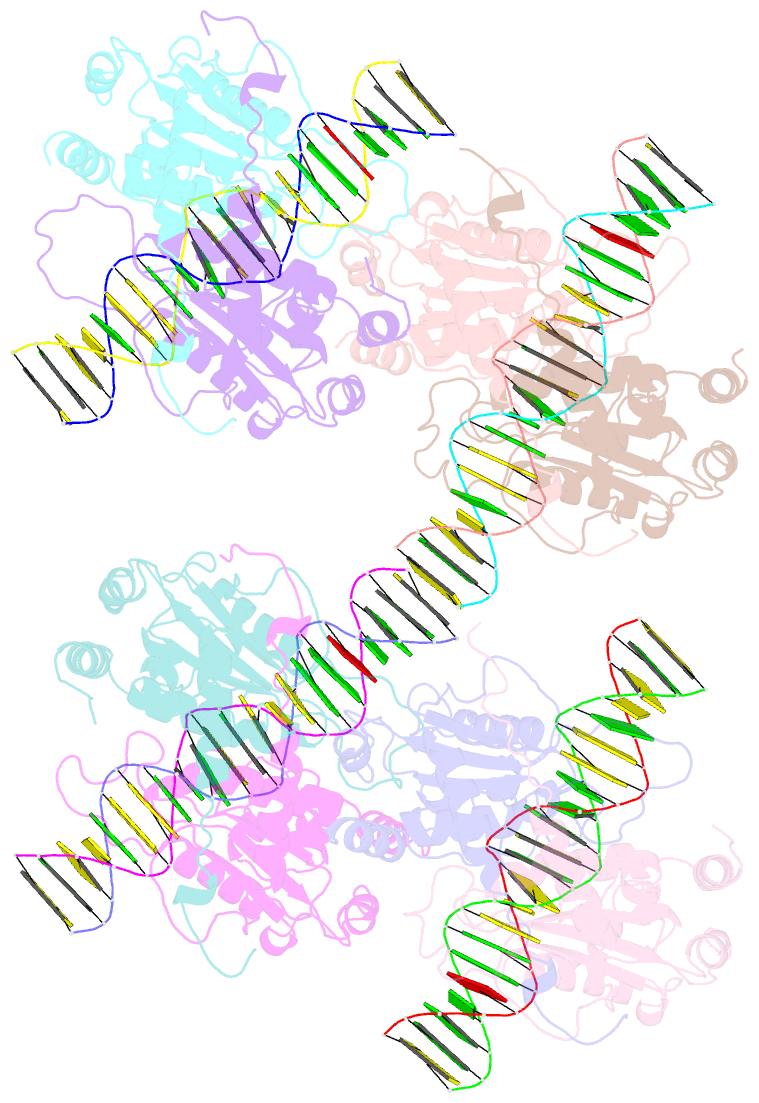
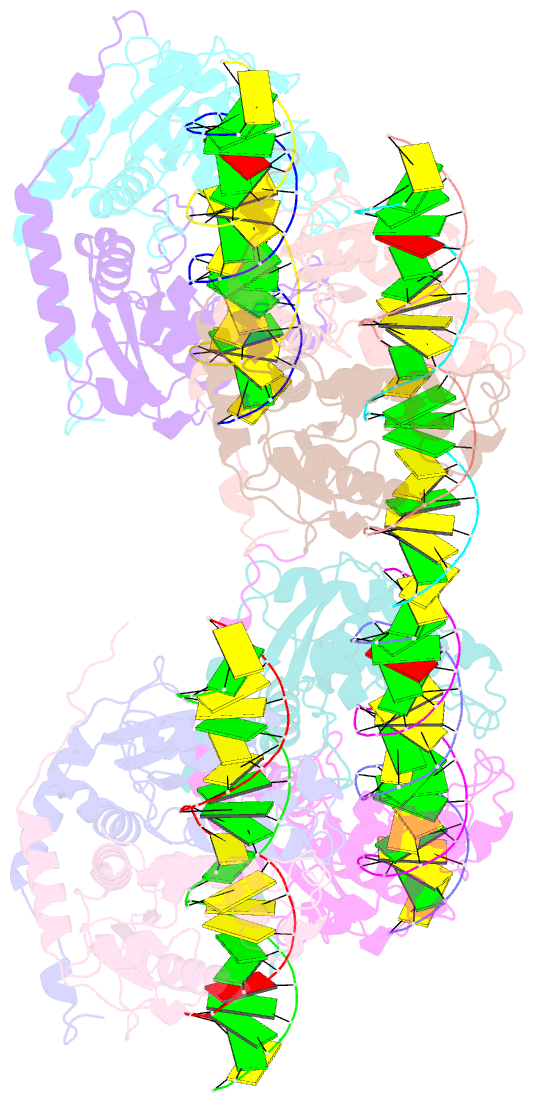
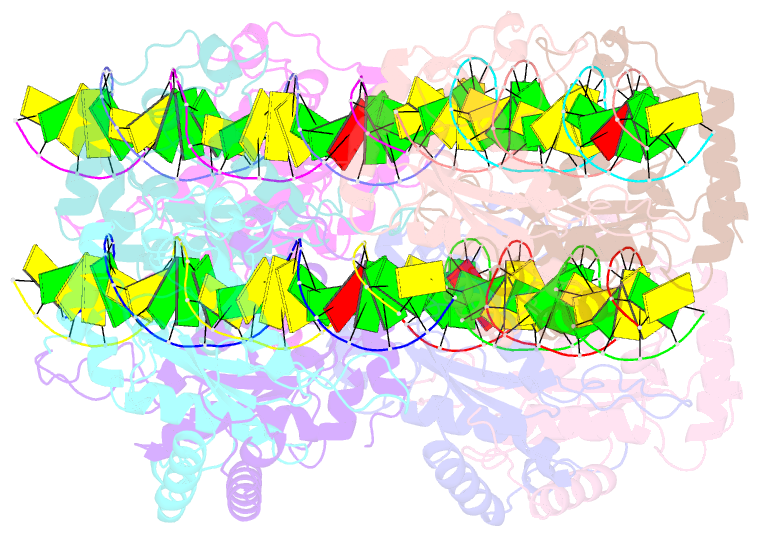
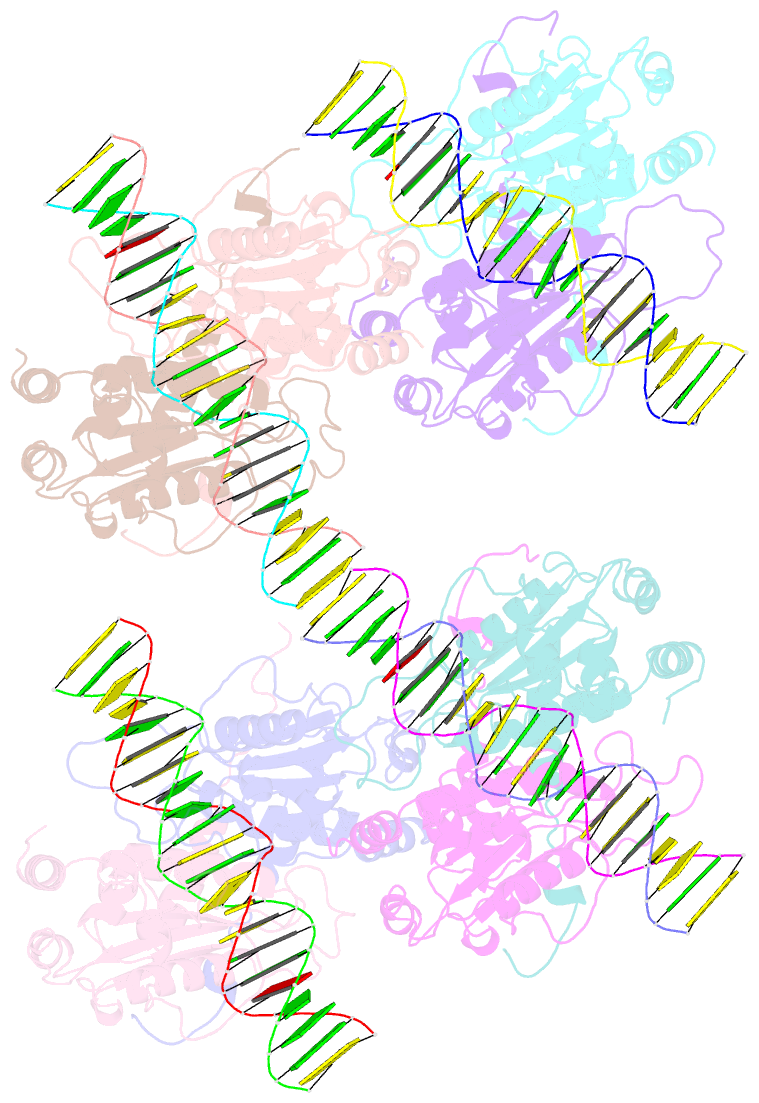
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3mx4; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
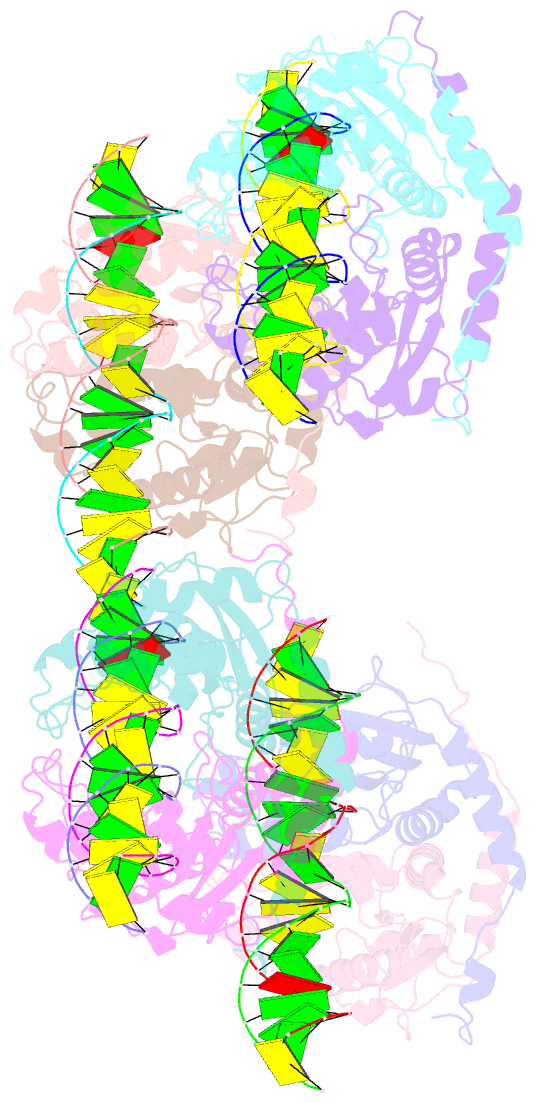
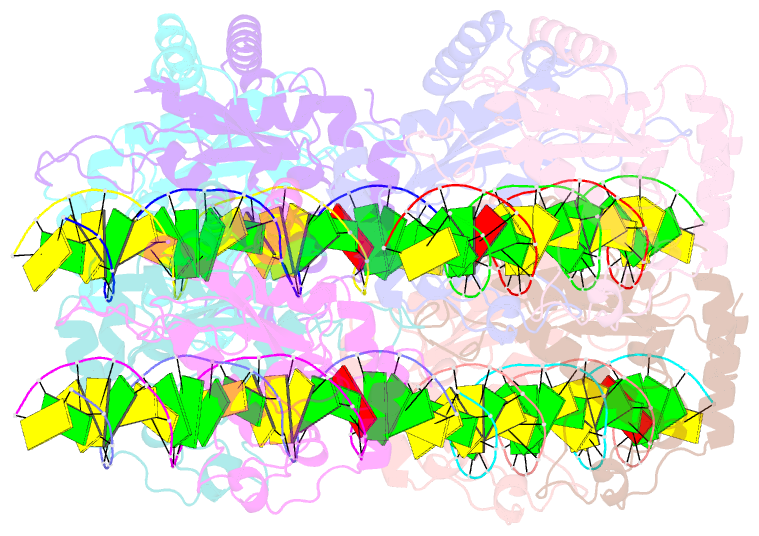
- DNA binding and cleavage by the giy-yig endonuclease r.eco29ki inactive variant e142q
- Reference
- Mak AN, Lambert AR, Stoddard BL (2010): "Folding, DNA Recognition, and Function of GIY-YIG Endonucleases: Crystal Structures of R.Eco29kI." Structure, 18, 1321-1331. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2010.07.006.
- Abstract
- The GIY-YIG endonuclease family comprises hundreds of diverse proteins and a multitude of functions; none have been visualized bound to DNA. The structure of the GIY-YIG restriction endonuclease R.Eco29kI has been solved both alone and bound to its target site. The protein displays a domain-swapped homodimeric structure with several extended surface loops encircling the DNA. Only three side chains from each protein subunit contact DNA bases, two directly and one via a bridging solvent molecule. Both tyrosine residues within the GIY-YIG motif are positioned in the catalytic center near a putative nucleophilic water; the remainder of the active site resembles the HNH endonuclease family. The structure illustrates how the GIY-YIG scaffold has been adapted for the highly specific recognition of a DNA restriction site, in contrast to nonspecific DNA cleavage by GIY-YIG domains in homing endonucleases or structure-specific cleavage by DNA repair enzymes such as UvrC.