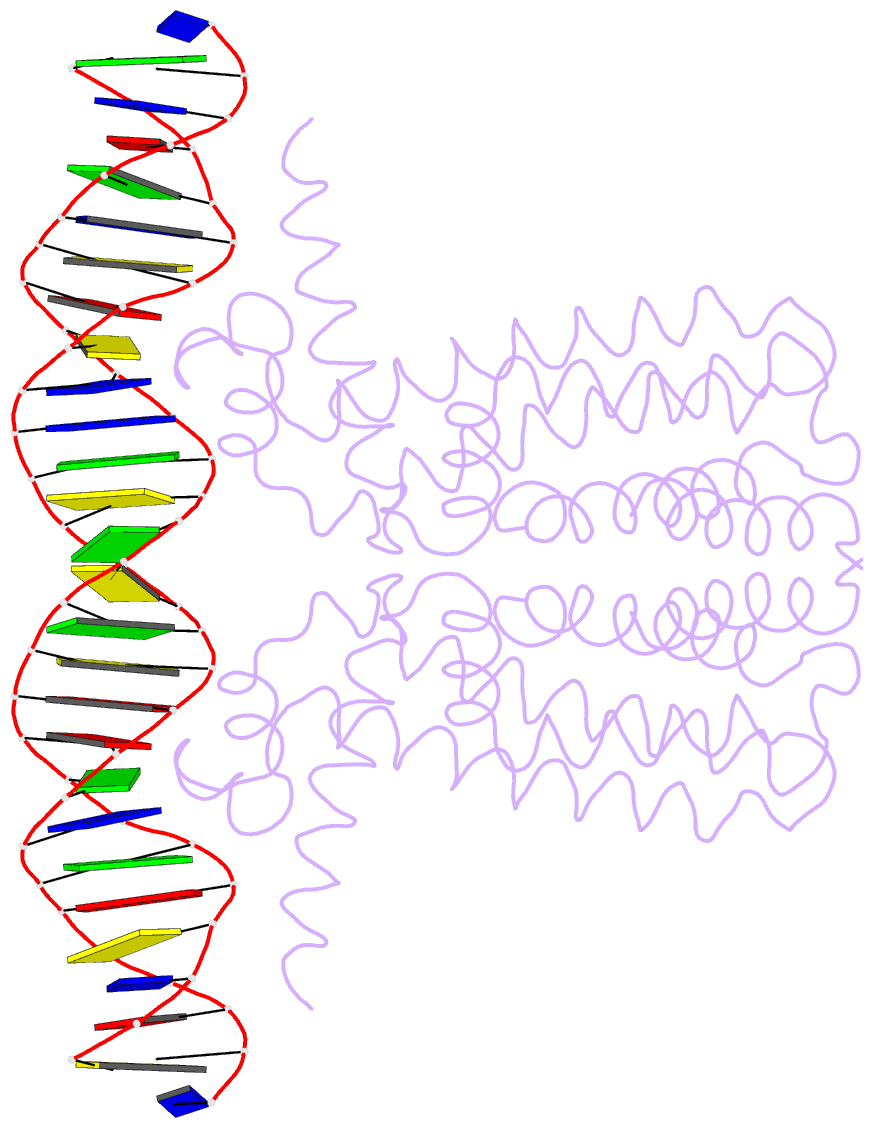
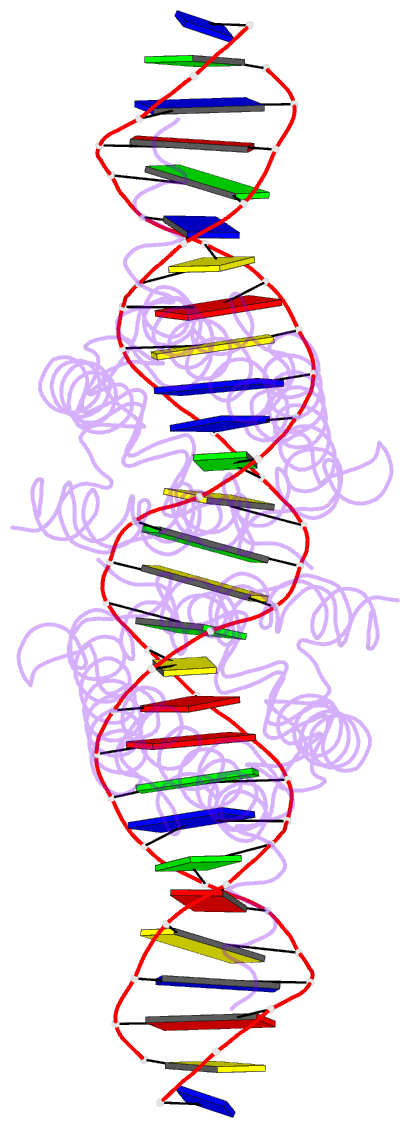
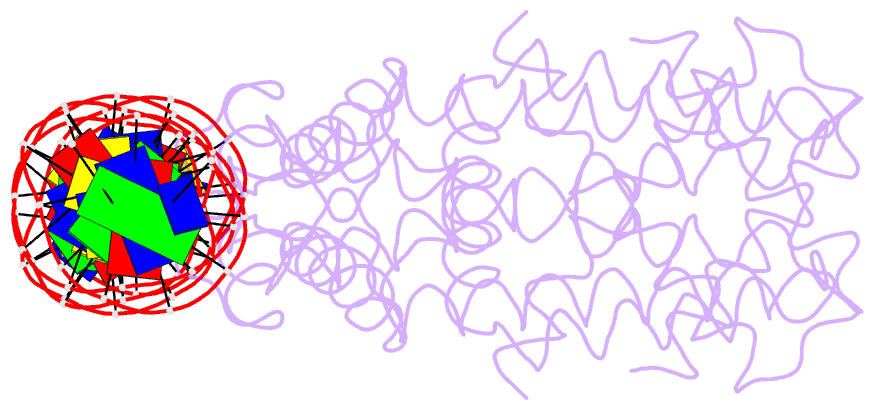
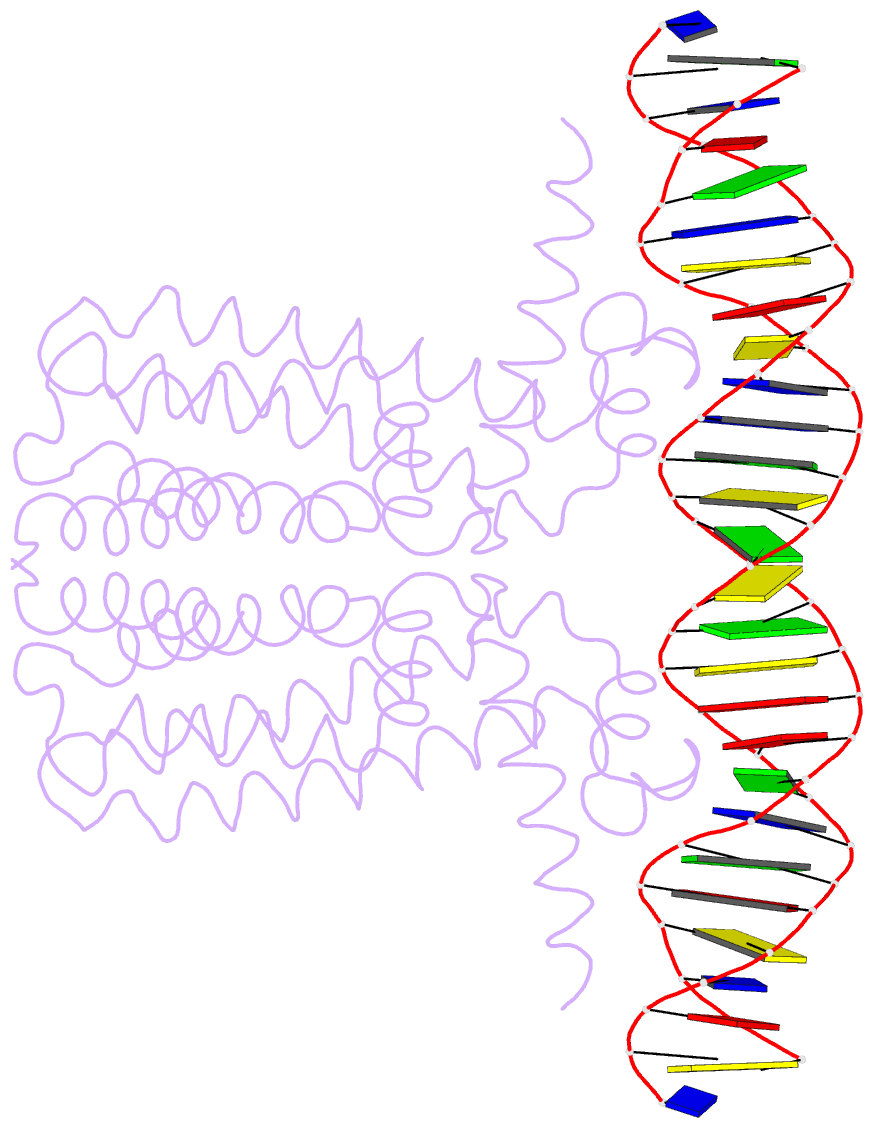
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3lsr; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.55 Å)
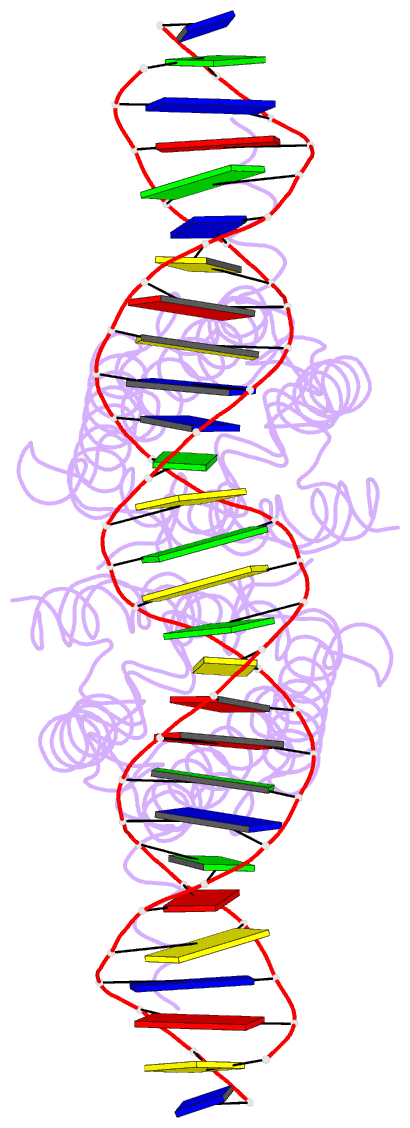
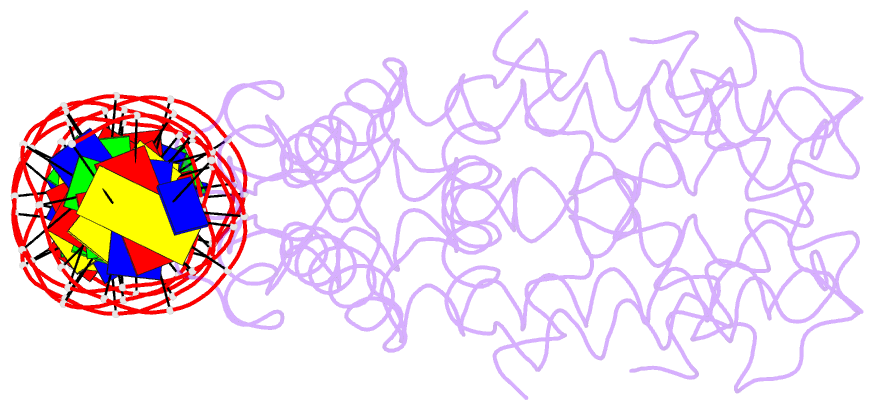
- Summary
- Crystal structure of dest in complex with duplex DNA
- Reference
- Miller DJ, Zhang YM, Subramanian C, Rock CO, White SW (2010): "Structural basis for the transcriptional regulation of membrane lipid homeostasis." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 17, 971-975. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1847.
- Abstract
- DesT is a transcriptional repressor that regulates the genes that control the unsaturated:saturated fatty acid ratio available for membrane lipid synthesis. DesT bound to unsaturated acyl-CoA has a high affinity for its cognate palindromic DNA-binding site, whereas DesT bound to saturated acyl-CoA does not bind this site. Structural analyses of the DesT-oleoyl-CoA-DNA and DesT-palmitoyl-CoA complexes reveal that acyl chain shape directly influences the packing of hydrophobic core residues within the DesT ligand-binding domain. These changes are propagated to the paired DNA-binding domains via conformational changes to modulate DNA binding. These structural interpretations are supported by the in vitro and in vivo characterization of site-directed mutants. The regulation of DesT by the unsaturated:saturated ratio of acyl chains rather than the concentration of a single ligand is a paradigm for understanding transcriptional regulation of membrane lipid homeostasis.