Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3n4m; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.987 Å)
- Summary
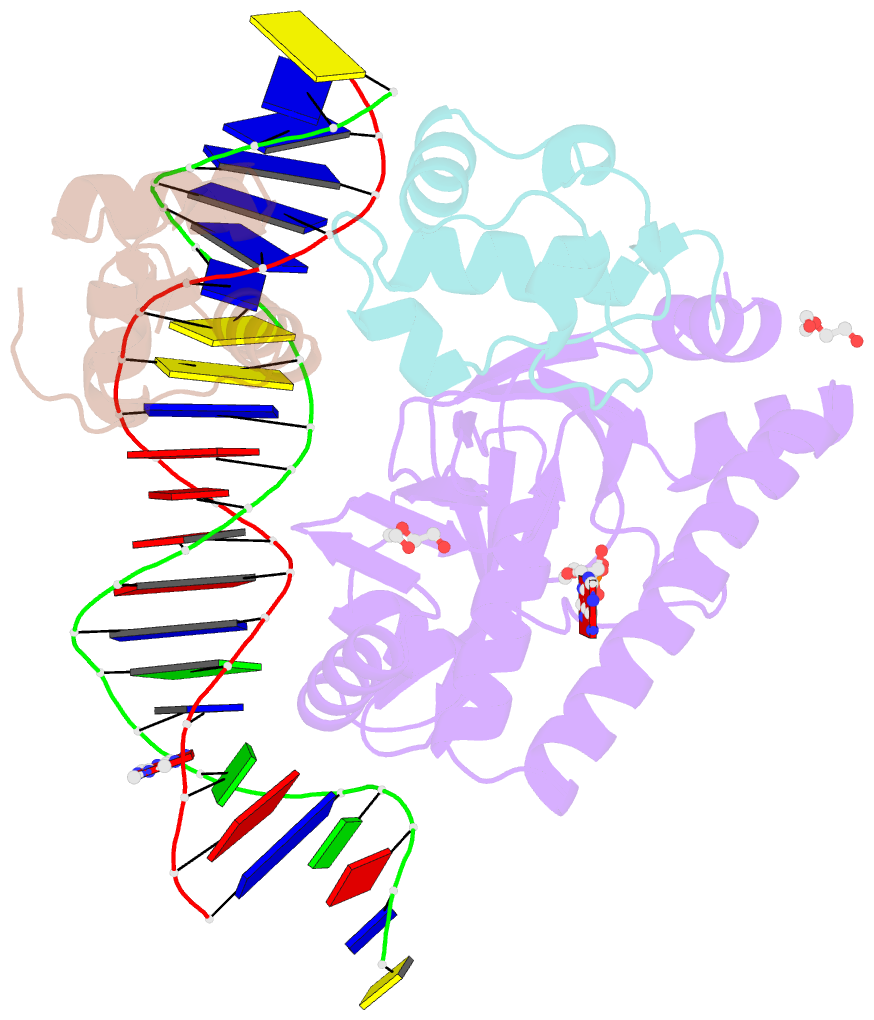
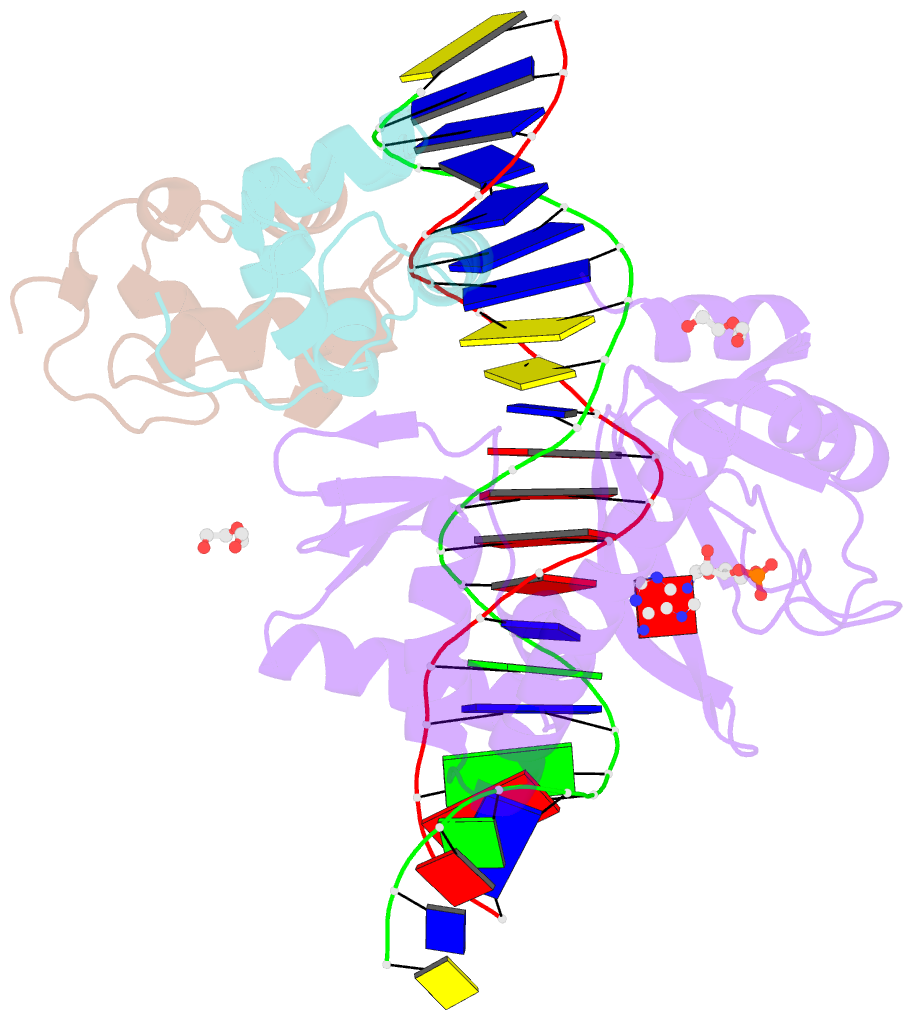
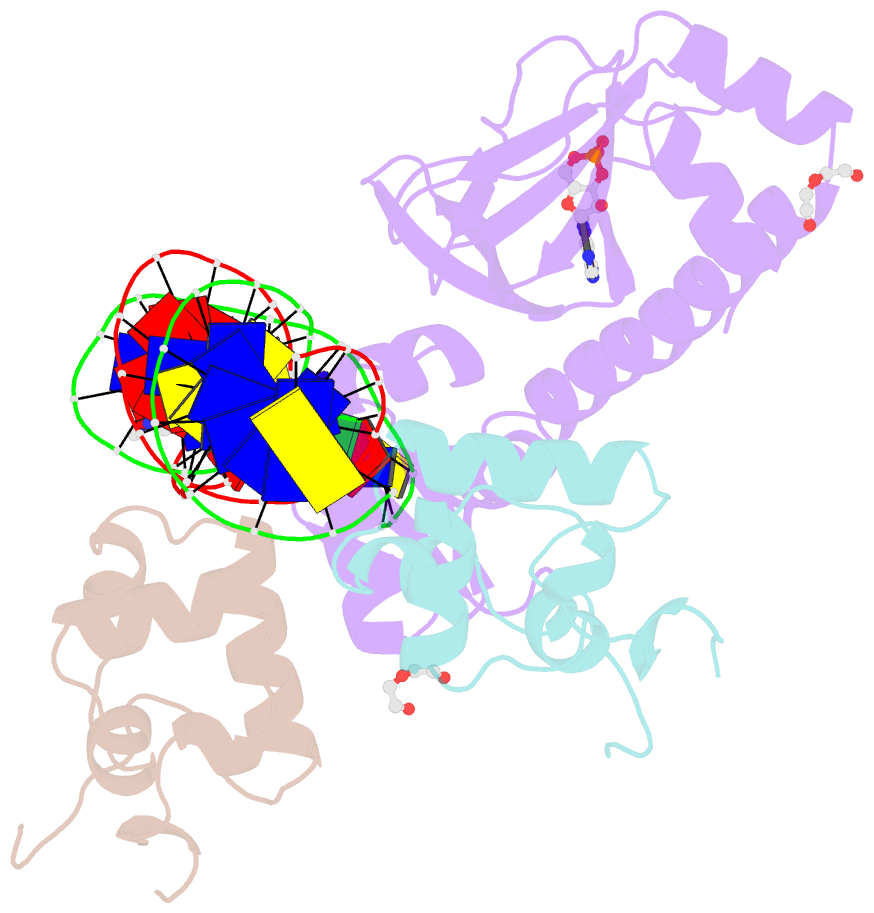
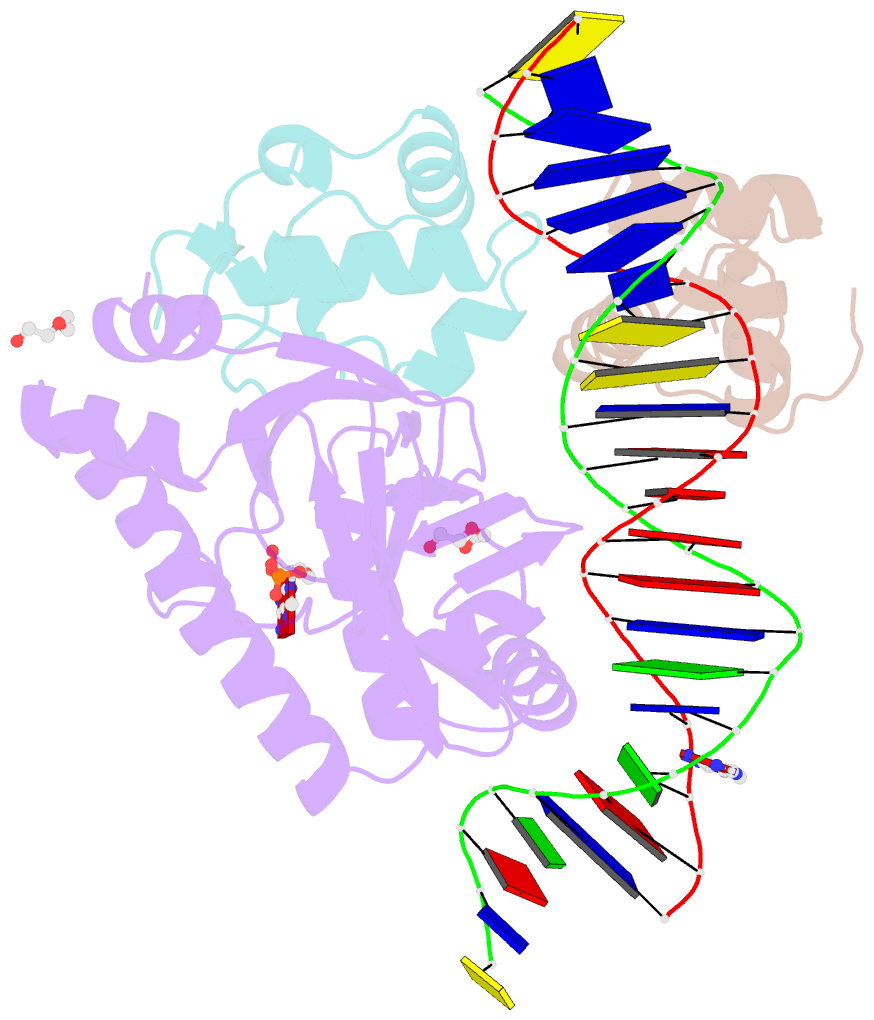
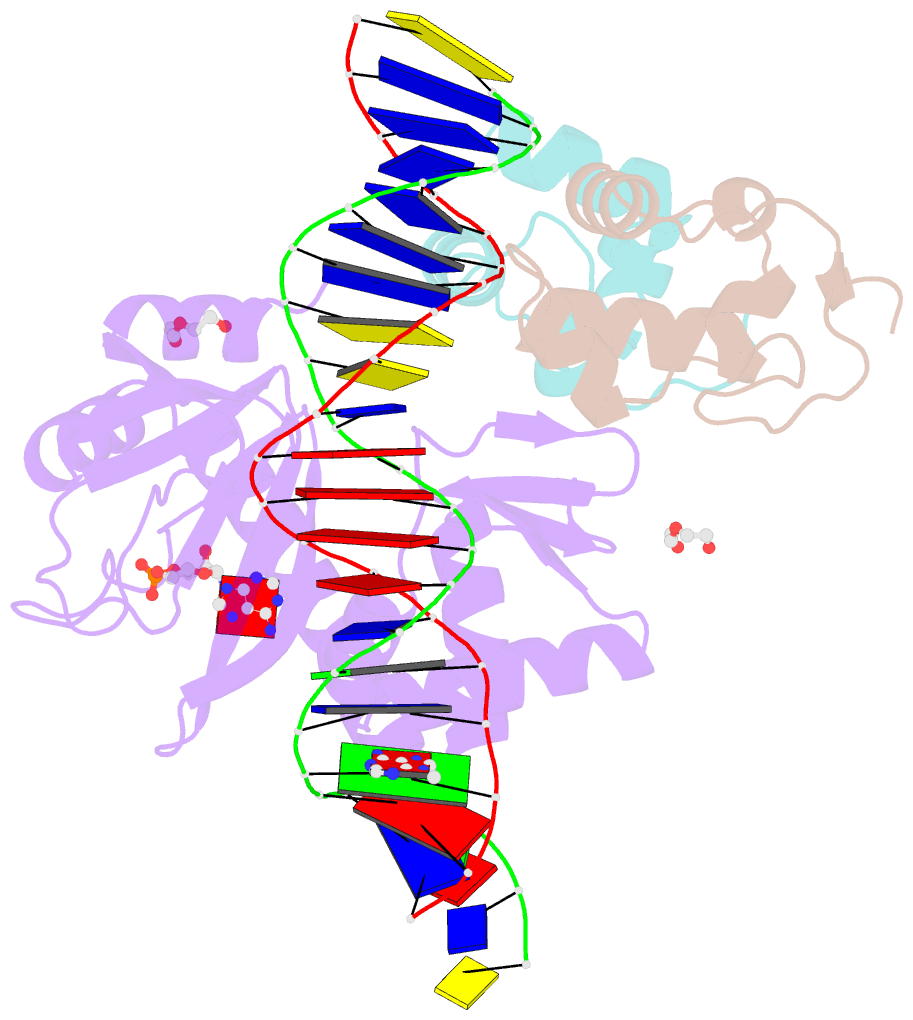
- E. coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit c-terminal domain in complex with cap and DNA
- Reference
- Lara-Gonzalez S, Dantas Machado AC, Rao S, Napoli AA, Birktoft J, Di Felice R, Rohs R, Lawson CL (2020): "The RNA Polymerase alpha Subunit Recognizes the DNA Shape of the Upstream Promoter Element." Biochemistry, 59, 4523-4532. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00571.
- Abstract
- We demonstrate here that the α subunit C-terminal domain of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase (αCTD) recognizes the upstream promoter (UP) DNA element via its characteristic minor groove shape and electrostatic potential. In two compositionally distinct crystallized assemblies, a pair of αCTD subunits bind in tandem to the UP element consensus A-tract that is 6 bp in length (A6-tract), each with their arginine 265 guanidinium group inserted into the minor groove. The A6-tract minor groove is significantly narrowed in these crystal structures, as well as in computationally predicted structures of free and bound DNA duplexes derived by Monte Carlo and molecular dynamics simulations, respectively. The negative electrostatic potential of free A6-tract DNA is substantially enhanced compared to that of generic DNA. Shortening the A-tract by 1 bp is shown to "knock out" binding of the second αCTD through widening of the minor groove. Furthermore, in computationally derived structures with arginine 265 mutated to alanine in either αCTD, either with or without the "knockout" DNA mutation, contact with the DNA is perturbed, highlighting the importance of arginine 265 in achieving αCTD-DNA binding. These results demonstrate that the importance of the DNA shape in sequence-dependent recognition of DNA by RNA polymerase is comparable to that of certain transcription factors.