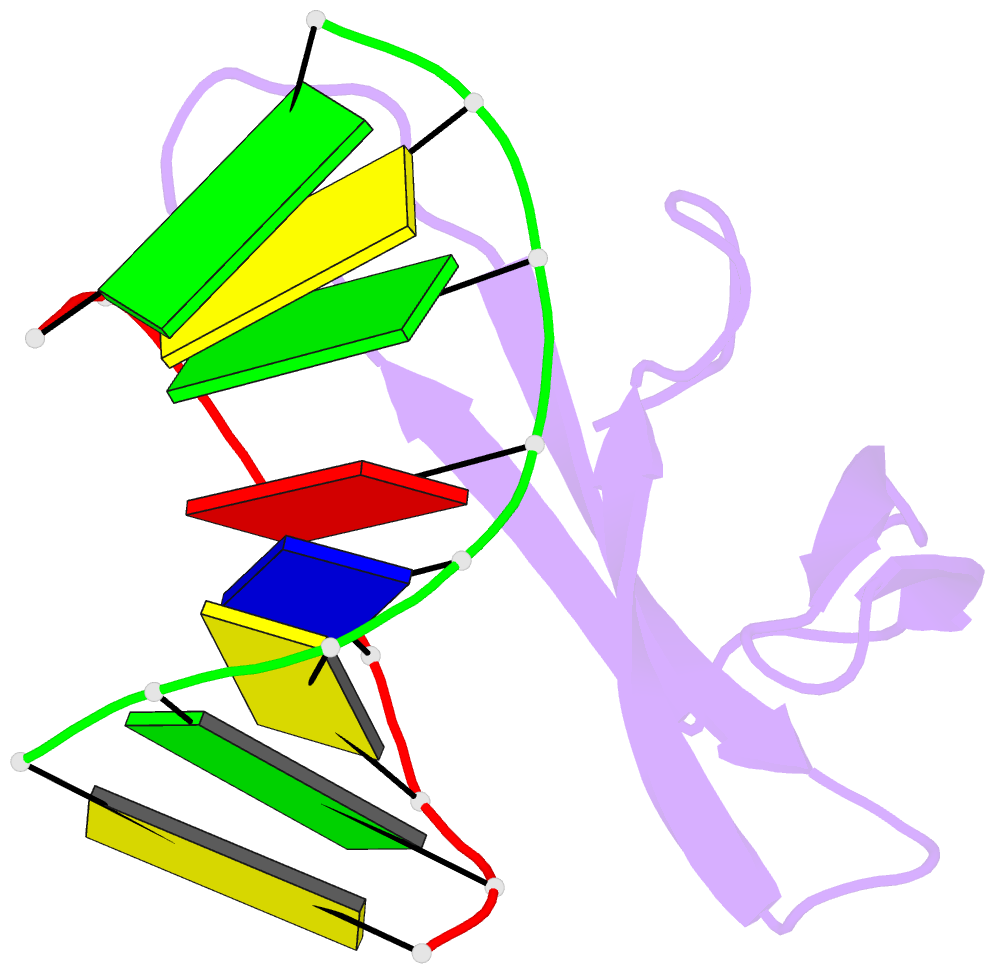
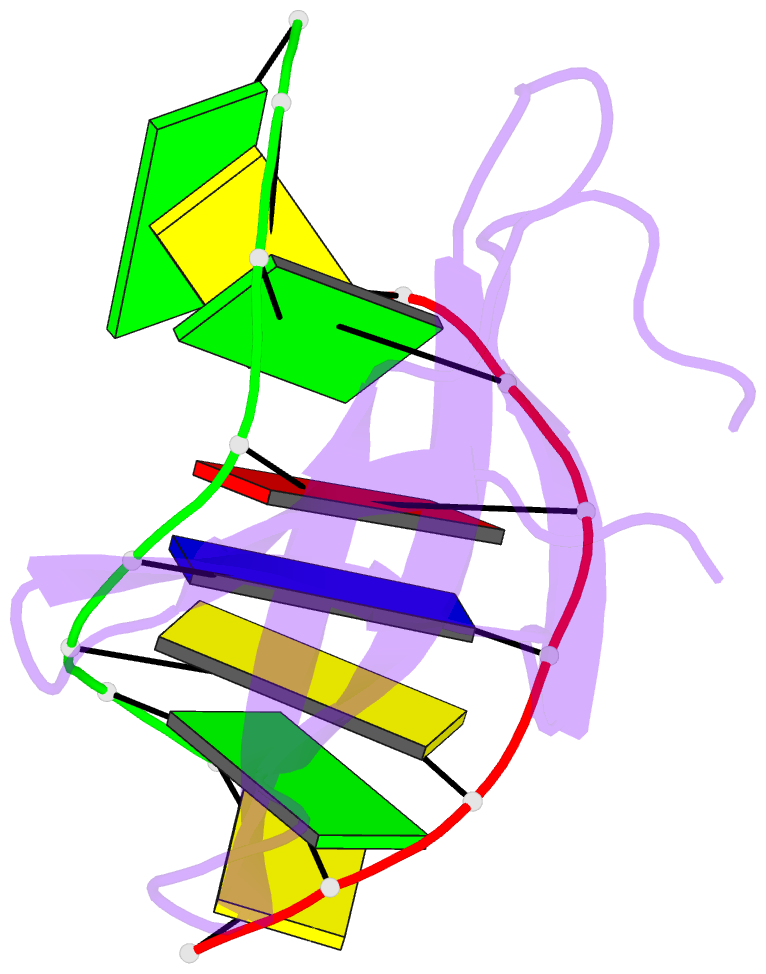
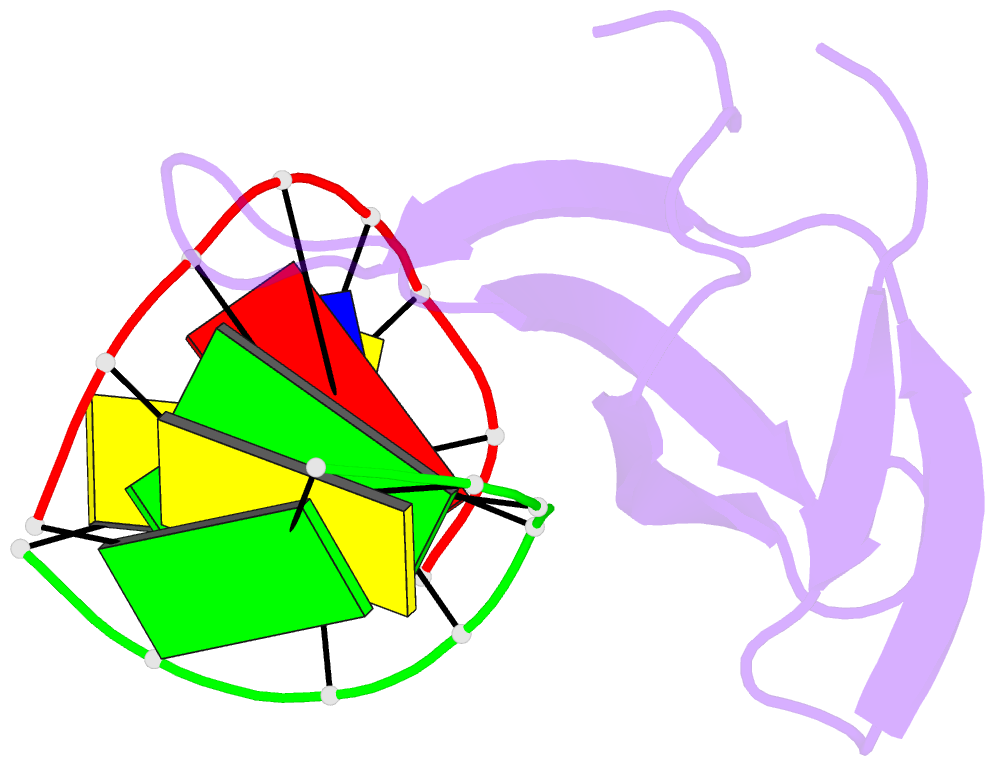
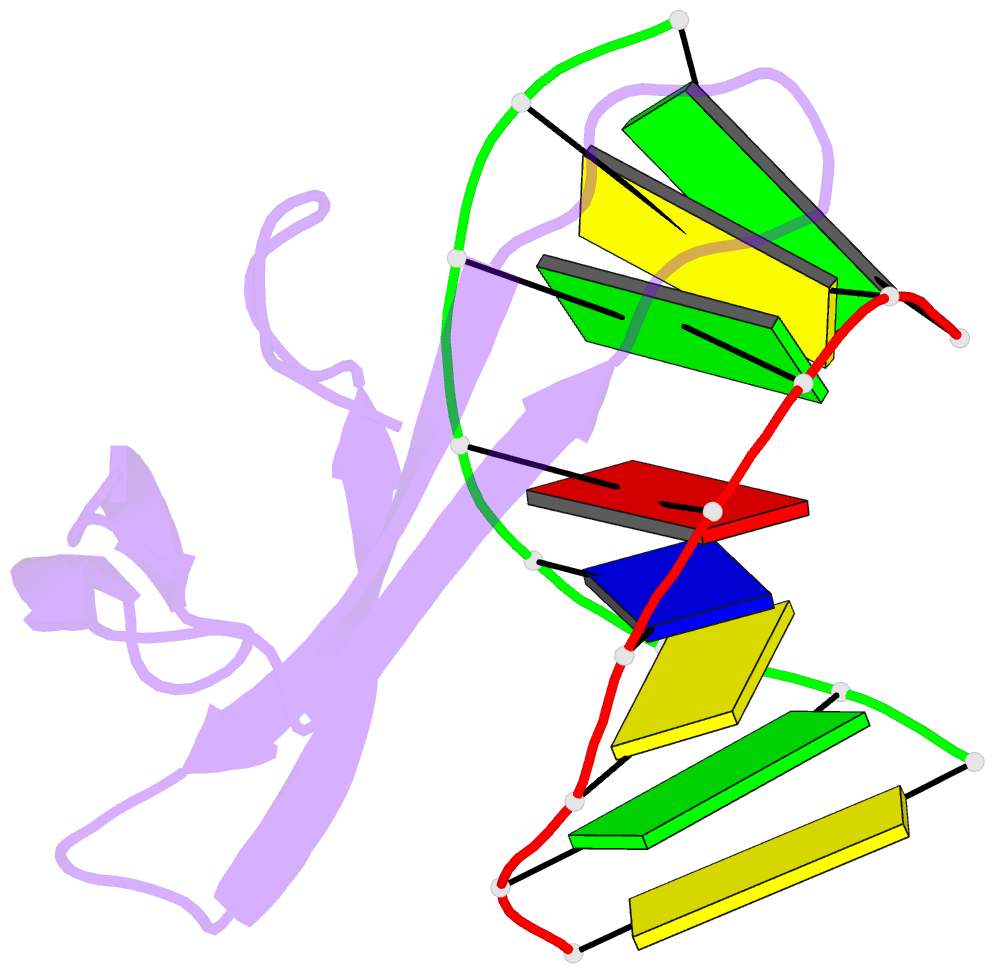
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3kxt; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.602 Å)
- Summary
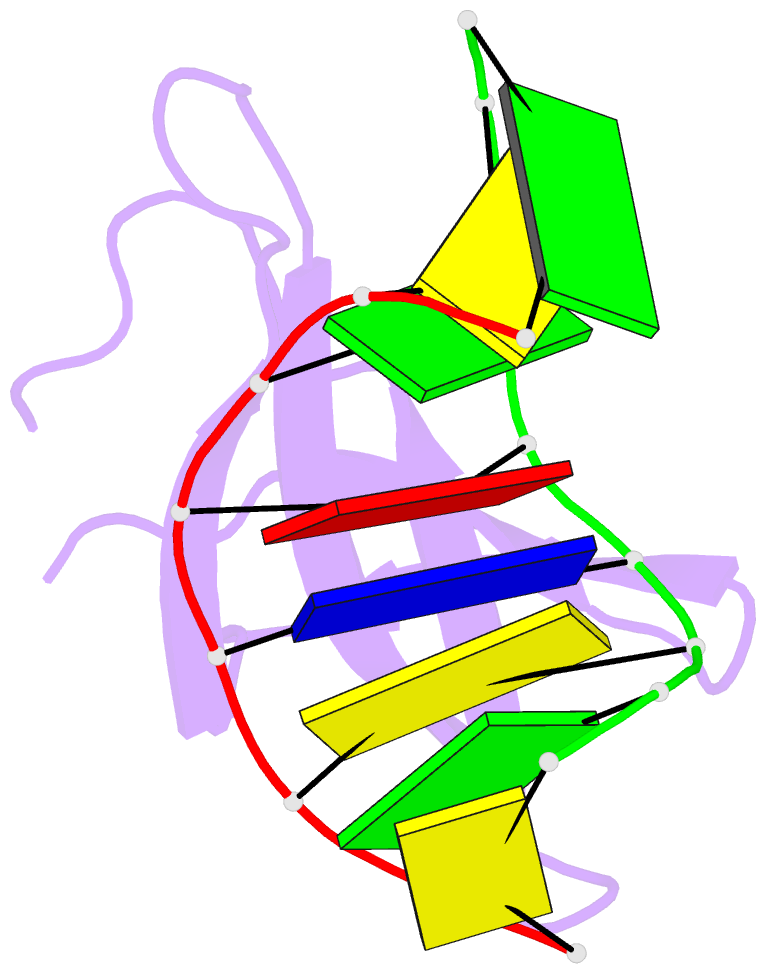
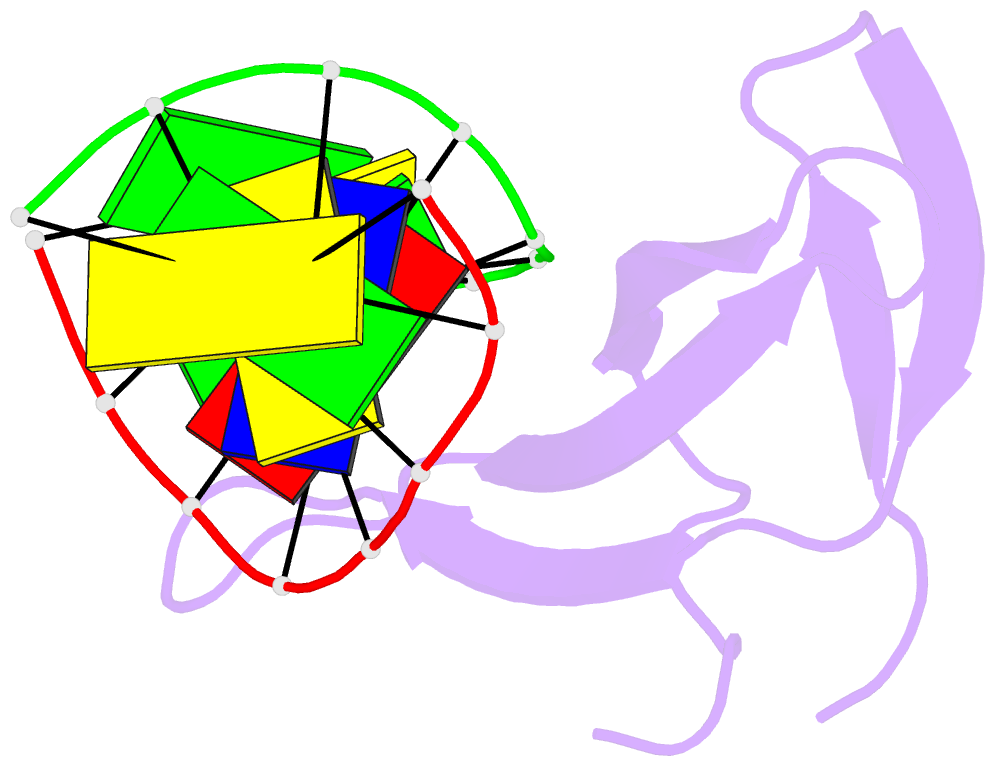
- Crystal structure of sulfolobus cren7-dsDNA complex
- Reference
- Feng Y, Yao H, Wang J (2010): "Crystal structure of the crenarchaeal conserved chromatin protein Cren7 and double-stranded DNA complex." Protein Sci., 19, 1253-1257. doi: 10.1002/pro.385.
- Abstract
- Cren7 is a crenarchaeal conserved chromatin protein discovered recently. To explore the mechanism of the DNA packaging in Crenarchaeota, the crystal structure of Cren7-GCGATCGC complex has been determined and refined at 1.6 A resolution. Cren7 kinks the dsDNA sharply similar to Sul7d, another chromatin protein existing only in Sulfolobales, which reveals that the "bending and unwinding" compacting mechanism is conserved in Crenarchaeota. Significant structural differences are revealed by comparing both protein-dsDNA complexes. The kinked sites on the same dsDNA in the complexes with Sul7d and Cren7 show one base pair shift. For Cren7, fewer charged residues in the beta-barrel structural region bind to DNA, and additionally, the flexible loop L(beta3beta4) is also involved in the binding. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays indicate that loop L(beta3beta4) is essential for DNA-binding of Cren7. These differences provide insight into the functional difference of both chromatin proteins, suggesting that Cren7 may be more regulative than Sul7d in the DNA-binding affinity by the methylation in the flexible loop L(beta3beta4) in vivo.