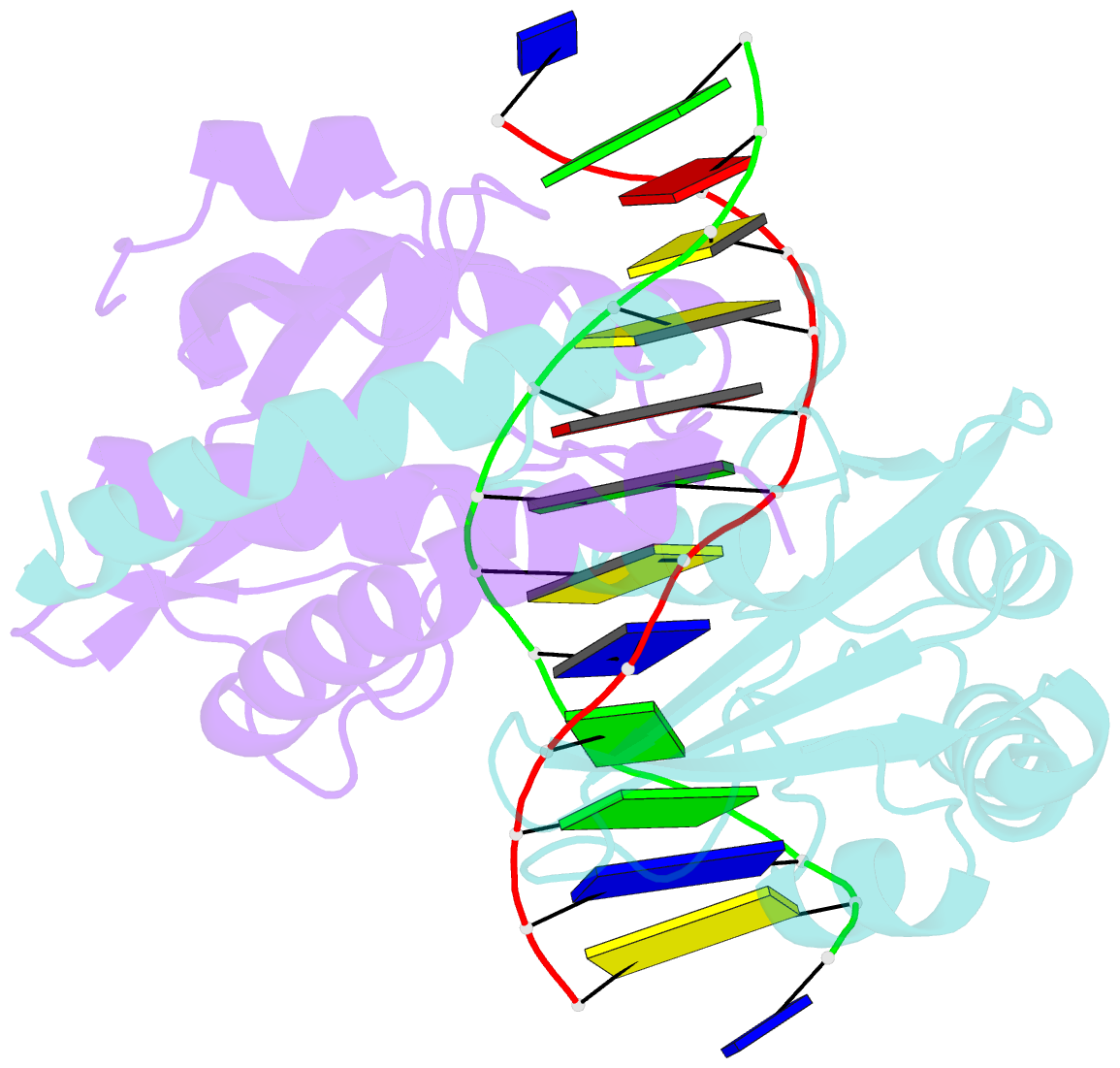
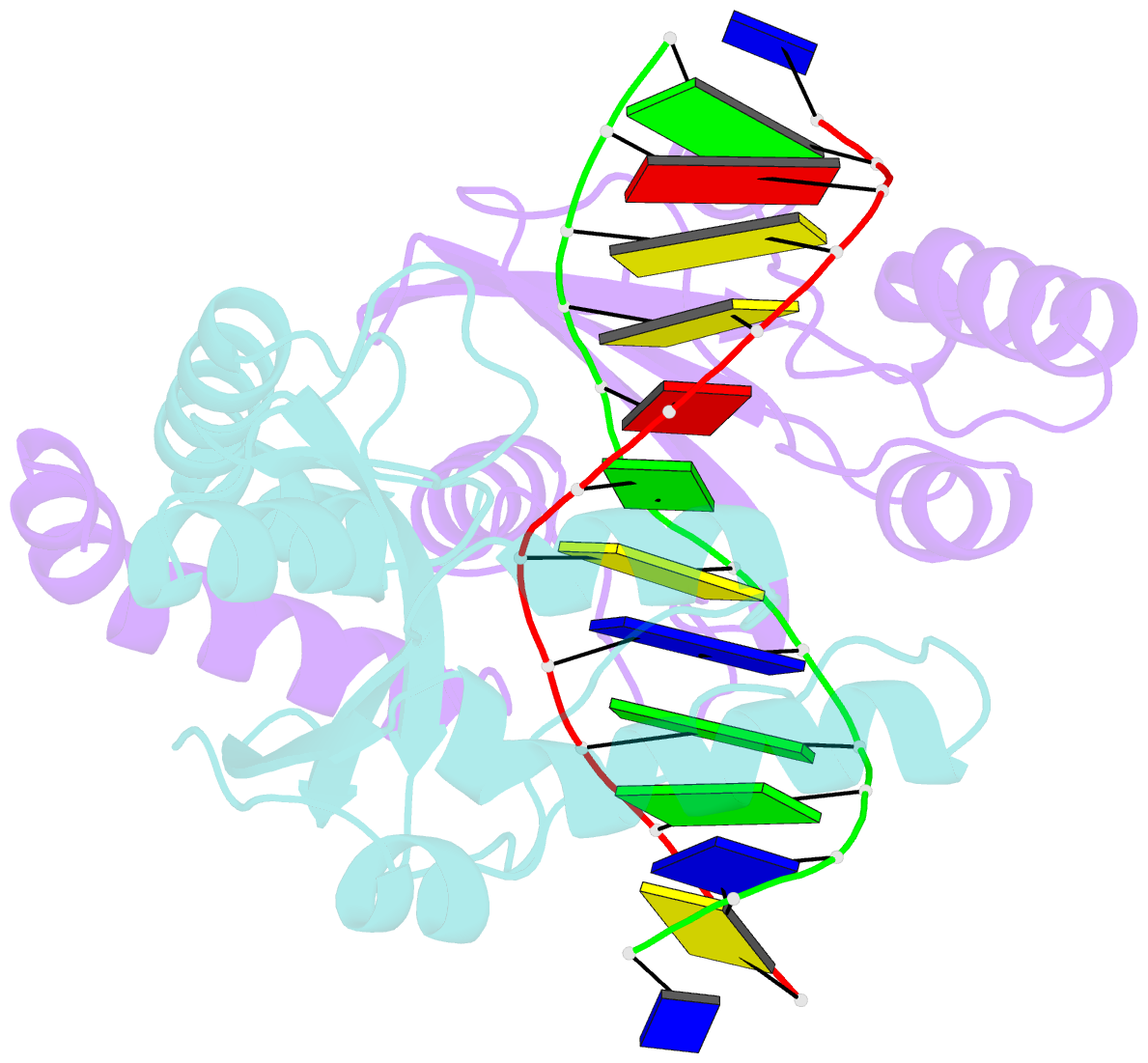
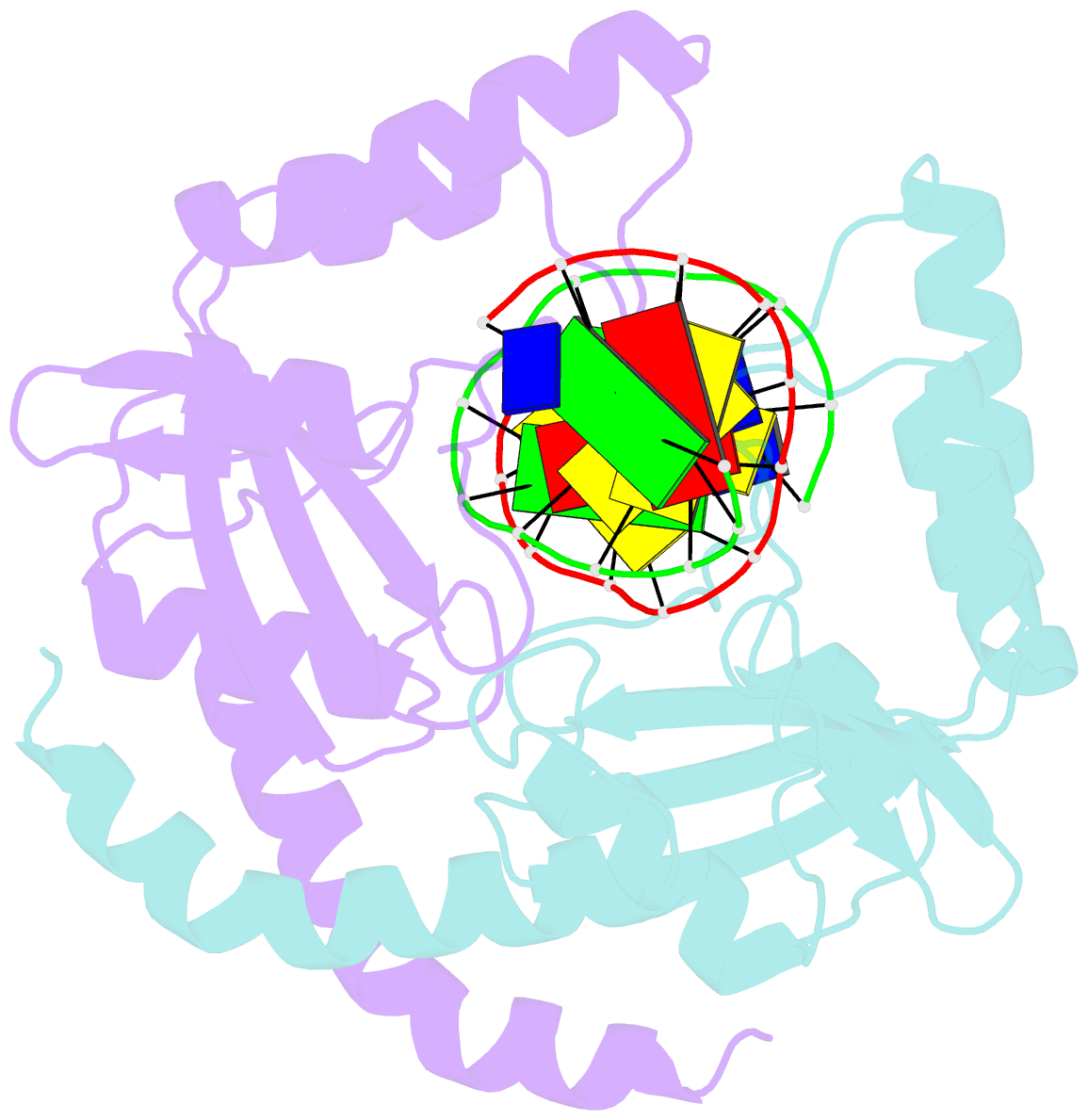
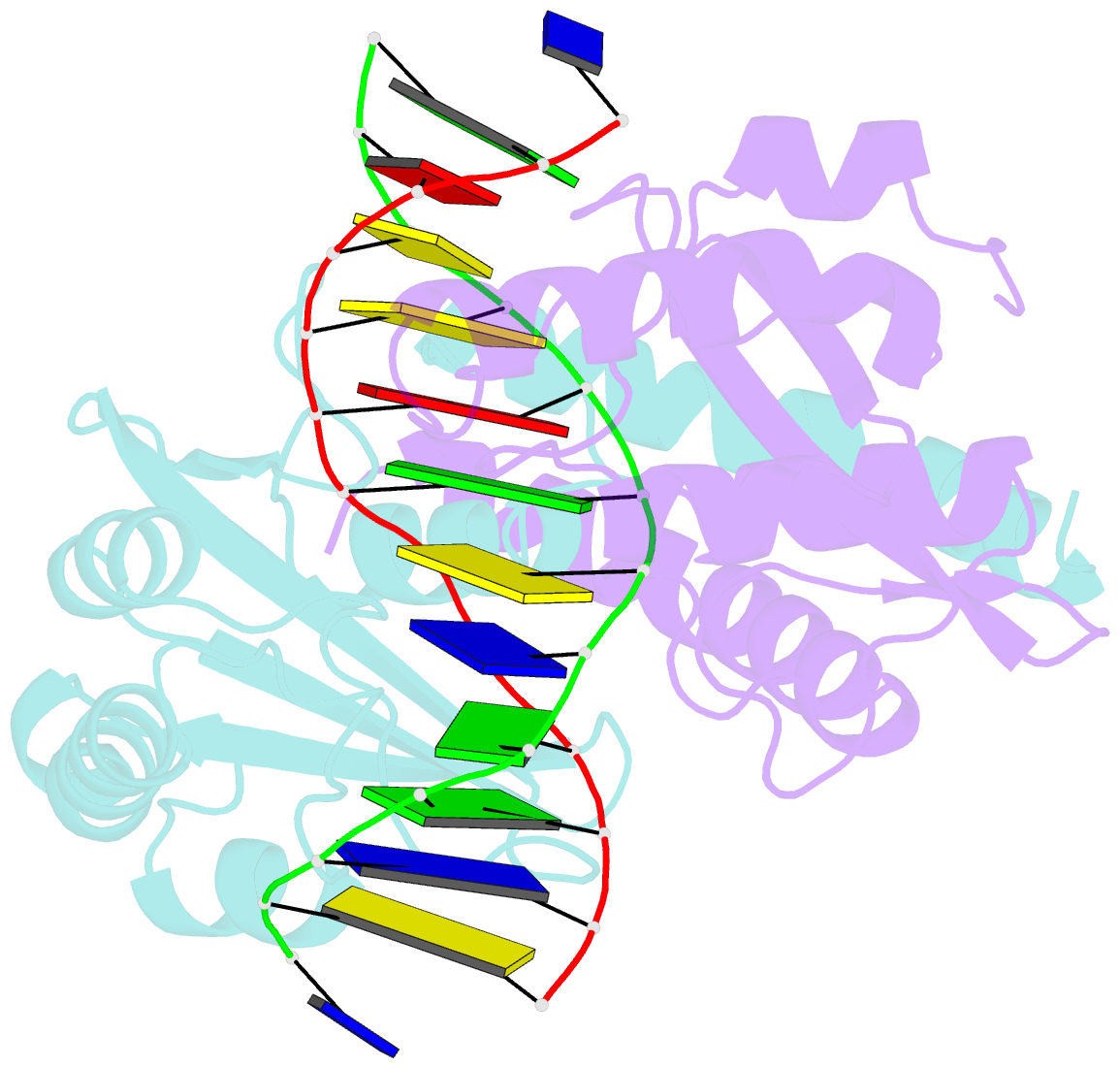
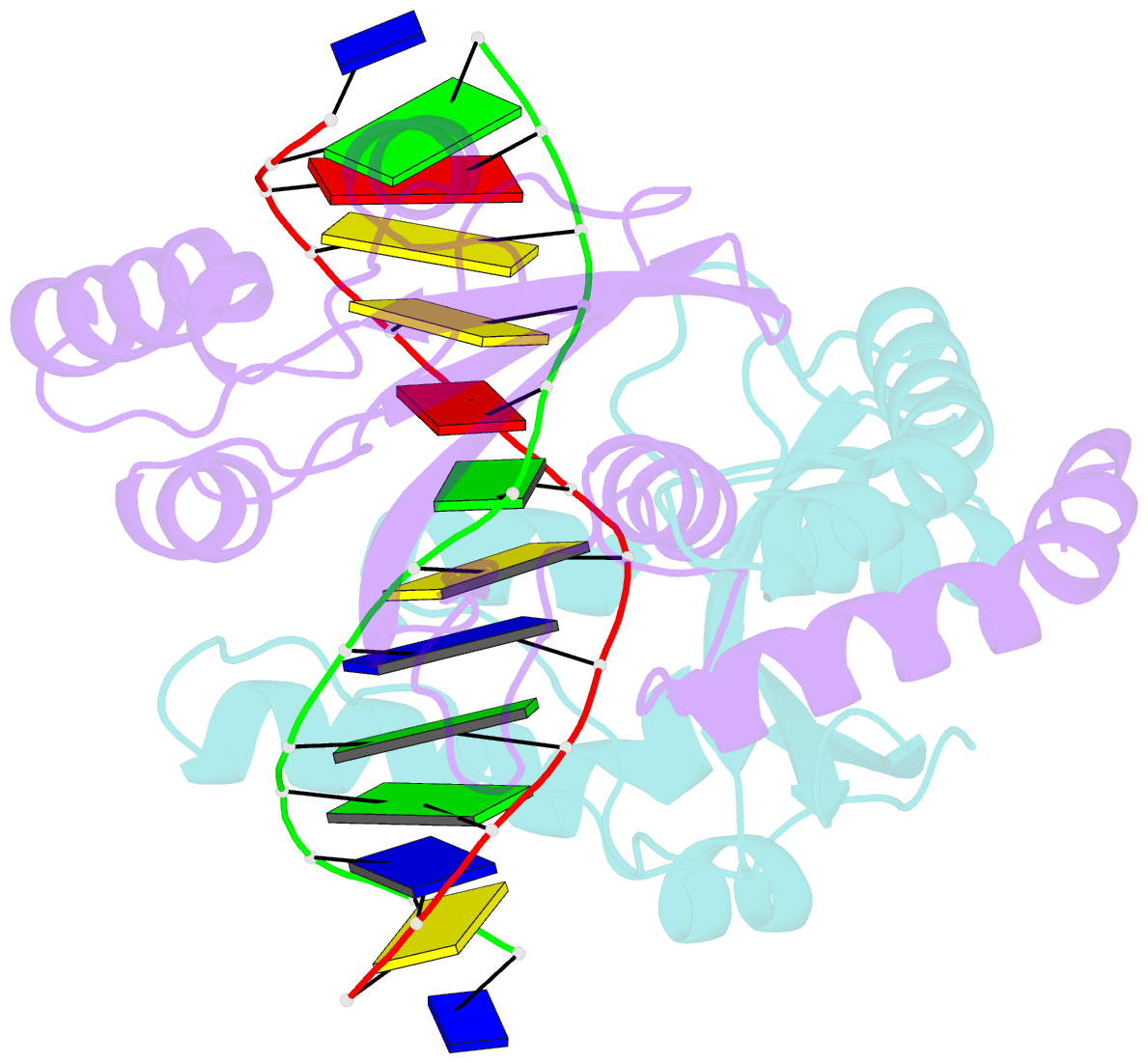
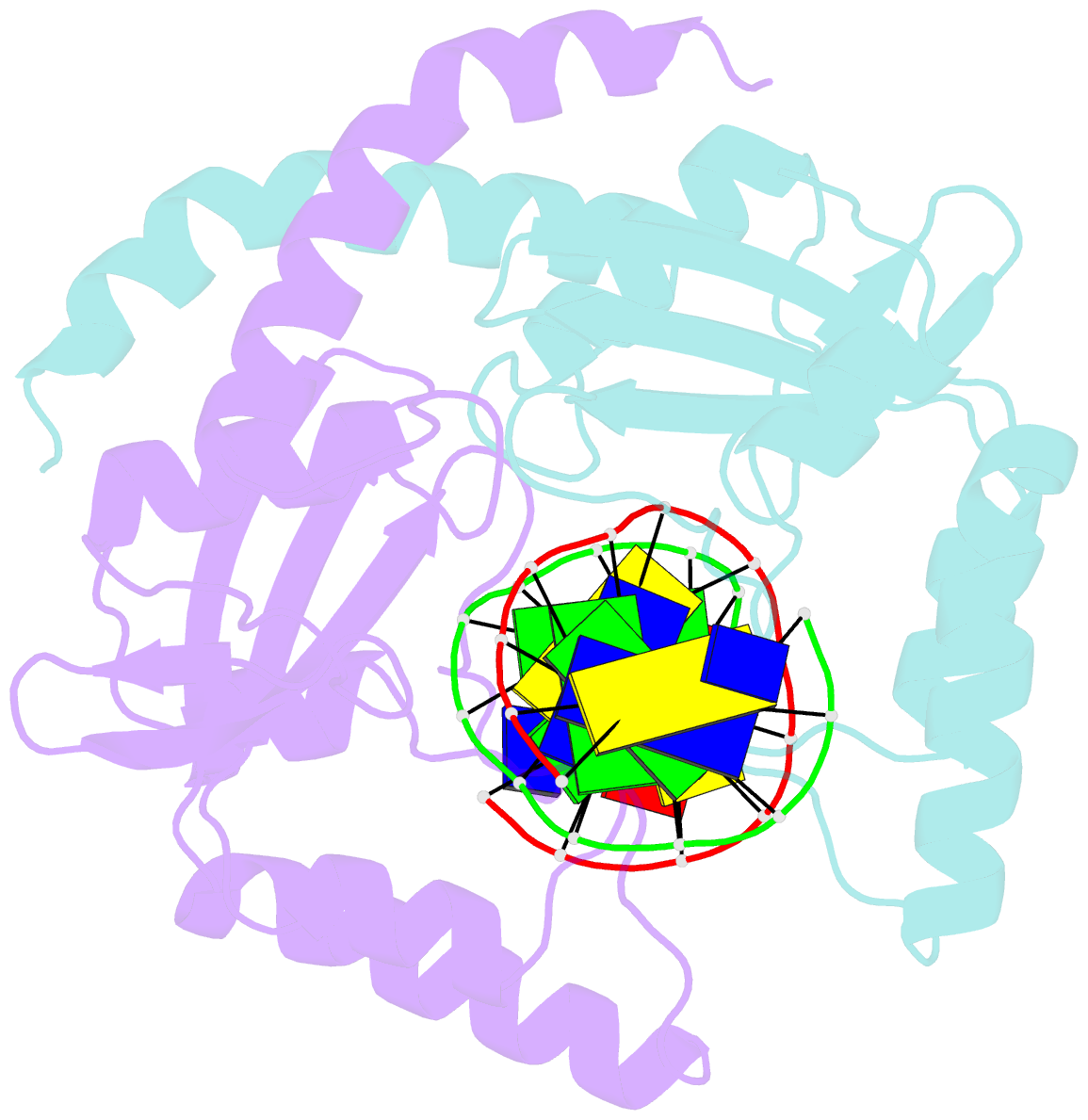
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 3pvi; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.59 Å)
- Summary
- D34g mutant of pvuii endonuclease complexed with cognate DNA shows that asp34 is directly involved in DNA recognition and indirectly involved in catalysis
- Reference
- Horton JR, Nastri HG, Riggs PD, Cheng X (1998): "Asp34 of PvuII endonuclease is directly involved in DNA minor groove recognition and indirectly involved in catalysis." J.Mol.Biol., 284, 1491-1504. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2269.
- Abstract
- The PvuII restriction endonuclease is a homodimer that recognizes and cleaves the DNA sequence 5'-CAGCTG-3' in double-stranded DNA, and the structure of this enzyme has been reported. In the wild-type enzyme, Asp34 interacts with the internal guanine of the recognition sequence on the minor groove side. The Asp34 codon was altered to specify Gly (D34G), and in vitro studies have revealed that the D34G protein has lost binding specificity for the central G.C base-pairs, and that it cuts the canonical sequence with 10(-4)-fold reduced activity as compared to the wild-type enzyme. We have now determined the structure at 1.59 A resolution of the D34G PvuII endonuclease complexed with a 12 bp duplex deoxyoligonucleotide containing the cognate sequence. The D34G alteration results in several structural changes relative to wild-type protein/DNA complexes. First, the sugar moiety of the internal guanine changes from a C2'-endo to C3'-endo pucker while that of the 3' guanine changes from C3'-endo to C2'-endo pucker. Second, the axial rise between the internal G.C base-pairs is reduced while that between the G.C and flanking base-pairs is expanded. Third, two distinct monomeric active sites are observed that we refer to as being "primed" and "unprimed" for phosphodiester bond cleavage. The primed and unprimed sites differ in the conformation of the Asp58 side-chain, and in the absence from unprimed sites of four networked water molecules. These water molecules, present in the primed site, have been implicated in the catalytic mechanism of this and other endonucleases; some of them can be replaced by the Mg2+ necessary for cleavage. Taken together, these structural changes imply that the Asp34 side-chains from the two subunits maintain a distinct conformation of its DNA substrate, properly situating the target backbone phosphates and indirectly manipulating the active sites. This provides some insight into how recognition of the specific DNA sequence is linked to catalysis by the highly specific restriction endonucleases, and reveals one way in which the structural conformation of the DNA is modulated coordinately with that of the PvuII protein.