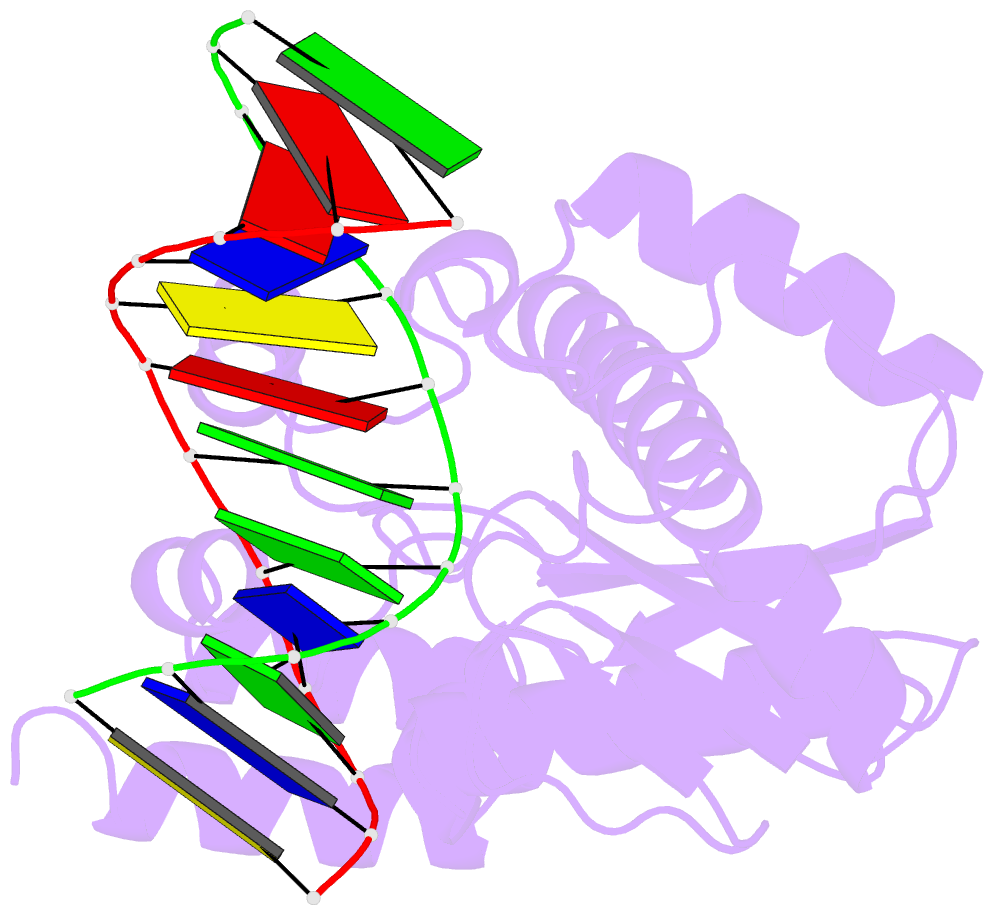
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3o3f; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA-RNA hybrid
- Method
- X-ray (2.0 Å)
- Summary
- T. maritima rnase h2 d107n in complex with nucleic acid substrate and magnesium ions
- Reference
- Rychlik MP, Chon H, Cerritelli SM, Klimek P, Crouch RJ, Nowotny M (2010): "Crystal Structures of RNase H2 in Complex with Nucleic Acid Reveal the Mechanism of RNA-DNA Junction Recognition and Cleavage." Mol.Cell, 40, 658-670. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.11.001.
- Abstract
- Two classes of RNase H hydrolyze RNA of RNA/DNA hybrids. In contrast to RNase H1 that requires four ribonucleotides for cleavage, RNase H2 can nick duplex DNAs containing a single ribonucleotide, suggesting different in vivo substrates. We report here the crystal structures of a type 2 RNase H in complex with substrates containing a (5')RNA-DNA(3') junction. They revealed a unique mechanism of recognition and substrate-assisted cleavage. A conserved tyrosine residue distorts the nucleic acid at the junction, allowing the substrate to function in catalysis by participating in coordination of the active site metal ion. The biochemical and structural properties of RNase H2 explain the preference of the enzyme for junction substrates and establish the structural and mechanistic differences with RNase H1. Junction recognition is important for the removal of RNA embedded in DNA and may play an important role in DNA replication and repair.