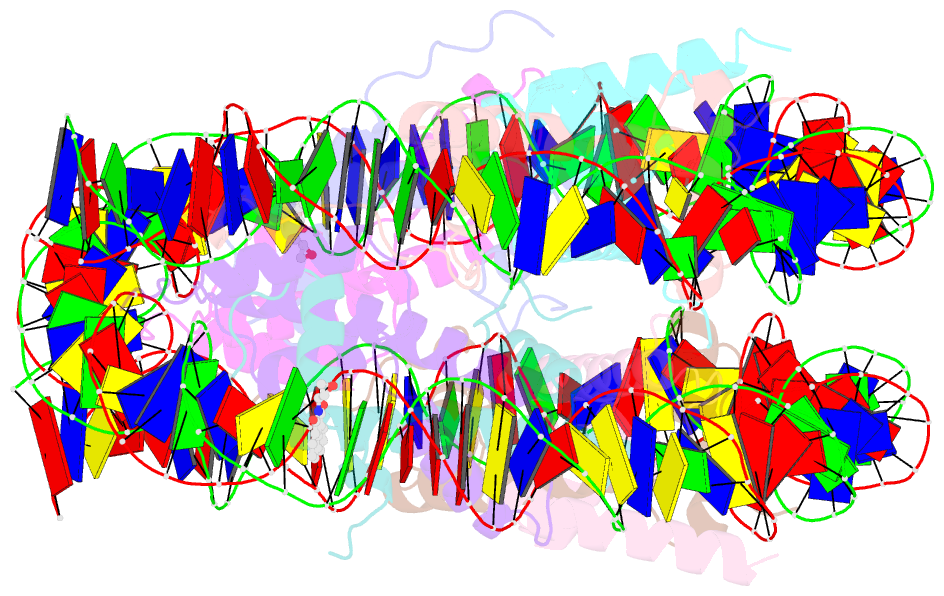
- DNA stretching in the nucleosome facilitates alkylation by an intercalating antitumor agent
- Reference
- Davey GE, Wu B, Dong Y, Surana U, Davey CA (2010): "DNA stretching in the nucleosome facilitates alkylation by an intercalating antitumour agent." Nucleic Acids Res., 38, 2081-2088. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1174.
- Abstract
- DNA stretching in the nucleosome core can cause dramatic structural distortions, which may influence compaction and factor recognition in chromatin. We find that the base pair unstacking arising from stretching-induced extreme minor groove kinking near the nucleosome centre creates a hot spot for intercalation and alkylation by a novel anticancer compound. This may have far reaching implications for how chromatin structure can influence binding of intercalator species and indicates potential for the development of site selective DNA-binding agents that target unique conformational features of the nucleosome.