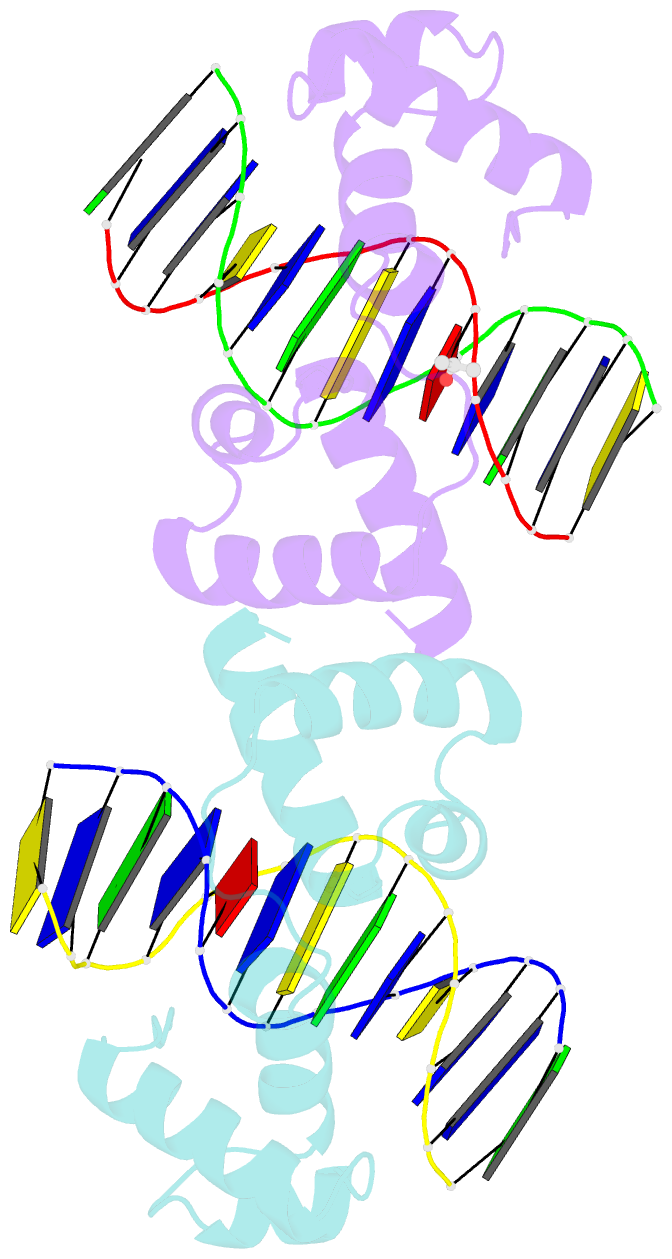
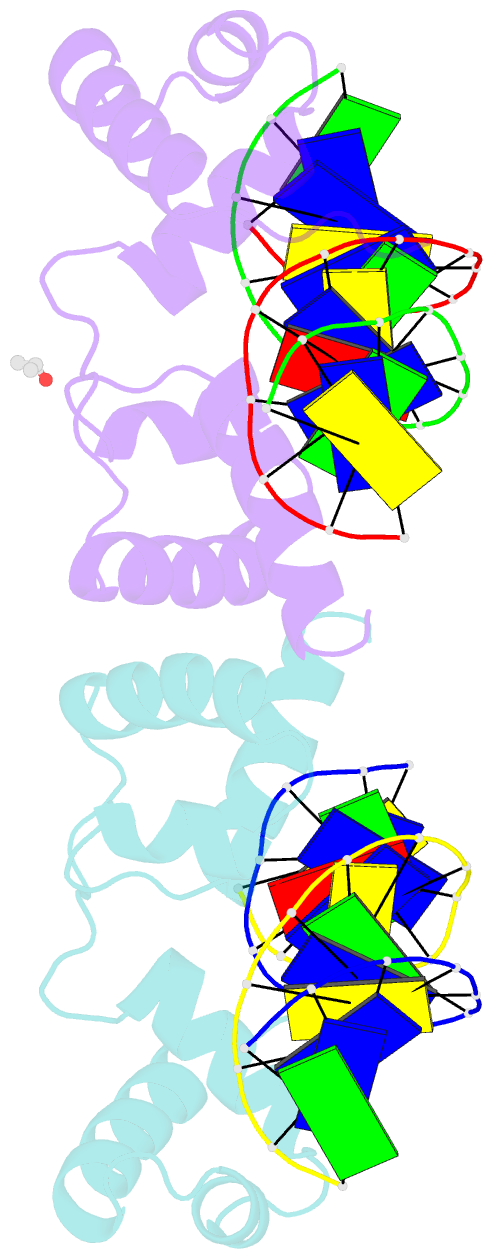
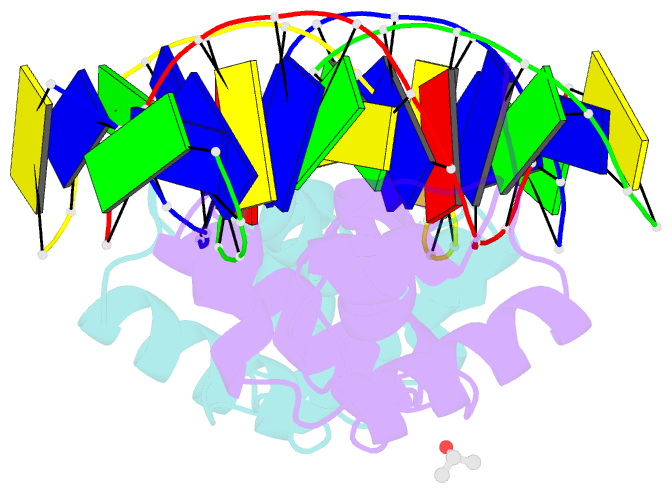
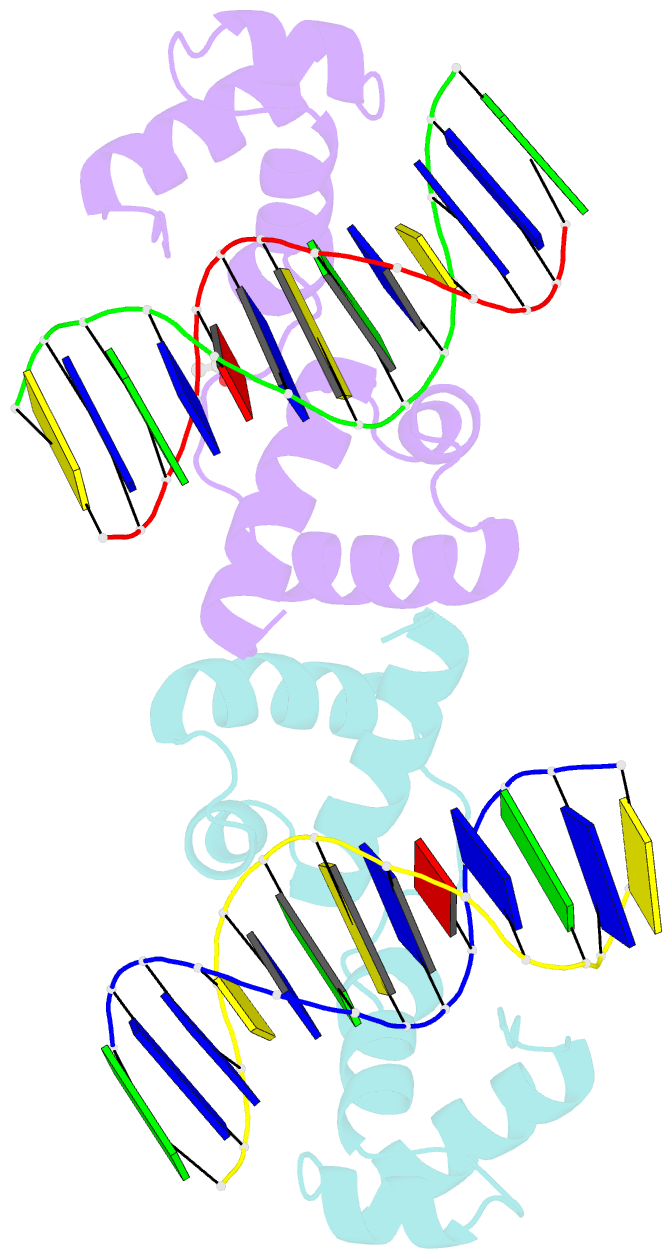
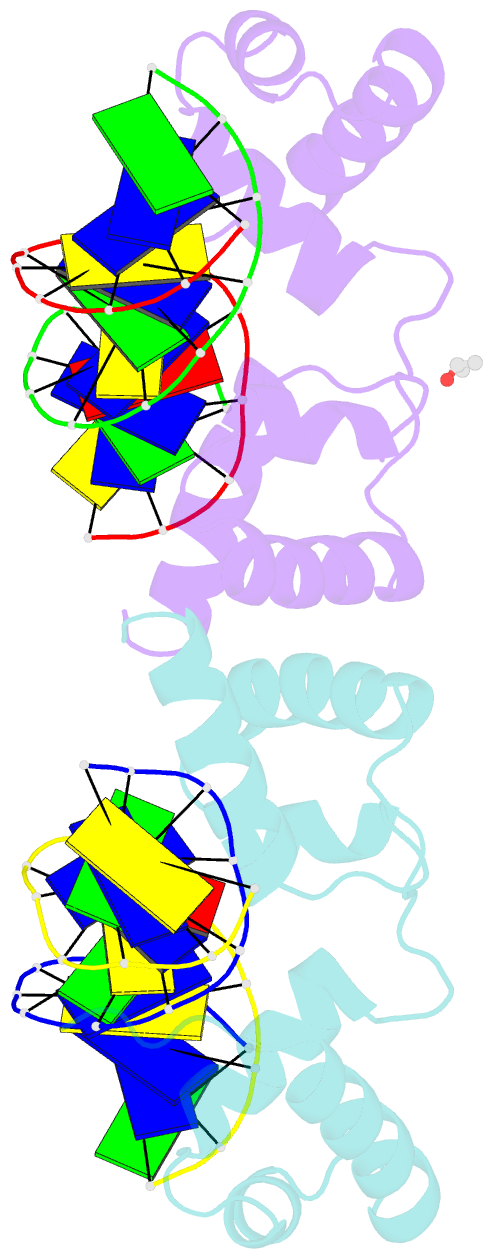
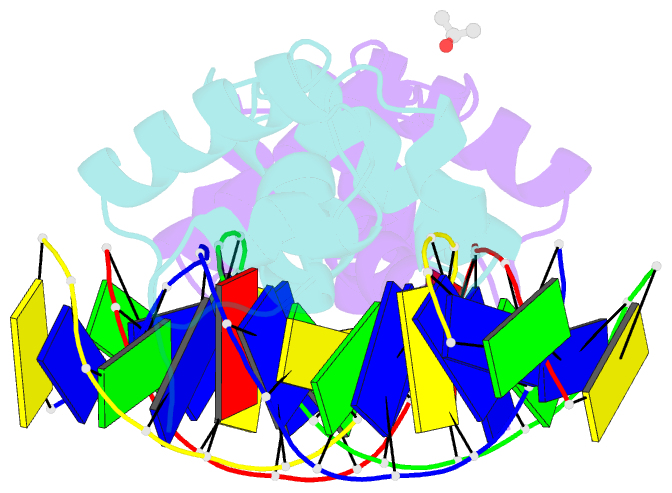
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3osf; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.032 Å)
- Summary
- The structure of protozoan parasite trichomonas vaginalis myb2 in complex with mre-2f-13 DNA
- Reference
- Jiang I, Tsai CK, Chen SC, Wang SH, Amiraslanov I, Chang CF, Wu WJ, Tai JH, Liaw YC, Huang TH (2011): "Molecular basis of the recognition of the ap65-1 gene transcription promoter elements by a Myb protein from the protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis." Nucleic Acids Res., 39, 8992-9008. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr558.
- Abstract
- Iron-inducible transcription of the ap65-1 gene in Trichomonas vaginalis involves at least three Myb-like transcriptional factors (tvMyb1, tvMyb2 and tvMyb3) that differentially bind to two closely spaced promoter sites, MRE-1/MRE-2r and MRE-2f. Here, we defined a fragment of tvMyb2 comprising residues 40-156 (tvMyb2₄₀₋₁₅₆) as the minimum structural unit that retains near full binding affinity with the promoter DNAs. Like c-Myb in vertebrates, the DNA-free tvMyb2₄₀₋₁₅₆ has a flexible and open conformation. Upon binding to the promoter DNA elements, tvMyb2₄₀₋₁₅₆ undergoes significant conformational re-arrangement and structure stabilization. Crystal structures of tvMyb2₄₀₋₁₅₆ in complex with promoter element-containing DNA oligomers showed that 5'-a/gACGAT-3' is the specific base sequence recognized by tvMyb2₄₀₋₁₅₆, which does not fully conform to that of the Myb binding site sequence. Furthermore, Lys⁴⁹, which is upstream of the R2 motif (amino acids 52-102) also participates in specific DNA sequence recognition. Intriguingly, tvMyb2₄₀₋₁₅₆ binds to the promoter elements in an orientation opposite to that proposed in the HADDOCK model of the tvMyb1₃₅₋₁₄₁/MRE-1-MRE-2r complex. These results shed new light on understanding the molecular mechanism of Myb-DNA recognition and provide a framework to study the molecular basis of transcriptional regulation of myriad Mybs in T. vaginalis.