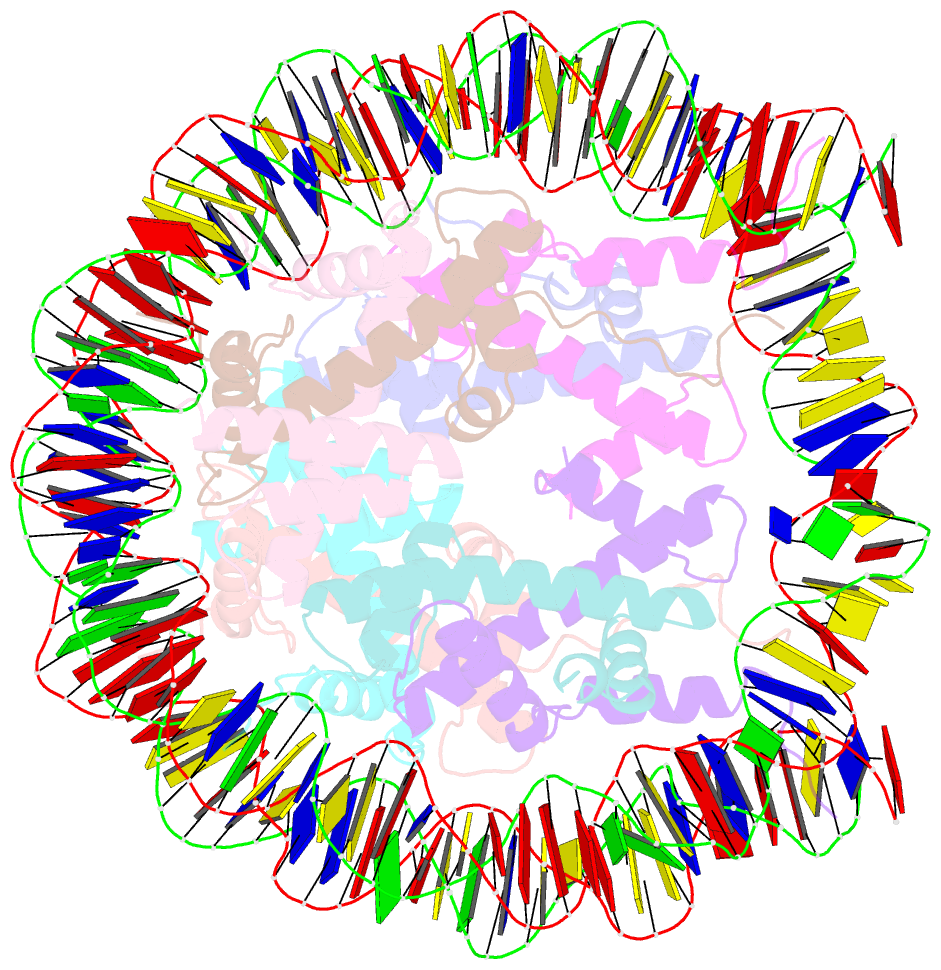
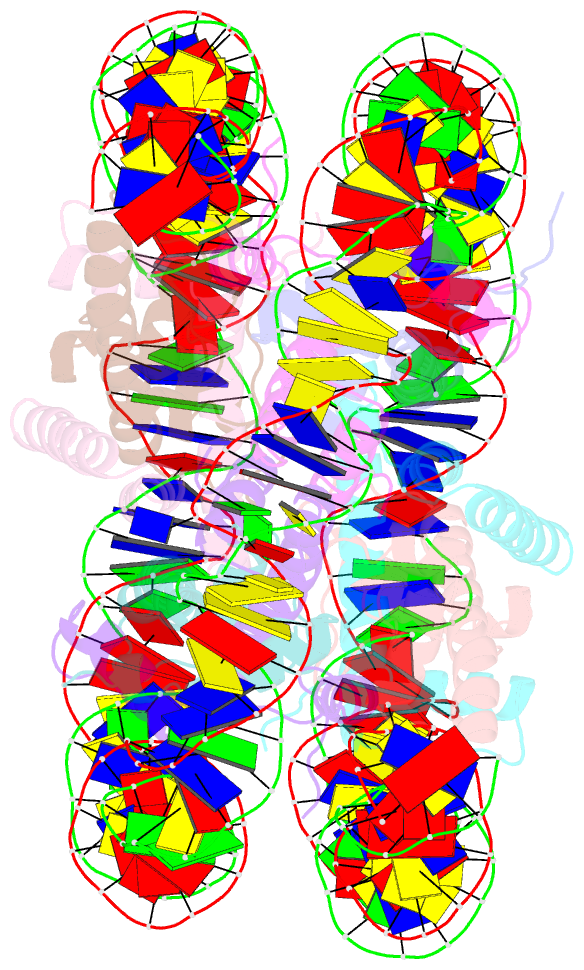
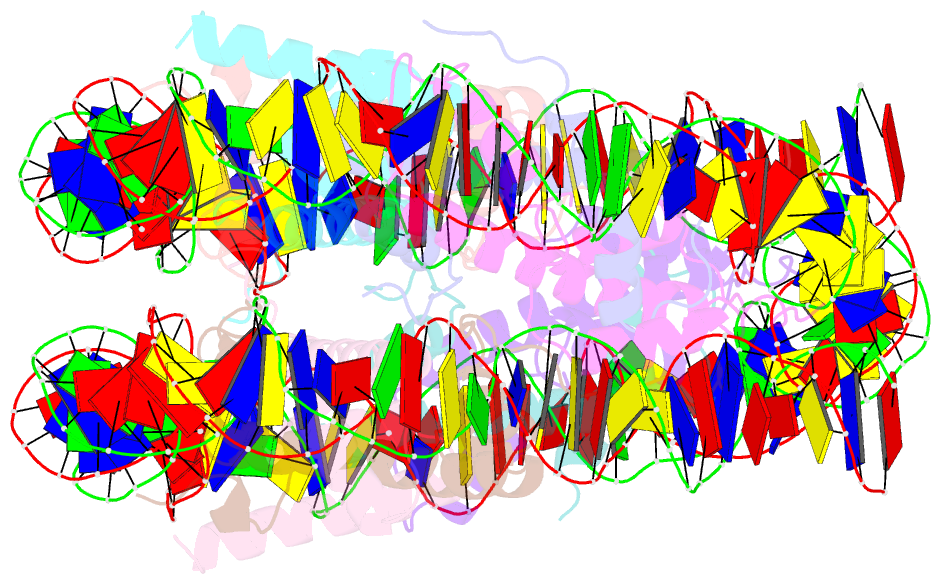
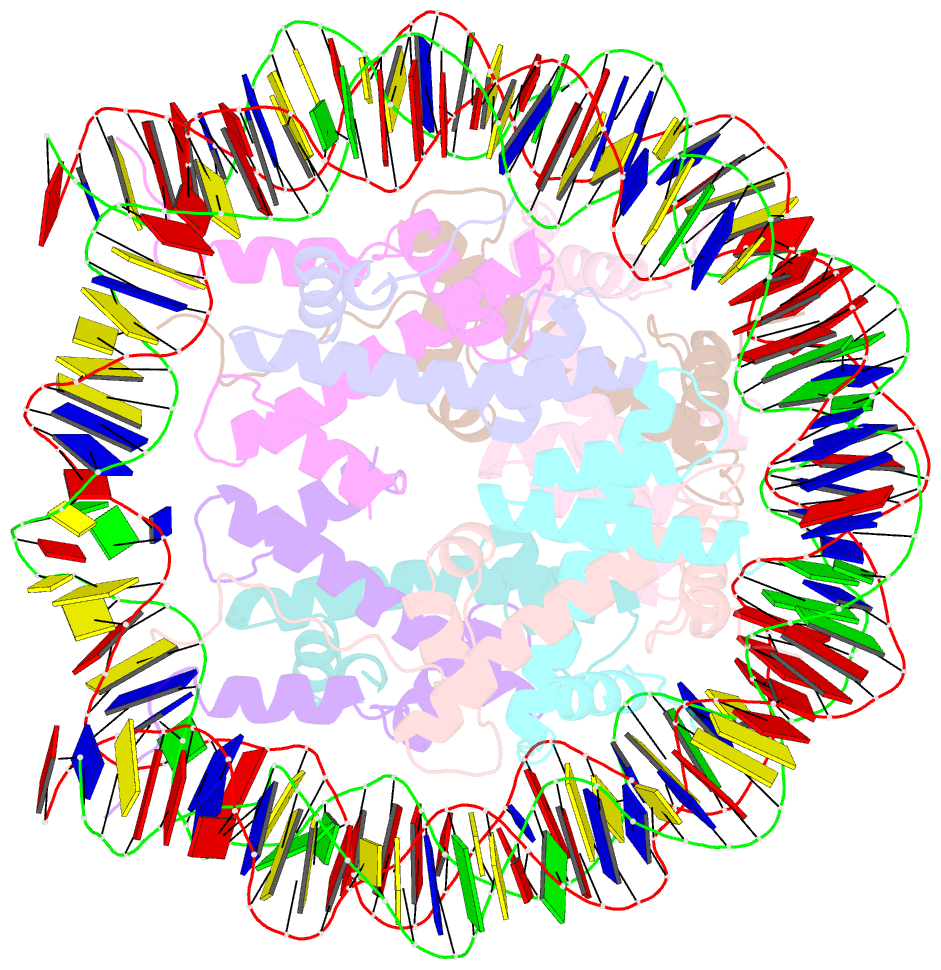
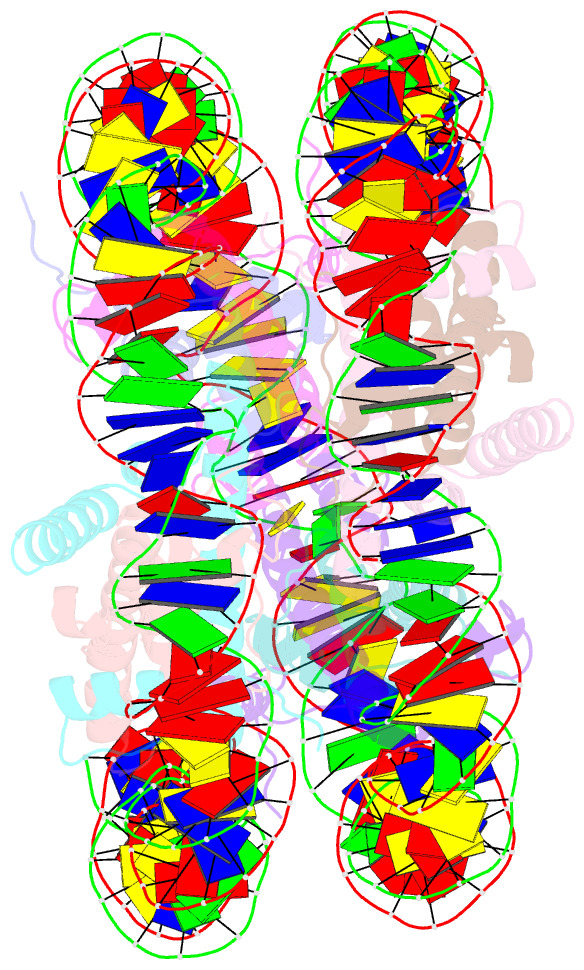
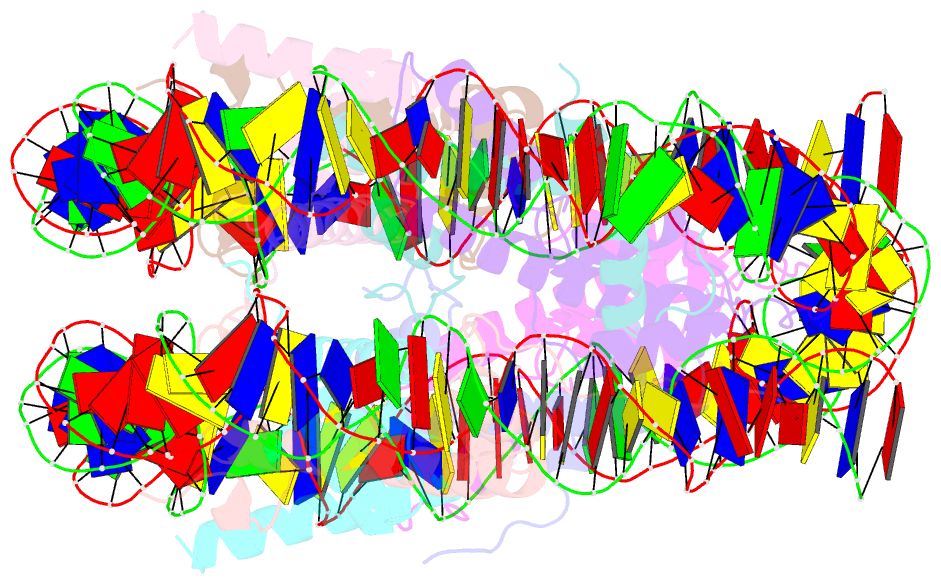
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3o62; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- structural protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.216 Å)
- Summary
- Nucleosome core particle modified with a cisplatin 1,3-cis-{pt(nh3)2}2+-d(gptpg) intrastrand cross-link
- Reference
- Todd RC, Lippard SJ (2010): "Consequences of Cisplatin binding on nucleosome structure and dynamics." Chem.Biol., 17, 1334-1343. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.10.018.
- Abstract
- The effects of cisplatin binding to DNA were explored at the nucleosome level to incorporate key features of the eukaryotic nuclear environment. An X-ray crystal structure of a site-specifically platinated nucleosome carrying a 1,3-cis-{Pt(NH₃)₂}²+-d(GpTpG) intrastrand cross-link reveals the details of how this adduct dictates the rotational positioning of DNA in the nucleosome. Results from in vitro nucleosome mobility assays indicate that a single platinum adduct interferes with ATP-independent sliding of DNA around the octamer core. Data from in vitro transcription experiments suggest that RNA polymerases can successfully navigate along cisplatin-damaged DNA templates that contain nucleosomes, but stall when the transcription elongation complex physically contacts a platinum cross-link located on the template strand. These results provide information about the effects of cisplatin binding to nuclear DNA and enhance our understanding of the mechanism of transcription inhibition by platinum anticancer compounds.